Simulation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Simulation
Description:
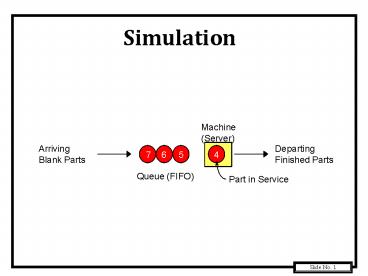
Simulation Machine (Server) Arriving Blank Parts Departing Finished Parts 4 5 6 7 Queue (FIFO) Part in Service Simulation Introduction Basic Concepts 10-Step Study ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:83
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Simulation
1
Simulation
2
Simulation Introduction
- Basic Concepts
- 10-Step Study Process
3
Simulation General Terminology1
Simulation model designed to imitate or mimic a
real-world system or process, usually via computer
Applications - Manufacturing facilities -
Transportation networks - Computer networks -
Business processes
Approaches - Monte Carlo - Discrete-Event -
Virtual - Live
4
Simulation Appropriateness1
- Proper Uses
- Enable study of internal interactions of complex
systems - Observe effect of system changes on system
behavior - Reveal ways to improve system by increasing
knowledge of system - Provide insights on relative importance of
variables - Experiment with new designs or policies before
implementation - Verify analytical solutions
- Enable training in cases where on-the-job
training is expensive - Animate system workings to enable visualization
5
Simulation Appropriateness2
- Not appropriate if
- Common sense solutions exist
- Substituted for obtainable analytical solutions
- Experiment is easier to conduct
- Costs exceed savings
- Resources are unavailable
- Data are not available
- System behavior is too complex
6
Simulation Advantages/Disadvantages
- Advantages
- Can run what ifs of new policies, procedures,
information flows without disrupting real system - Can test system designs before committing
resources - Can speed-up or slow-down system operation
- Can yield insight regarding relative importance
and interaction of variables - Can reveal bottlenecks
- Can increase understanding of how system operates
- Disadvantages
- Requires special training and software
- Can be difficult to interpret results
- Can be time consuming and expensive
7
Simulation Model Types
- Model Representation of a system for the
purpose of studying that system. - Static Represents a system at particular point in
time - Dynamic Represents systems as they change over
time - Deterministic Models with no random variables as
inputs - Stochastic Models with one or more random
variables as inputs, which leads to random
outputs
8
Simulation 10-Step Study Process1
Simulation Step Description 1. Problem
Formulation State problem set objectives plan
study 2. Model Building Determine basic
assumptions and essential features to
characterize system validate 3. Data
Collection Obtain pertinent data
efficiently 4. Model Translation Construct
computer program model 5. Verify
(Debug) Computer program performing properly?
9
Simulation 10-Step Study Process2
Simulation Step Description 6.
Validate Computer model representing real
system well? 7. Experimental Design Initial
conditions, run length, of replications, 8.
Production Run Run model to estimate
performance measures 9. Analysis Correlation,
analysis of variance, regression,
hypothesis testing, etc 10.
Conclusions Document, present, and implement
results