LO - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
LO
Description:
* * * * * * * Semua bahagaian ada chloropalast tapi daun paling byk * * LO s Explain why photosynthesis is so important to energy and material flow for life on ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:40
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: LO
1
(No Transcript)
2
- LOs
- Explain why photosynthesis is so important to
energy and material flow for life on earth - Know why plants tend to be green in appearance
- Understand that photosynthesis is a two fold
process composed of the light-dependent reactions
(i.e., light reactions) and the light independent
reactions
3
Basic questions??
- What do plants eat?
- Why do plants need light?
- Why do plants need water?
- Why are plants green?
4
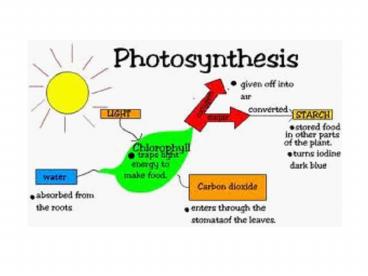
Photosynthesis
- Process that captures energy from the sun
- Energy stored in carbohydrates
- Oxygen is byproduct
5
Photosynthesis
- Almost all plants are photosynthetic autotrophs,
as are some bacteria and protists
- Autotrophs generate their own organic matter
through photosynthesis - Sunlight energy is transformed to energy stored
in the form of chemical bonds
6
AN OVERVIEW OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
- Photosynthesis is the process by which
autotrophic organisms use light energy to make
sugar and oxygen gas from carbon dioxide and
water
Carbondioxide
Water
Glucose
Oxygengas
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
7
CO2 and water are waste products of cellular
respiration
Oxygen used for cellular respiration
8
WHY ARE PLANTS GREEN?
Plant Cells have Green Chloroplasts
The thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast is
impregnated with photosynthetic pigments (i.e.,
chlorophylls, carotenoids).
9
Sunlight
- Electromagnetic energy (radiation)
- Packets of energy (photons)
- Range of wavelengths
10
Plant Pigments
- Found in chloroplasts
- Absorb some visible wavelengths
11
Plant Pigments
- Carotenoids absorb photons of green,
- blue violet wavelengths
- Chlorophylls absorb photons of red
- violet-blue wavelengths
12
The feathers of male cardinals are loaded with
carotenoid pigments. These pigments absorb some
wavelengths of light and reflect others.
Reflected light
Sunlight minus absorbed wavelengths or colors
equals the apparent color of an object.
13
Why are plants green?
Reflected light
Transmitted light
14
Energy needs of life All life needs a constant
input of energy 1. Heterotrophs (Animals) Get
energy from eating others Make energy through
respiration
- 2. Autotrophs self-feeder (Plants)
- Produce their own energy
- Convert energy of suclight -- chemical energy
- Make energy and synthesise sugars through
PHOTOSYNTESIS
15
Photosynthetic Autotrophs
- Solar energy powers glucose synthesis
- Uses
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
- Captured energy
- Produces
- Glucose
- Oxygen
16
(No Transcript)
17
Heterotrophs
- Consume other organisms
- Cannot produce their own food
- Food ultimately comes from autotrophs
18
- Photosynthesis looks and sounds like a complex
process - Two stages of Photosynthesis
- Light reaction ( with a solar energy captured and
transformed into chemical energy - Calvin cycle the chemical energy is used to
make organic molecules
19
- The location and structure of chloroplasts
Chloroplast
LEAF CROSS SECTION
MESOPHYLL CELL
LEAF
Mesophyll
Intermembrane space
CHLOROPLAST
Outer membrane
Granum
Innermembrane
Stroma
Grana
Thylakoidcompartment
Stroma
Thylakoid
20
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplast
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
- LIGHT ENERGY WATER
- Light energy is used to split water molecules
known as Photolysis chemical is broken down by
photons - ATP is produced during photolysis
- ATP and H ions will be used to fix CO2 to make
organic molecules - Photosynthesis relies on water and sunlight
for its initial reaction
24
(No Transcript)
25
AN OVERVIEW OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
- The light reactions convert solar energy to
chemical energy - Produce ATP NADPH
Light
Chloroplast
NADP?
ADP P
Calvin cycle
- The Calvin cycle makes sugar from carbon dioxide
- ATP generated by the light reactions provides the
energy for sugar synthesis - The NADPH produced by the light reactions
provides the electrons for the reduction of
carbon dioxide to glucose
Light reactions
26
Plants and animals need each other to survive.