Autonomic Nervous System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Autonomic Nervous System
Description:
Autonomic Nervous System Controls automatic functions at subconscious level _____ nervous system - nerves emerge from thoracic and lumbar vertebral regions ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:50
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Autonomic Nervous System
1
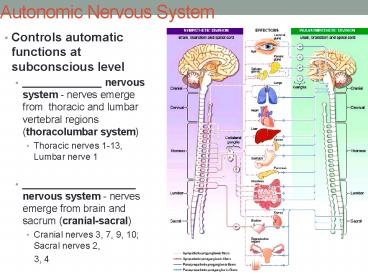
Autonomic Nervous System
- Controls automatic functions at subconscious
level - ______________ nervous system - nerves emerge
from thoracic and lumbar vertebral regions
(thoracolumbar system) - Thoracic nerves 1-13, Lumbar nerve 1
- ____________________ nervous system - nerves
emerge from brain and sacrum (cranial-sacral) - Cranial nerves 3, 7, 9, 10 Sacral nerves 2,
- 3, 4
2
Table 13-3. Effects of Sympathetic and
Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
Sympathetic System Parasympathetic System
Effect Effect Heart rate Increases
Decreases Force of heart
contraction Increases No significant
effect Diameter of bronchioles Increases
(dilates) Decreases (constricts) Diameter
of pupil Increases (dilates)
Decreases (constricts) GI motility,
secretions,and blood flow Decreases
Increases Diameter of skin blood
vessels Decreases No significant
effect Diameter of muscle blood
vessels Increases No significant
effect Diameter of blood vessels to
kidney Decreases No significant effect
3
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
- Sympathetic nervous system
- 1º neurotransmitter_____________________
- Released from Sympathetic POSTganglionic neurons
- ADRENERGIC neurons - neurons that release
norepinephrine - Epinephrine/norepinephrine also released from
adrenal medulla - To elicit an effect, effector organ must contain
receptor for epi/norepi
4
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
- 1. ______- adrenergic receptors cause
vasoconstriction of skin, GI tract, and kidney
(dont need to digest, make urine, or bleed
profusely) - 2. _______-adrenergic receptors - increase heart
rate and force of contraction - 3.________-adrenergic receptors - cause
bronchodilation (relaxation)
5
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
- Parasympathetic nervous system
- 1º neurotransmitter__________________
- CHOLENERGIC neurons - release acetylcholine
- (Even though norepinephrine is the
neurotransmitter associated with the sympathetic
nervous system, the PREganglionic neuron in BOTH
the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic systems is a
CHOLINERGIC neuron that releases ACETYLCHOLINE) - 2 types
- Nicotinic receptors- found on POSTganglionic
neurons in BOTH the Sympathetic and
Parasympathetic systems - Muscarinic receptors- found on the target organs
and tissues supplied by the postganglionic neuron
of the parasympathetic nervous system
6
Summary receptor types
7
Reflexes
- Reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to
stimuli. They serve to protect the body and
maintain homeostasis - ____________ reflexes - involve contraction of
skeletal muscles - _______________ reflexes - regulate smooth
muscle, cardiac muscle, and endocrine glands - _______________ reflex - stimulus and response
are on same side of body - ________________ reflex - starts on one side of
body and travels to opposite side
8
Reflex Arc
- 5 Components
- Sensory receptoractivated by stimulus
- Sensory neurontransports AP to gray matter of
spinal cord or brain stem (cranial n.) and
synapses with other neurons - Interneuronsensory info integrated with info
from other sensory neurons - Motor Neuronresponse is sent out via motor
neuron - Target organeffector cell
9
Stretch Reflex (tap knee)
- Monosynaptic (1) reflex arc ipsilateral reflex
- Involves 1 sensory neuron and 1 motor neuron
- Signals also sent to
- Antagonistic muscle (inhibitory)
- Cerebellum/Cerebrum
10
Withdrawal Reflex
- Also called flexor reflex ipsilateral reflex
- Several interneuron synapses
- Several segments of spinal cord
- Results in
- Contraction of muscles
- Before cerebrum is aware
- Inhibition of antagonist muscles
11
Crossed Extensor Reflex
- Contralateral reflex
- Withdrawal reflex initiated
- Afferent sensory neuron synapses with
interneurons - Causes contraction of opposite extensor muscles
12
CNS Moderation of Reflexes
- Upper CNS (brain) normally produces an inhibitory
effect on the reflex arcs (muffled effect) - With injury, intact reflex arcs caudal to spinal
cord trauma become __________________ - Trauma to a portion of the reflex arc results in
either ______________ or absent reflexes