A F R I C A - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 54
Title:
A F R I C A
Description:
Genocide in Sudan Through a system of torture, ... Niger River is rich in natural mineral land EAST-Rift Valley grasslands Animal reserves Southern- rich ... & Eco ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:238
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: A F R I C A
1
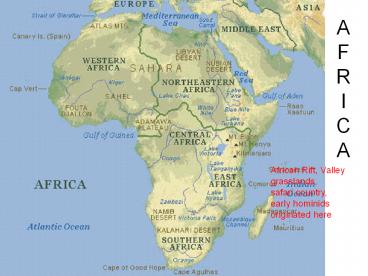
AFRICA
African Rift, Valley grasslands, safari country,
early hominids originated here
2
Africa is a continent of diverse geographic
people, resources, culture, and
societies. North- Sahara- Arabic traders Nile
river valley West- Tropical Jungle, Niger River
is rich in natural mineral land EAST-Rift Valley
grasslands Animal reserves Southern- rich
resources, dry plateau.
3
A Satellite View
- The Sahara
- desert separates North/ Arabic
- from the Sub-Saharan/Black
- region
4
Africa
- History- points in early history
- Colonialism Legacy of
- Resources
- Sudan
- Rwanda
- Apartheid in South Africa
- History of South Africa
- White Afrikanner colonialism
- Apartheid
- Nelson Mandela
- Truth and Reconciliation
5
Mediterranean Sea
Atlas Mts.
Libyan Desert
The Complete Topography Of AFRICA
Tropic of Cancer 20 N
Red Sea
Sahara Desert
Nile River
Sahel
Niger River
L. Chad--gt
Great Rift Valley
lt--Gulf of Aden
L. Albert--gt
? Mt. Kenya
Equator 0
Congo River
L. Victoria
? Mt. Kilimanjaro
Indian Ocean
L. Tanganyika-gt
Ruwenzori Mts.
Atlantic Ocean
Zambezi River
Namib Desert
Kalahari Desert
Limpopo River
Tropic of Capricorn20 S
Orange River
Drajensburg Mts.
Pacific Ocean
6
Great Rift Valley
3,000 miles long
7
Mt. KilimanjaroSnow on the Equator?
8
Natural Resources
9
The African Savannah13 million sq. mi.
10
African Rain Forest
- Annual rainfall of up to 17 ft.
- Rapid decomposition (very humid).
- Covers 37 countries.
- 15 of the land surface of Africa.
11
Key points in Early African History
- Hominids orginate in Africa- five million yrs
ago - 5000 BC Ancient Egyptian civilizations in NE
Africa domesticated animals, grew crops along the
NILE- Art, Writing, Irrigation, Empire,
Government, Architecture - Ancient iron-age groups of people settled all
parts of Africa with AGRICULTURE and
- TRADE of RESOURCES trading gold, copper,
precious stones, animal hides, ivory and metal
goods
12
Look at the Colored tribal regions And the gray
country boundaries
13
Early Africa
- There were many great empires in Sub-Saharan
Africa over the past few millennia, especially in
West Africa and Southern Africa where important
trade routes and good agricultural land allowed
large states to develop. - CHRISTIANITY-spreads into north Africa Coptic
Christians- Egyptians - Trade between Mediterranean countries and West
Africa across the Sahara Desert, was important
and this is how - Islam spreads into northern Africa in the
700-1000 - The arrival of Islam created a significant
political and social change - Leaders converted to Islam- Arabic and Muslim law
in administration - Mix of Arab and Native culture
- The Portuguese explore and again spread
Christianity into No and West Africa in the
1500s. - The DUTCH in the 1600s begin colonization of
southern Africa
14
Africa and the age of exploration
- Portuguese explorers Vasco Da Gama and Prince
Henry, the Navigator, were 1st to explore Africa
looking for an oceanic route to the Indies.
trading European wheat and cloth for African gold
and slaves. - The Portuguese wanted, to find a route to India
and kept trying to circumnavigate Africa. - Beginning in the 17th century, the Netherlands
began exploring and colonizing Africa. - To compete with the Portuguese, two Dutch
companies were founded the West Indies Company,
with power over all the Atlantic Ocean, and the
East Indies Company, with power over the Indian
Ocean. - the Dutch built 16 forts in different places,
partly overtaking Portugal as the main
slave-trading power. - The Dutch left a lasting impact in South Africa,
a region ignored by Portugal that the Dutch
eventually decided to use as station in their
route to East Asia. They founded Cape Town in
1652, starting the European exploration and
colonization of South Africa.
15
Ancient African Societies
16
African Slave Trade
- The earliest African slave trade across
the-Sahara. - When camels were introduced into Africa from
Arabia in the 900s slaves were carried north
mostly as servants. Women became servants and
became part of harems - The Atlantic slave trade developed later, and
would have a much bigger impact. As colonies in
the New world grew the demand for slave labor
grew. - Workers were needed for agriculture, mining and
other tasks. To meet this new demand, a
trans-Atlantic slave trade developed. Slaves
purchased in those West African regions known as
the Slave Coast, Gold Coast, were often captives
of internal warfare or were exchanged with
European slave traders for firearms, rum, fabrics
and seed grain. - The AFRICAN SLAVE TRADE DEPLETED Africa of able
bodied MEN and hurts their economic development
17
(No Transcript)
18
Slavery led to 7 million Africans being shipped
out of Africa
19
EuropeanNationalism
Industrial Revolution
Source for Raw Materials
MissionaryActivity
These create fierce competition Economic and
political motives overlap
European Motives For Colonization
Markets forFinishedGoods
Military NavalBases
SocialDarwinism
Places toDumpUnwanted/Excess Popul.
EuropeanRacism
Soc. Eco.Opportunities
WhiteMansBurden
20
Exploration to Colonization
- European exploration of Africa in the 17th and
18th centuries was very limited. Instead they
were focused on the slave trade, which only
required coastal bases and items to trade. The
interior exploration and colonization of the
African interior would start well into the
1800s. - Many explorers felt that it was their duty to
introduce Western civilization and Christianity
to "savage" black African peoples - SOCIAL DARWIN, SURVIVAL OF THE FITTEST, WHITE
MANS BURDEN to IZE Civilize, Christianize,
Westernize the native people
21
European Colonialism
- Imperialism- extending ones control over
another - Colonialism- annexing territory outright and
establishing governments to rule over people - Thru the 1800s the Industrial revolution and
economic competition led European nations to
COMPETE FOR COLONIES and the division of Africa.
driven by small groups of wealthy financiers - Europeans convene the BERLIN CONFERENCE 1844 to
establish how AFRICA would be partitioned
resulting in.. - Scramble for Africa- most sudden case of
colonization 1875-1902 Europeans colonized 90 of
Africa in less that 20 years - Colonial Administration of colonies
- Europeans were encouraged to settle in colonies
creating DOMINANT MINORITY SOCIETIES, - Colonial administrators used one ethnic group
over another the DIVIDE AND CONQUER technique
giving one group power over another to
administer. Thus was the case in RWANDA as we
will see. - In most cases colonial administrators could not
fully administer the territories and relied on
local power thus creating various factions with
in the societies.
22
Legacy of European Colonialism
- European colonialism had a devastating impact on
Africa. - Africa is PLAGUED with, economic, political and
humanitarian problems - Profits from colonialism and empire building DID
NOT MATCH EUROPEAN EXPECTATIONS - Exploiting the native people and the land
- THIS led to major political problems b/c of
random borders that were created without regard
for ethnic groups and land - WAR, corruption in military governments, famine,
and disease all hamper economic progress. - The struggle to rebuild is proving difficult.
23
Africas Problems
- The Legacy of European Colonialism has created
- Political corruption, Militaristic dictators,
lack of respect for rule of law, human rights
violations are all common reasons for some of the
causes of Africas problems. - The artificial boundaries created by colonial
rulers brought together many different ethnic
people within a new nation that did not reflect
the cultural and ethnic diversity.
24
Current problems in Africa
- Dictatorship- no democracy little free enterprise
and RAMPANT POLITICAL CORRUPTION and political
Instability - Health Epidemics- AIDS, clean water
- Lack of Infrastructure- roads, hospitals,
schools, extracurricular opportunities. - Inability to transform raw materials and natural
resources to economic activity jobs - ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT lacks
25
The legacy of Belgian Colonialism
- King Leopold of Belgium-takes the Congo as his
personal kings colony. - He forced the natives to provide him with quotas
of Ivory, rubber and other natural resources for
his own personal wealth - He started the brutality of natives by having
their hands CUT OFF as a way to force them to
provide him with resources. - His forces would also take the women and children
and brutalize them - These practices were then taken by on by rebels
and leaders as a system of brutality.
26
5-8 Million Victims! (50 of Popul.)
It is blood-curdling to see them (the soldiers)
returning with the hands of the slain, and to
find the hands of young children amongst the
bigger ones evidencing their bravery...The rubber
from this district has cost hundreds of lives,
and the scenes I have witnessed, while unable to
help the oppressed, have been almost enough to
make me wish I were dead... This rubber traffic
is steeped in blood, and if the natives were to
rise and sweep every white person on the Upper
Congo into eternity, there would still be left a
fearful balance to their credit. --
Belgian Official
27
- King Leopold's legacy http//news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/
africa/3516965.stm
28
South Africa
- Originally colonized by the Dutch then the
British. A Dominant Minority Society was created - Discovery of Diamonds, GOLD, wineries, Tourism,
and European investments. Makes SA a modern nation
29
South Africa
- The system of Apartheid officially segregated the
whites, mixed and blacks and oppressed and
suppressed human rights. - In 1994 After an anti-Apartheid movement.
Apartheid ends and Nelson Mandela becomes the
first black President - Mandela credited Mahatma Gandhi as a major source
of inspiration in his life, both for the
philosophy of non-violence and for facing
adversity with dignity.
30
(No Transcript)
31
1993 Black Hawk Down Occurs in SOMALIA
Genocide in Rwanda
1994 after years of ethnic fighting genocide
breaks out in Rwanda US DOES NOT WANT TO INTERVENE
32
A Brief History of Hutus and Tutsis
- Hutus first settled in the Great Lakes region of
Central Africa between 500 and 1000 BC.
Generally, Hutus were an agricultural people who
lived in large family groups. They agreed to
raise crops for the Tutsi in return for
protection. - The Tutsis, a tall, nomadic, warrior people, who
began arriving in the Great Lakes region from
Ethiopia some four hundred years ago, settled
among the Hutus - They intermarry - adopting their language,
beliefs and customs, the two lived in harmony.
- The Hutu make up about 85 of the population and
the Tutsi only about 15
33
Causes of the Hutu Tutsi conflict
- Colonialism identifies economic differences. The
Tutsis as cattle-herders were often in a position
of economic dominance to the soil-tilling Hutus.
That is not to say that all Tutsis were wealthy
and all Hutus were poor, but in many areas, like
Rwanda, the minority Tutsis ruled the Hutus - Colonial rule, in the late 19th Century, did
little to bring the groups together. - The Belgians, who ruled what would later become
Rwanda and Burundi, saw the Tutsi, who were
taller and a bit lighter, as superior to the
Hutus - They forced Hutus and Tutsis to carry ethnic
identity cards. The colonial administrators
further exacerbated divisions by only allowed
Tutsis to attain higher education and hold
positions of power - The animosity of the Tutsis by the Hutus has
grown since their independence
34
Before the Genocide
- Since the end of colonialism the fighting between
Hutus and Tutsis has existed leading to the
massacre of ½ a million and more in refugees - 2,500 UN peace keeping forces have been in
central Africa since 1990 overseeing a cease-fire
accord agreement - Belgian troops have also been stationed trying to
keep ethnic tensions under control
35
The Genocide begins
- Hutus turned on Rwanda's Tutsi minority on the
night of April 6, 1994, after a plane carrying
the presidents of Rwanda and neighboring Burundi
was shot down. - Bands of Hutu thugs, working mostly with machetes
and astonishingly relentless enthusiasm, killed
almost 1 million men, women and children and
turned another 2 million into refugees, all for
the crime of being Tutsis
36
Genocide in Rwanda
- Between APRIL AND JUNE 100 days 800,000 Rwandans
were Killed as the world stood by. (8000 per day) - This Ethnic Genocide occurred between the HUTUs
and TUTSIS. - Most of the Victims were the Tutsis and moderate
Hutus - The Perpetrators--- were the Hutus led by an
extremist group the Interahamwe. - The west and the UN were aware of this massacre
AS it was happening
37
- The Ethnic conflicts between Hutus and Tutsis
created hundreds of thousands of refugees
spilling over into neighboring Zaire and Burundi
38
800,000 killed in 100 days systematic slaughter
of men, women and children
1 million refugees
39
Lieutenant-General Roméo A. DallaireCommander of
the United Nations Assistance Mission for Rwanda
during the 1994 Rwandan Genocide
- Dallaire did everything he could, pleading for
2000 more peacekeepers to be added to his
insufficiently equipped 3000 man force. - If they had answered Gen. Dallaire's pleas, the
U.N. could have stopped the slaughter of hundreds
of thousands of Rwandans. Instead, following the
deaths of 10 Belgian Peacekeepers assigned to
protect the President, most white Europeans left
RWANDA and his forces were cut down from 3000 to
a mere 500 men, - A Good Man In Hell
40
Roméo A. Dallaire
- Gen. Romeo Dallaire, frustrated, and disheartened
by the U.N.'s passive attitude, repeatedly
confronted his superiors and the extremists. - He was unable to prevent horrific events from
unfolding. - They essentially watched as one of the most
horrible genocides in human history took place
before their very eyes.
41
UN admits Rwandan genocide failure
- The United Nations Security Council has
explicitly accepted responsibility for failing to
prevent the 1994 genocide in Rwanda. - UN council members acknowledged that their
governments lacked the political will to stop the
massacres.
Massacre in church in Nibouye A technical college
in the south Project Rwanda- Orphanage
42
Why was there no U.S. response
- Clinton administration officials identify
factors, including the "Somalia syndrome."
Congress and the Clinton administration were
reluctant to send U.S. troops into more
humanitarian missions after the disastrous
retreat from Mogadishu
- Rwanda was a country of no strategic importance
and President Clinton has been criticized for
lack of leadership and lack of national interest
in responding to the genocide in Rwanda
43
End of the Genocide
- The Tutsi rebels, called the (RPF) Rwandan
Patriotic Front led by the now president, Paul
Kagame, - Put an end to the massacre by overthrowing the
Hutu leaders and capturing the capital Kigali. - Elections have been held and both groups are
represented in the government
Paul Kagame
44
DARFUR
45
About Darfur, Sudan
- The Sudan is located in North Africa. Neighboring
countries include Chad, to the west, and Saudi
Arabia, to the east across the Red Sea. - Darfur is located in the western region of Sudan,
Africa.
46
How It Began
- An outbreak of civil war in Darfur, entirely
separate from Khartoums 21-year assault against
the African peoples of southern Sudan. - The people of Darfur rose up in a rebellion early
in 2003 and militarily. - The Islamic government of Sudan, is deliberately
destroying the African tribal peoples of the
region. - What the U.N. and Western diplomats are calling
ethnic cleansing, it is actually an ongoing
genocide.
47
Genocide in Sudan
- Through a system of torture, rape and murder, the
government sponsored Arab militia, known as the
Janjaweed, has succeeded in killing almost one
half million black tribal Africans since February
of 2003. Their goal is to eliminate the black
tribal African farmers in that region. - WHY
48
Genocide in Sudan
- 4 million are starving.
- Estimated 500 people a day die in the region.
- Disease takes its toll on a great number of
people in the refugee camps, - There are inadequate medical supplies, shelter,
food, as well as poor sanitation for the
excessive number of people who need it. The
international community has taken notice- the
U.S. Congress recently labeled the situation in
Darfur a genocide. - A team of U.N. human rights investigators
reported that the government and the Janjaweed
have instituted a "reign of terror".
49
Genocide in Sudan
- Like in the Rwandan genocide in 1994, nothing
substantial has been done to stop the atrocities
in Darfur. - Two "cease-fires", in 2004 and 2006, have not
prevented the violence from continuing, and the
situation is becoming increasingly dire.
50
A Genocide warning
- The Principal victims include the Dinka and Nuer
peoples in southern Sudan and the Nuba in central
Sudan. - The Sudanese government a military regime based
in the north led by Omar al- Bashir is Primarily
responsible for the devastation. - The genocide warning has been issued based on the
following actions. - 1. Divide and Destroy strategy of pitting ethnic
groups against each other with enormous loss of
civilian life. - 2. The use of mass starvation as a weapon of
destruction. Food supplies and livestock have
been destroyed
51
A Genocide warning
- 3. Rape and enslavement of women and children by
the government allied militia. - 4. Bombings of hospitals, clinics, schools, and
other civilian and humanitarian targets. - 5. Disruption and Destabilization of the
communities of those who flee the war zones to
other parts of Sudan. - Taken together these actions threaten the
destruction of an entire group.
52
WHY
- OIL sits under the land in DARFUR and the Arab
military government, which came to power after a
Coup take over of a democratically elected
government, can get OIL revenues only if it gets
the land. - Why Target China?
- China is the leading foreign investor in Sudan,
with an annual trade value of roughly 1 billion.
In the past several years, - China has developed a number of oil fields, built
a 900 plus mile pipeline, as well as a refinery
and a port. Sudan represents China's largest
overseas investment, worth at least 3 billion,
and Sudan is the third largest supplier of oil to
China. - China's trade in oil with Sudan has close
connections with arms dealing. Many of the
helicopter gunships used by Khartoum were
purchased from China using expected revenues from
oil extracted in South Sudan. - Amnesty International has documented the effect
of China's arms exports to Sudan, noting that
Chinese equipment has been used by the Government
of Sudan and Janjaweed in operations in Darfur.
53
CHINA
- It is incumbent upon China to do all it can to
address the tragedy in Darfur and Chad. As a key
supplier of arms and funds to the Khartoum
government, China is especially responsible for
the continued violence in Darfur at the hands of
the Government of Sudan and the Janjaweed. - Furthermore, by virtue of its close relationship
with the Government of Sudan, China is one of
only a few actors that can exert pressure to end
the targeting of civilians in Darfur, and fulfill
commitments Khartoum has made to disarm the
Janjaweed and adhere to its responsibility to
protect civilians in Sudan.
54
The Death Toll
- The death toll exceeds 100,000 and may be more
than 400,000 - About 2 million civilians have been driven from
their homes, their villages torched and their
property - thousands of women raped