Korean%20War%20 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Korean%20War%20
Description:
Korean War 1950-1953 Korea part of Japan since 1910 August 8, 1945 - Soviet Union declared war against Japan and invaded Korea and Manchuria August 15, 1945 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:205
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Korean%20War%20
1
(No Transcript)
2
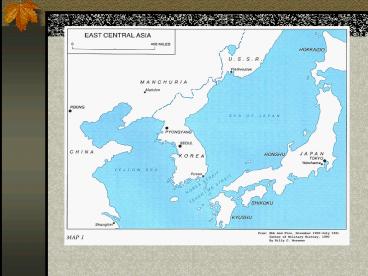
Korean War 1950-1953
- Korea part of Japan since 1910
- August 8, 1945 - Soviet Union declared war
against Japan and invaded Korea and Manchuria - August 15, 1945 - Japan surrendered and agreed to
give up all territories it had acquired since
1894 - Allies agreed Korea would become independent
country - U.S. troops occupied southern part of Korea (up
to 38th parallel), Soviet forces occupied the
north - 1947 U.N. declared election should be held for
Koreans to chose type of government for whole
country - Soviets refused
3
Split
- South Korea
- May 8, 1948 Elections held - People of southern
part of Korea (U.S. occupied) elected a national
assembly - They claimed the entire country and called it the
Republic of Korea. Their first leader was Syngman
Rhee he was against communism
4
Split
- North Korea
- Soviets refused to permit elections.
Communists, trained by Soviet Union, claimed the
entire country - September 9, 1948 established Democratic
Peoples Republic of Korea with Kim il Sung as
their leader - Despite the name, it was far from democratic
5
Korean War1950-1953
Kim Il-Sung
Syngman Rhee
Domino Theory
6
War June 25, 1950
- U.S. removed its troops in 1949
- 70.000 N. Koreans attacked S. Koreans. Within 2
days, they were close to capturing the capital,
Seoul - U.N. demanded that Communists retreat back to
38th parallel N. Koreans ignore it - U.N. asked its members to aid S. Korea.
- June 30 President Truman ordered U.S. air,
ground, and naval forces to South Korea under
U.N. flag - Congress called it a police action did NOT
declare war - June 30 N. Korean Army (KPA) captured capital
7
Enemy mortar round lands directly on a Marine
ridgeline position
8
Millions of Korean refugees were uprooted from
their homes and attempted to flee to safety
9
Armada assembled for Inchon invasion, worlds
last great amphibious landing
10
(No Transcript)
11
Inchon landing September 15, 1950
- U.S. troops under Gen. Douglas MacArthur and
recapture Seoul - October 1 S. Korean U.S. forces invade N.
Korea - October 19 Allied forces capture Pyongyang
North Koreas capital - Communists retreat farther north
12
Marines carry a wounded comrade in the assault on
Seoul
13
American air power destroying supply warehouses
in N. Korea
14
China gets involved
- MacArthur demands N. Koreans surrender, but is
rejected - U.S. troops moved toward Yula River, chasing N.
Koreans - Yula River - Border between North Korea and China
- China warned Allied troops not to advance any
closer towards its border - MacArthur pressed on, hoping to end the war
before winter set in - 300,000 Chinese troops attacked in October
November
15
(No Transcript)
16
Retreat
- Faced against a huge Chinese force, Allies
retreat in December - December 24 KPA recaptured their capital and
crossed into South Korea - January Communists capture Seoul. Allies dig
in. - March KPA Chinese armies retreat from Seoul
Allies cross into N. Korea again - Both sides dig in and fight along battle line
north of 38th parallel - Truce talks begin but, fighting continued for 2
more years
17
After Chinese offensive in Nov. 1950, 98,000 N.
Koreans evacuate along with U.N. troops
18
U.N. forces move up behind fleeing Chinese
19
See-saw fighting along 38th parallel
20
MacArthur fired
- As the war dragged on, Gen. MacArthur pushed for
bombing China and using other all-out measures
(nuclear bomb) - President Truman vetoed this idea because he
thought it would lead to another world war - MacArthur made public statements disagreeing with
the President - President Truman removed him from command April
1951 - He appears before Congress Old soldiers never
die, they just fade away speech
21
The Shifting Map of Korea1950-1953
22
Armistice signed July 27, 1953
- N. Korea leader Kim Il Sung
- America Gen. Mark Clark
- Chinese commander
23
Results of Korean War
- 3 million Koreans died
- Millions left homeless
- 1 million Chinese soldiers died
- 54,246 American soldiers died
- Lessons learned
- If America wanted to confront communism, she
needed to do it carefully confrontation with N.
Korea quickly got out of hand - Chinese had worlds largest army prepared to die
for communism - USSR had supplied Chinese with modern weapons
- There were limits to Americas power
24
(No Transcript)
25
Today
- Last attempt to negotiate reunification of Korea
failed in 1991 - N. Korea is a totalitarian state with Kim Jong-il
(Sungs son)as its leader - Its people suffer from malnutrition
- It has nuclear weapons
- U.S. and S. Korea troops still face Communist N.
Korea troops posted on the border
26
Today
27
Anti-American propaganda poster
28
Today
- U.S. Assistant Secretary of State attending 6
party talks aimed at persuading North Korea to
dismantle its nuclear weapons


























![READ⚡[PDF]✔ Korean Slang: As Much as a Rat's Tail: Learn Korean Language and Culture PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10071131.th0.jpg?_=20240703072)
![Download [PDF] Korean Hangul Writing Workbook: Korean Alphabet for Beg PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10082826.th0.jpg?_=20240722023)


