Membrane Structure - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Membrane Structure
Description:
Title: Slide 1 Author: Stephen D. Ebbs Last modified by: D P Althoff Created Date: 7/9/2005 3:53:30 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Membrane Structure
1
Membrane Structure FunctionSpring 2013 -
Althoff Reference Mader Windelspecht Ch. 5)
Lec 05
2
- ____________________ the boundary between
the cells inside workings and the world outside
it. - Keys to consider 1) ____________ for
exchange between inside and outside the
cell 2) _________________ are exchanged
3
A Little History
- Beginning of 20th century researchers noted
lipid soluble molecules entered cells more
rapidly than water soluble molecules - In ______________________________ determined
phospholipid content of a cell just enough to
form a bilayer around the cells
In ______________________________
proposed proteins also part of membrane. Model
they proposed was sandwich-like, further
enhanced by Robertson in late 1950s.
4
A Little History
- Robinsons ______ _________ model. late1950s
BILAYER PHOSPHOLIPID SANDWICH,
- Singer Nicolson __________ model, 1972.
EMBEDDED PROTEIN MOLECULES
5
(No Transcript)
6
PHOSPHOLIPID
OUTSIDE THE CELL
INSIDE THE CELL
(similar to Mader p86 Fig. 5.1)
7
Components of the PLASMA MEMBRANE
Lipids
Proteins
- Phospholipids bilayer (meaning 2 layers)
- Exterior portions are hydrophilic (2 places)
- Interior portion of the bilayer is hydrophobic
- Provides essential structure to this portion of
the cell
- Protein molecules are embedded in the plasma
membrane - Serve to stabilize and shape the plasma membrane
- Various (many) proteins perform specific
functions 1) channel 2) transport 3) cell
recognition 4) receptors 5) enzymes 6) form
junctions
8
PLASMA MEMBRANE A matrix of proteins
Proteins
- Some proteins span the entire bilayer distance
(__________________ proteins) - Some proteins reach the inside surface only
OUTSIDE
INSIDE
9
Fluidity of the Plasma Membrane
- At room temperature, the __________________
of the plasma membrane has the consistency of
olive oil - Result ___________________
- _____________________ those not attached to the
cytoskeletoncan move within the fluid lipid
bilayer - This fluidity is critical to the _________ of
proteins, particularly enzymes which speed up
chemical reactions
10
Lipid Movement
11
Plasma Membrane PROTEINS
- CHANNEL proteins _________________, control
passage of molecules - CARRIER proteins ____________ combine with a
substance and move it across the membrane - CELL RECOGNITION proteins _________ looking
for pathogens, alert immune system - RECEPTOR proteins __________, bind with other
molecules resulting in shape change that brings
about cellular response - ENZYMATIC proteins ________, facilitate/speed
up metabolic reactions directly - JUNCTION proteins ___________________ form
junctions between cells
12
CHANNEL
CARRIER
RECOGNITION
JUNCTION
RECEPTOR
ENZYMATIC
13
When Function Goes _____
- CHANNEL proteins faulty chloride (Cl-) channel
results in cystic fibrosis (thick mucus collects
in airways, pancreatic ducts, liver ducts) - CARRIER proteins inability to use energy
transport for sodium potassium (NaK-)transport
may cause obesity for some - CELL RECOGNITION proteins can explain rejection
of organ transplants, liked to MHC (major
histocompatibility complex) glycoprotein - RECEPTOR proteins why some are pygmies.
Membrane receptors faulty and cannot interact
with growth hormone - ENZYMATIC proteins diarrhea impact of cholera
bacteria toxin released on enzyme adenylate
cyclase, which reduces water Na retention in
large intestine
14
Plasma Membrane Permeability
- _______________________________ the plasma
membrane is choosy about the passage of
molecules into and out of the cell.
Energy Not Required
Energy Required
- ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- EXOCYTOSIS
- ENDOCYTOSIS
- DIFFUSION
- FACILITIATED TRANSPORT
15
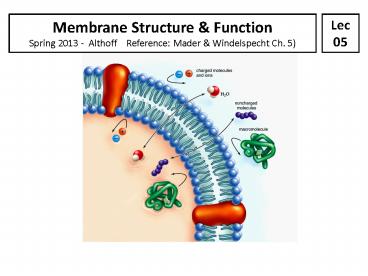
Some sugars, amino acids ions
3
Lipid-soluble molecules, H20,
1
gases
2
Some sugars amino acids
4
macromolecules
5
macromolecules
(Mader p89 Fig. 5.4)
16
Direction of molecule passage
Key process
DIFFUSION
- Toward _______ concentration
- Toward _______ concentration
- Toward _______ concentration
- Toward _______ of cell
- Toward _______ of cell
FACILITATED TRANSPORT
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
EXOCYTOSIS
ENDOCYTOSIS
17
Requirement
Key process
- Concentration gradient
- Channels or carrier AND concentration gradient
- Carrier plus energy
- Vesicle fuses with plasma membrane
- Vesicle formation
DIFFUSION
FACILITATED TRANSPORT
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
EXOCYTOSIS
ENDOCYTOSIS
18
PROCESS OF DIFFUSION (Mader p91 Fig. 5.5)
DIFFUSION is spontaneous and ___ chemical energy
is required
19
PROCESS OF OSMOSIS (Mader p93 Fig. 5.8)
20
_______ the Cell EUKARYOTIC CELLS
MULTICELLUAR ORGANISMS
- Must make the ____________ between cells
- Permits ________________ between cells
- Permits _________________ between cells
- Components and construction ______ between plants
and animals - We consider these _________________
structures examples for plants __________
plasmodesmata examples for animals
__________________
21
PLANTS -- Outside
CELL 1
CELL 2
CYTOPLASMA
PLASMODESMATA
CELL WALL -- PRIMARY
22
ANIMAL Extracellular Matrix
- MESHWORK OF _______________________
- Examples structural proteins
________________ matrix strength __________
______ resilience - Examples rigid packing gel permits
________________ of nutrients, metabolites, and
hormones between blood and tissue cells
23
ANIMAL Extracellular Matrix
INSIDE
OUTSIDE
(Mader p99 Fig. 5.13)
24
Extracellular Matrix Rigid or Flexible?
- RIGID ______ is rock solid because the
extracellular matrix includes mineral salts
(i.e., calcium salts) deposited outside the cell - FLEXIBLE _________
25
Animal Cell JUNCTIONS
ADHESION JUNCTIONS
- _________ sheet of cells results
- Attach to ____________, within the cell via
cytoplasmic plaques, intercellular filaments - Common in heart, stomach, and bladder where
___________ must stretch
CELL 1
CELL 2
26
Animal Cell JUNCTIONS
TIGHT JUNCTIONS
- ____________ fastening
- Plasma membrane proteins _______ to each other
- Common in kidney where urine passes through
intestines have this type of lining to __________
______________ from entering lining
CELL 1
CELL 2
27
Animal Cell JUNCTIONS
GAP JUNCTIONS
CELL 1
CELL 2
- Permits ______________
- __________ plasma membrane channels join
- Common in the ________ muscle _____________
(stomach) - Permit _____________ to facilitate synchronous
contraction
28
Know Where You Are Inside or Outside
the Eukaryotic Cell RELATIVE TO THE
_____________________
INSIDE looking out OUTSIDE looking in
COMPONENTS Cell wall (plants) Nucleus Ribosomes
Plasmodesmata (plants) Golgi
apparatus Extracellular matrix
(animals) Adhesion junctions (aniamls) Gap
junctions (animals)
Yes
No
No
Yes
29
Know What Requires Energy What Doesnt
Relative to _________________ of the Plasma
Membrane
Energy Required Direction of
passage
Passage type Diffusion Endocytosis Exocytosis
Active Transport Facilitated Transport
No
Yes
Toward outside
Toward lower concentration Toward
outside Toward higher concentration
Toward inside