CB 6.9 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
CB 6.9
Description:
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Stuart Reichler Last modified by: Stuart Reichler Created Date: 9/5/2006 5:38:28 PM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:57
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: CB 6.9
1
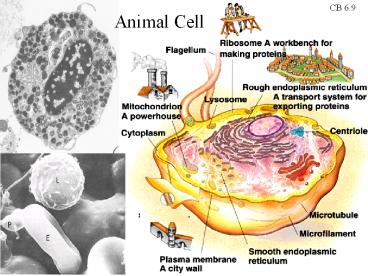
CB 6.9
Animal Cell
2
Bonds holding atoms together to make molecules
- Covalent
- Strong
- Sharing Electrons
- When broken chemical reaction
- energy consumed or released
- Ionic
- Weak
- Positive and Negative atoms attracted to each
other
3
nonpolarcovalent bond
ionic bond
methane
water
polarcovalent bond
4
Four types of molecules that are primarily found
in living systems (biomolecules)
- Carbohydrates/ Sugars
- Nucleotides- DNA/RNA
- Amino Acids- Proteins
- Lipids- fats/phospholipids
5
CB 6.2
6
Biomolecules contain many carbon atoms
CB 4.5
7
Biomolecules contain many carbon atoms
CB 4.5
8
CB 4.5
Biomolecules contain many carbon atoms
9
Biomolecules contain many carbon atoms
CB 4.5
10
CB 4.10
Combinations of different other atoms changes the
characteristics of the biomolecule.
11
Four types of molecules that are primarily found
in living systems (biomolecules)
- Carbohydrates/ Sugars
- Nucleotides- DNA/RNA
- Amino Acids- Proteins
- Lipids- fats/phospholipids
12
CB 5.7
Carbohydrates- rings of carbon with oxygen
13
CB 5.8
Carbs- provide energy and structural support
14
CB 5.26
Nucleotides
15
Different bases combine on the sugar/phosphate
backbone to store information...
CB 5.26
16
CB 16.7
Certain nucleotide bases pair with each other
Ionic bond
too big
A
A
too small
T
T
just right
T
A
17
Chains of DNA can store information
18
CB 5.25
Information flow in cells
Protein
19
CB 5.17
The basic structure of amino acids
20
CB 5.17
the 20 Amino Acids
21
Amino acids connect together to make proteins.
CB 5.20
22
- Proteins are the doers of the cell.
- They act as
- Enzymes
- Structural Support
- Transporters
- Signals
23
CB 5.13
Lipids and Fats- membranes/energy storage
Polar/ Hydrophilic head
Non-polar/ Hydrophobic tail
24
CB 5.14
Lipids- membranes
25
CB 6.9
26
CB 7.2
Membranes act as barriers separating inside from
outside
27
CB 7.7
Membranes have associated proteins