Small Intestinal Wall - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title:
Small Intestinal Wall
Description:
... acids from the liver coat the fat droplets in duodenum Keeps them from re-forming into globules again Arranges them to make them more water soluble ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:152
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Small Intestinal Wall
1
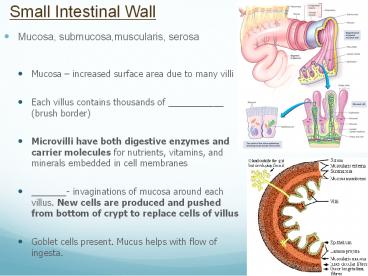
Small Intestinal Wall
- Mucosa, submucosa,muscularis, serosa
- Mucosa increased surface area due to many villi
- Each villus contains thousands of ___________
(brush border) - Microvilli have both digestive enzymes and
carrier molecules for nutrients, vitamins, and
minerals embedded in cell membranes - _______- invaginations of mucosa around each
villus. New cells are produced and pushed from
bottom of crypt to replace cells of villus - Goblet cells present. Mucus helps with flow of
ingesta.
2
Nervous System and Small Intestines
- _____________ nervous system provides stimulation
for intestinal motility, secretions, and blood
flow. - _____________ nervous system decreases
circulation to the intestines. - Intestinal tract is constantly functioning and is
never at rest.
3
Small intestine Motility
- Peristalsis
- Circular contractions prevent backflow of
ingesta, longitudinal muscles propel ingesta
caudally - Dilation of bowel with ingesta stimulates
peristalsis - CCK and Prostaglandins can both affect motility.
- Fats/protein in the intestine stimulate the
mucosa to release CCK, which increases intestinal
motility (opposite of the effect on the stomach) - Prostaglandins can increase GI motility and
secretions which can lead to colic. - Segmental contractions slow the movement of
ingesta to allow time for it to be both mixed
with intestinal enzymes and absorbed through the
intestinal wall. - Many times diarrhea is caused not due to
increased peristalsis, but lack of segmental
contractions.
4
Small Intestine Digestion
- _____________, _____________, _____________
- Absorbed intact across SI wall
- _____________, _____________, _____________
- Chemically digested via enzymes in the lumen and
enzymes on the microvilli b/c they are too large
to pass through the mucous membrane
5
Carbohydrate Digestion
- Starch is broken into disaccharides by amylase
found in the saliva and from the pancreas - Disaccharides are broken down into
monosaccharides by enzymes (lactase, sucrase, and
maltase) in microvilli - Monosaccharides can then be transported across
microvilli and absorbed into blood - Microvilli enzymes are dependent on diet
(Lactose-intolerant animals/diarrhea)
Food Enzyme Source Broken into Fate
Starch Amylase Saliva, Pancreas Disaccharide
s lactose sucrose
maltose Lactase Brush border Monosaccharides
Sucrase glucose Absorbed Maltase
galactose Absorbed fructose Absorbed
6
Protein Digestion
- Protein chains are broken into smaller
polypeptides by pepsin - Polypeptides are broken down into peptides
(several amino acids) by pancreatic proteases - Peptides are broken down into amino acids,
dipeptides, and some tripeptides by peptidases
are then absorbed
Food Enzyme Source Broken into Fate
Protein Pepsin Stomach Polypeptides Protease
s SI (Pancreas) Peptides Peptidases Brush
border Amino acids Absorbed di-peptides
Absorbed tri-peptides Absorbed
7
Fat Digestion
- Agitation of the pyloric antrum emulsifies
(breaks down) fat globules (triglycerides) into
smaller droplets - Bile acids from the liver coat the fat droplets
in duodenum - Keeps them from re-forming into globules again
- Arranges them to make them more water soluble
- Pancreatic lipases (fat-digesting enzymes)
penetrate bile acid coating - Digest triglycerides to form glycerol, fatty
acids, and monoglycerides (micelles) which are
absorbed through the microvilli - Vitamins A, D, E, K are often absorbed with the
micelles
Food Enzyme Source Broken into Fate
Lipids Bile acids SI (Liver) small fat
droplets Lipases SI (Pancreas) glycerol Absor
bed fatty acids Absorbed monoglyceride
s Absorbed
8
(No Transcript)
9
Large Intestine
- Species variation in structure
- Components
- 1. ________ - blind sac at ileocecal junction
- 2. ________
- 3. ________
- Primary functions -
- Store feces
- Recover fluid and
- electrolytes
- Hindgut fermentation (non ruminant herbivores)
- Equine, guinea pigs, rats, rabbits, swine
10
Large Intestines
- ____________ simple, tubular colon poorly
developed cecum - __________ __________ very large colon and cecum
(hindgut) - Fermentation site
- Modifications of cecum and colon allow
fermentative digestion in hindgut - similar to rumen
- VFAs (produced by microbes) absorbed from cecum
and colon for energy needs (similar to rumen) - Possible areas of impaction
- Flexures, Small colon
- Cause of colic
11
Horse Hindgut
- Consists of 4 sections
- Cecum, Ventral colon (right and left halves),
Dorsal colon (right and left halves), Small colon - Cecum is composed of
- Base, Main body, Apex
- Cecum and dorsal and ventral colons have
longitudinal bands that separate the structure
into a series of sacs called ________ - The role of the small colon is to absorb
electrolytes, water, and any VFAs that were not
previously absorbed.
12
Rectum
- Terminal portion of the large intestine an
extension of colon - Capable of more expansion than colon
- Mucus-secreting glands ___________ feces to aid
their passage - Has sensory receptors that detect stretching or
distention and stimulates defecation response.
13
Anus
- Internal sphincter under ________ control
- (Parasympathetic system causes relaxation,
Sympathetic system causes constriction) - External sphincters under __________ control
- As rectum distends, stretch receptors cause
partial relaxation of internal sphincter. Fecal
material moves into the Internal Sphincter Canal
which stimulates more stretch receptors
increasing urge to defecate. - Stretching of Anal mucosal receptors increase the
sense or need for defecation - Surgery or disease in anal region can damage
sphincter muscles and nerves, causing incontinence
14
Livers Role in the GI Tract
- ________, __________, and/or ___________
materials absorbed from GI tract before they
reach blood. - Removes toxins, infectious agents, old blood
cells that enter the body via the GI tract. - Glucose, amino acids, and vitamins are stored or
metabolized. - Glucose absorbed by the GI tract can be stored in
the liver as _____________ (glycogenesis). When
glucose is needed in the blood, glycogen is
broken down by the liver (glycogenolysis).
_____________________ is the process of glucose
being made in the liver by using amino acids. - Major source of blood __________
- Albumin
15
Gallbladder
- The liver produces _______ which contains bile
acids, cholesterol, and bilirubin - Bile is secreted into bile ducts, which lead to
the hepatic duct, which leads to the
____________for storage (not horse) - The gallbladder stores bile until it is
stimulated by CCK (due to fat in SI), causing it
to contract. - Contraction forces bile down the common bile duct
into the duodenum, where it aids in the digestion
of fat.
16
Pancreas Role in the GI Tract
- Exocrine and endocrine gland
- Exocrine functions
- Produces _________, _________, ___________
- Secretes _____________ (HCO3-)into duodenum
- Neutralizes acidity of stomach contents and
maintains pH in duodenum needed for proper enzyme
function - Endocrine functions
- Produces ___________ _________
- Regulates blood glucose levels
- Insulin moves glucose from the blood to the
bodys tissues. Glucagon stimulates
gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in the liver.