Protein Synthesis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Protein Synthesis
Description:
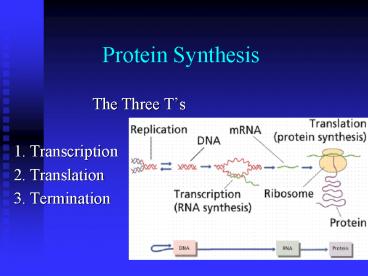
Protein Synthesis The Three T s 1. Transcription 2. Translation 3. Termination Transcription in Eukaryotes ie: Animal cells Protein Synthesis in Prokaryotes ie ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:145
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Protein Synthesis
1
Protein Synthesis
- The Three Ts
- 1. Transcription
- 2. Translation
- 3. Termination
2
Transcription in Eukaryotesie Animal cells
3
Protein Synthesis in Prokaryotesie single
celled Bacteria
4
(No Transcript)
5
Where does All this Happen
6
Protein Synthesis
- Nucleic Acids (DNA RNA) carry the hereditary
information. - This information is contained in codons.
- What are Codons?
A codon is a set of three base pairs (A, T, C, G)
that directs or codes for amino acids. (ex. GCU
Alanine)
7
(No Transcript)
8
How Many Amino acids?
- There are 20 essential amino acids, however they
can be combined in any order, just like the four
nucleotides. This permits the production of the
many different proteins which let organisms grow
and function.
9
Transcription
- This process occurs in the nucleus.
- A section of DNA called a gene is unwound and
unzipped.
10
- A RNA copy of one of the DNA strands is made.
This strand is made complimentary to the
nucleotides on the the DNA Strand. - DNA Bases Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
- RNA Bases Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine
11
(No Transcript)
12
- DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of
RNA. - A regulatory protein binds to the promoter
sequence. - An enzyme (RNA Polymerase) binds to the promoter.
- Together they open the DNA double helix.
- RNA Polymerase proceeds down one strand moving in
the 3 to 5 direction, as it does it assembles a
complementary strand of RNA. - Each ribonucleotide is inserted into the growing
RNA strand following the rules of base pairing. - Transcription stops when the termination sequence
is reached. - The completed RNA copy is now called messenger
RNA or mRNA and carries the coded message to the
ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
13
DNA Strand 1 AGCTATCGAGCAT
DNA Strand 2 TCGATAGCTCGTA
RNA copy AGCUAUCGAGCAU
14
Transcription
RNA polymerase (enzyme) attaches to the promoter
region of the DNA
15
Translation
- The small subunit of the ribosome binds to a site
on the 5 end of the start of the message strand - The ribosome moves downstream (5?3) until it
encounters the start codon AUG - At this time, the large subunit joins and the
initiator t-RNA enters the scene - After this, the tRNA binds to the p site on the
ribosome - The first amino acid that starts this sequence of
peptide bonds is Methionine (one of the 20
a.a.s) - Eucaryotes methionine Bacteria f Met
(modified)
16
T RNA
17
1. Ribosome attaches to mRNA and reads first
codon. 2. A transfer RNA molecule (tRNA for
short) brings the correct amino acid to the
ribosome drops it off. ex AUG (codes for
methionine) tRNA brings methionine to ribosome.
18
3. The ribosome moves on to the next codon and
another tRNA brings the next amino acid. 4. The
amino acids in the growing chain are linked
together by a peptide bond. The growing chain is
called a polypeptide or protein molecule. 5.
When the ribosome reaches a STOP codon the
polypeptide is released and the mRNA falls off.
19
Elongation more specifically!
- As another tRNA arrives with its associated a.a.
and binds to the next codon site, it becomes
covalently linked to the incoming a.a. with a
peptide bond - The initiator tRNA is released from the P site
- The ribosome moves downstream (5?3)
- The more recently-arrived tRNA w/ its peptide
moves to P site and opens the A site for the
arrival of a NEW tRNA and its corresponding a.a.
20
Termination
- End of the message is a STOP codon
- STOP codons UAA, UAG, UGA
- Protein release factor sees these codons at the A
site and tells the polypeptide chain to release
from the ribosome site - Ribosome splits into its subunits until it is
time to make more protein!
21
Termination
22
Check out this link for an animation on Protein
Synthesis
- http//www.lewport.wnyric.org/jwanamaker/animation
s/Protein20Synthesis20-20long.html