1-D Equations - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title:
1-D Equations
Description:
Speed vs. Velocity During your 8 mi. trip, which took 15 min., you end up 3 mi. from home. ... Linear Motion Author: Amy Last modified by: Kelly Ingle Created Date: – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:68
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 1-D Equations
1
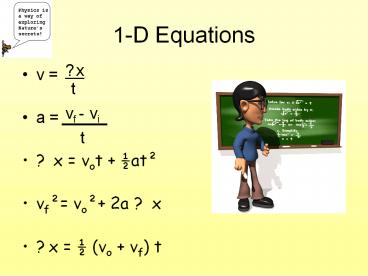
1-D Equations
?x
- v
- a
- ? x vot ½at²
- vf² vo² 2a ? x
- ?x ½ (vo vf) t
t
vf - vi
_____
t
2
Speed vs. Velocity
- During your 8 mi. trip, which took 15 min., you
end up 3 mi. from home. Your speedometer displays
your instantaneous speed, which varies throughout
the trip. - Your average speed is 32 mph (distance / time).
- Your average velocity is your displacement
divided by 15 minutes, which is 12 mph in a SE
direction. - At any point in time, your velocity vector points
tangent to your path. - The faster you go, the longer your velocity
vector.
North
3
Positive Velocity VS. Negative Velocity
http//www.physicsclassroom.com/
4
Speeding up VS. Slowing Down
http//www.physicsclassroom.com/
5
Acceleration
- A change in velocity
- Recall velocity has both speed AND direction
therefore, any change in speed or direction is
acceleration
- Change in velocity divided by time
- m/s2, km/h/s
- speed up, slow down or change directions
6
Constant Acceleration
7
Free Fall, Acceleration due to Gravity
- The position of the free-falling object at
regular time intervals, every 0.1 second, is
shown. - The distance which the ball travels every
interval of time is increasing.
http//www.physicsclassroom.com/
8
The direction of the velocity changes as the car
moves around the curve, so that the velocity v2
is not the same as the velocity v1 even though
the speed has not changed.
9
The direction of the velocity changes whena ball
bounces from a wall. The wall exerts a force on
the ball in order to produce this change.
10
VERTICAL MOTION!!!!
- What do you know about falling objects??
- Do heavier objects fall faster?
11
Acceleration due to Gravity
Assume an object is being launched upwards, then
gravity will reduce the speed of the object.
Conversely, gravity increases the speed of a
falling object.
Near the surface of the Earth, all objects
accelerate at the same rate (ignoring air
resistance).
This acceleration vector is the same on the way
up, at the top, and on the way down!
a -g -9.8 m/s2
9.8 m/s2
Interpretation of -9.8 m/s2 Velocity decreases
by 9.8 m/s each second, meaning velocity is
becoming less positive or more negative. Less
positive means slowing down while traveling up,
more negative means speeding up while falling
down.
12
http//visual.physics.tamu.edu/vp218/LabManual/Fig
ure02_22.jpg
13
Free Fall
- Motion under the influence of gravity only
- The force of gravity accelerates objects towards
earth at 9.81 m/s²
http//www.physicsclassroom.com/
14
Do heavier objects fall faster?
- Feather Hammer On Moon!
No air resistance
Real scenario
http//www.physicsclassroom.com/
15
Problems
- A ball is thrown into the air and rises for 3
seconds before it begins to fall. Draw this
situation and then describe the velocity and
acceleration of the ball. - You throw a ball straight up into the air with an
initial velocity of 40 m/s. Describe the motion
at each second. Estimate the velocity and
acceleration at each point!
16
Practice Makes Perfect
- TIPS Helpful Hints
- Use same method and formulas
- If you read object was dropped you know vo 0
m/s - a g 9.81 m/s² downward or -9.81 m/s2
- More practice Seagulls will drop clams
repeatedly onto a hard surface from high up in
the air until the shell cracks. If a seagull
flies to a height of 54 m, how long will it take
the clam to fall to the ground?