The Monk who loved peas - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
The Monk who loved peas
Description:
How to Make a Living Thing The Monk who loved peas Gregor Mendel Monk, failed teacher, pea-lover, genetic genius From growing peas, Mendel noticed that offspring did ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:108
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Monk who loved peas
1
The Monk who loved peas
- How to Make a Living Thing
2
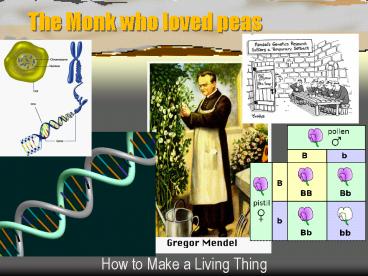
Gregor Mendel
- Monk, failed teacher, pea-lover, genetic genius
- From growing peas, Mendel noticed that offspring
did not always have the same traits as the
parents - But then the parents trait would show up again
in a grandchild, or 2nd generation - So Mendel began to experiment, attempting to grow
peas with certain traits, or characteristics
3
The Proof is in the Peas
- Peas were an excellent choice for his research
for two reasons - They can self-pollinate, creating offspring with
the same traits as the parent - Or, they can cross-pollinate with other peas
4
The Experiment
- Mendel looked at one characteristic at a time
(color, height, shape) - If a pea plant has a white flower, then it
self-pollinates, youll have offspring with white
flowers - What happens if a purple-flowered pea plant
cross-pollinates a white-flowered pea plant?
5
Mendels Discovery
- Mendel noticed the offspring of a purple-flowered
pea plant and a white one was always purple - BUT, the grandchildren or 2nd generation, would
have 1 white-flowered pea plant for every three
purple ones
6
Dominant Traits
- Dominant traits are the ones always showing up in
the first generation - The purple-flowered pea plant
- In a Punnett Square, dominant traits are
symbolized by a capital letter
7
Recessive Traits
- Fade into the back
- The white-flowered pea plant
- These traits reappear in the 2nd generation
- MUST be paired with another recessive allele
8
Incomplete Dominance
- Sometimes, one trait is NOT dominant over the
other - Each allele provides some influence
- Hair texturecurly, straight, and wavyis an
example in humans
9
Genes
- The instructions for one particular trait are
called a gene - You have 2 forms of the same gene for every
characteristic - 1 from Mom, 1 from Dad
- Hair color, eye color, height, hitchhikers
thumb, etc.
10
Alleles
- The form of a trait given by one parent
- So, for each gene, you have 2 alleles
- Either dominant (capital letter) or recessive
(lower-case)
11
Genotype and Phenotype
- Both inherited traits form a genotype
- --Aa rr etc.
- The appearance of a characteristic is the
organisms phenotype - --a purple flower wrinkled peas wavy hair
12
Genetic Probability and Pedigrees
- Probability is the mathematical chance of an
outcome - Aa x Aa has a 25 chance of getting aa as an
outcome 25 AA 50 Aa - Pedigrees are like family trees for determining
the probability of genetic diseases like cystic
fibrosis