Relapsing back to problem use - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Relapsing back to problem use
Description:
Blow to the head rehabilitation Straitjacket chocolate * * Chronic relapsing model * * * * * * Chronic relapsing model ... Jane Case 3: Freddy Addiction as: ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:147
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Relapsing back to problem use
1
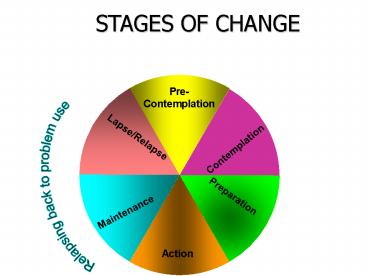
STAGES OF CHANGE
Relapsing back to problem use
2
Stages of Change
3
PRE-CONTEMPLATION Characteristics
- No problem
- See no reason to change
- Lack of awareness
4
PRE-CONTEMPLATION Tasks of Change
- Information Both factual and personal
- Consider circumstances which indicate a need for
change - Engagement of client, create positive relationship
5
Stages of Change
6
CONTEMPLATIONCharacteristics
- Ambivalence
- Fear of change
- Wishful thinking
- Interest in the problem
7
CONTEMPLATIONTasks of Change
- Examine the ambivalence
- Weigh and consider alternatives
- Examine pros and cons of particular actions
8
Stages of Change
9
PREPARATIONCharacteristics
- Readiness to consciously engage in change process
- Temporal imminence of change
10
PREPARATION Tasks of Change
- Gather information about options
- Make initial contact
11
Stages of Change
12
ACTION Characteristic
- Change in behaviour
13
ACTIONTasks of Change
- Understanding factors supporting the behaviour
- Strategies which will support behavioural change
- Communication with others
14
Stages of Change
15
MAINTENANCECharacteristics
- Consolidation of changes
- Need for support
- Skills development
16
MAINTENANCETasks of Change
- Establish support system
- Practice behavioural changes
- Act on relapse prevention plans
17
Stages of Change
Relapsing back to problem use
18
LAPSE/RELAPSE Characteristics
- Initial return to use
- Re-establishing previous pattern
19
LAPSE/RELAPSE Tasks of Change
- Reconnecting with supports
- Examining and learning from lapse experience
- Reviewing and modifying relapse prevention
strategies
20
EMPOWERMENT AND SELF CHANGE
- Understanding motivation
- Autonomy
- Motivational interventions
- FRAMES
21
FRAMES
- F eedback
- R esponsibiltiy
- A dvice
- M enu of options
- E mpathic style
- S elf efficacy
22
How does it balance?
23
Case 1 Rod
- 19 year old
- Smokes cannabis 3 out of 7 days in a week. Takes
Es on weekends. Drinks 5 units alcohol day - Spends most of his spare cash on drugs and
alcohols - Impulsive and suffers with depression
24
Case 2 Jane
- 45 year old restaurant manager
- Taking nitrazepam (prescribed by GP) for 2 years
- Anxious and depressed
25
Case 3 Freddy
- 29 year old
- Crack cocaine user past 5 years
- Using heroin to come down off the crack past 2
years - Initially smoking, now injecting
26
Addiction as
- A biological (disease) model
- A psychological model
- A social model
- BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL MODEL
27
Summary Addiction
- Behaviour is no longer a matter of considered
choice
28
Summary Addiction as a function of
- THE DRUG
- Positive and negative re-inforcers
- THE PERSON
- Impulsive, sensation seeking
- THE SITUATION
- Opportunity, lack of alternatives, social
influences
29
- The End
- Any questions ?
- bhagat.sharma_at_nepft.nhs.uk