Facilitated Diffusion - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
Facilitated Diffusion
Description:
Facilitated Diffusion & active transport Facilitated Diffusion Integral proteins help molecules through membrane. 3 characteristics No energy is used Specific May ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:91
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Facilitated Diffusion
1
Facilitated Diffusion active transport
2
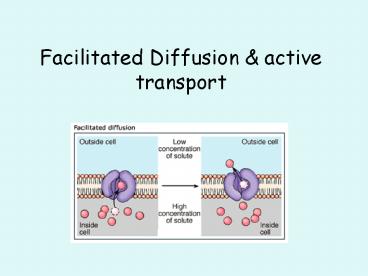
Facilitated Diffusion
- Integral proteins help molecules through
membrane. - 3 characteristics
- No energy is used
- Specific
- May become saturated
- Example glucose
Glucose molecules entering a cell using
facilitated diffusion.
Hint integral means a part of, integral
proteins go through the plasma membrane (also
called transmembrane proteins). Perpherial
proteins are only on the surface of the membrane.)
3
Active Transport
- Need to move molecules up a concentration
gradient. - Uses cellular energy in from of ATP.
Ions moving across membrane by active transport.
Think why does the cell need to use energy to
pump the yellow balls out? Think about the
concentration gradient is it moving uphill or
downhill?
4
Active Transport Coupled Channels
- Molecule that is needed in the cell is moved
through protein with another substance. - Na diffuses back into cell allowing second
molecule through.
Coupled channel.
Hint Find Na on your periodic table what is it?
5
Active Transport Proton Pump
- Hydrogen ions (H) are actively pumped out of a
cell - Diffusion causes H ions to return through a
protein. - When H returns ATP is produced.
- Chemiosmosis (part of photosynthesis and
respiration)
Chemiosmosis.
Hint take another look at your periodic table.
What is a hydrogen atom without an electron?
6
Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis
- Endocytosis
- Cells form a vesicle to move large solid
materials into the cell. - Exocytosis
- Cells moving large materials out of the cell.
Hint when have we used the prefixes endo and
exo before? Look at our Latin roots.
7
Two types of endocytosis
- Phagocytosis
- Solid objects moved into the cell. (phago mean
to eat.) - Pinocytosis
- Liquids moved into the cell. (pino means to
drink)
8
Summary should be at least 4 sentences.
- Name 3 features of facilitated diffusion.
- Name 2 ways active transport is different than
passive transport. - How do cells get large objects inside?
What does Garfield have wrong about osmosis?