Spread of World Religions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Spread of World Religions
Description:
Spread of World Religions World Religions Map Muslim Art & Architecture The Muslim religion prohibited the picturing of human and natural forms. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:238
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Spread of World Religions
1
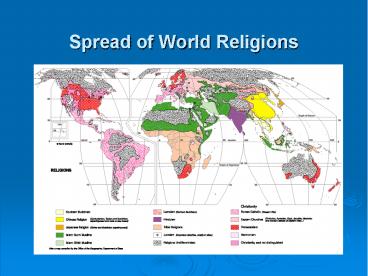
Spread of World Religions
- World Religions Map
2
Islam The Beginnings632-1500
3
Muslim Mosque in Mecca
4
Kaaba, sacred shrine to Allah in Mecca
5
D144Kaaba
6
Hajj
- Muslims performing the Hajj (a pilgrimage to
Mecca). - The simple white garments symbolize the equality
of believers.
7
Muslim Pilgrimage
8
Bedouins in Mecca
9
Muslims at Prayer
10
Muslim obligations Almsgiving
11
Jihad
- Jihad among extremists refers to Holy Wars
against the infidels or of Territorial expansion.
- Among moderates, Jihad refers to Defense of
ones faith and or an inner struggle to rid
oneself of evil and submit to Allah.
12
Religion in America
- Religion in America
13
Emergence of Shia
- Claim that Alis descendents were the true
successors to Muhammad - Shia community recognizes the Imans, the
successors to Alis Spiritual Authority - Recognizes Koran only, not Koran but Sunna
(traditional teachings) as authoritative.
14
Caliph
- Caliph or Deputy refers to the Islamic rulers
after the death of Muhammad. - Abu-Bakr is first Caliph (632-624)
- The first four caliphs expanded the kingdom
still further. - Caliphs have both religious civil authority.
15
Eras of Islamic Civilization
- 570-632 Muhammad-Founder
- 632-661 First four Caliphs - Expansion in
Mideast. - 661-750 Ummayad Dynasty-(Centered in Damascus)
Conquer the Sassanid Empire
16
Eras of Islamic Civilization cont.
- 750-1258 Abbasid Dynasty, Golden Age at Baghdad.
House of Wisdom - 1000s-1400s Seljuks Mongols- Baghdad sacked,
House of Wisdom burned. - 1453-WW I Ottoman Empire- conquer the rest of
the Byzantine Empire
17
D162Muslim Exp.Map
18
The Umayyad Caliphate
- Flourish from 661 to 750
- Centered in Damascus
- Nearly took Constantinople (674-77) but were
deterred by Greek Fire - Captured Spain but were defeated by Charles
Martel at Tours in 732. - Weakness of Umayyadsonly Arabs Muslims could
hold top positions - Abbasids who accepted Muslims of all ethnicities.
Promoted religious tolerance.
19
(No Transcript)
20
Achievements
- Spread Islam into India, North Africa, Spain.
- Conquered the Sassanid and ½ of the Byzantine
Empire - In Spain, built the Alhambra and the Cordoba
Mosque
21
The Abbasid Caliphate
- Flourished from 750 to 1258
- Centered in Baghdad
- House of Wisdom
- Great libraries, academies, and schools.
- Translated classical Greek scholarship into
Arabicpreserving it for posterity - Achievements in Medicine, astronomy, and
Mathematics - Muslim states in West break away from Abbasid
control beginning in 756. - Seljuk Turks convert to Islam and conquer
Abbasids (1055) but allow Abbasids to continue to
rule - Genghis Khans Grandson topples Abbasids in 1258
22
(No Transcript)
23
162MMap
24
Historic Contributions of the Islamic
Civilizations
- Al Razi (d. 925) Medical expert of the Abbasid
Dynasty who studied optics Caesarian operations
and more. - Most famous treatise On Small Pox and Measles
25
Historic Contributions of the Islamic
Civilizations
- Ibn Sina (Avicenna) (d. 1037) A Muslim scholar
of the Abbasid Dynasty who excelled in both
Medicine and Philosophy - His Canon of Medicine was translated into Latin
in the 12th century and by the 16th century was
in its 35th edition.
26
Historic Contributions of the Islamic
Civilizations
- Aveorres (d. 1198) Philosopher of the Abbasid
Dynasty who tried to harmonize Islamc faith with
Aristotelian logic.
27
House of Wisdom
28
Astrolabe
- Used for astronomy for navigation.
- It is believed that the Muslim al-Fazari
(d.777A.D.) was the first scientist in the
MidEast to make an astrolabe, following the
arrival of an Indian mission to Baghdad.
29
Distillation of Alcohol
- Developed about 800
- Al-kuhl means the essense
30
Muslim Medicine
- Muslim physicians were active in the advancement
of surgical techniques, and were among the first
to use narcotic and sedative drugs in operations.
31
Omar Khyyam
- Of the Abbasid Dynasty was the author of the
Rubaiyat and the Book of 1001 Nights. - A Book of Verses underneath the Bough A jug of
wine, a loaf of breadand thou beside me in the
wildernessOh Wilderness were paradise enow!
32
Harun Al Rashid (800s)
- An esteemed ruler of the Abbasid Dynasty who
exchanged gifts, and established friendly
relations with Charlemagne (ruler of the greatest
Christian Kingdom in Europe at that time).
33
Cordoba, Spain
- From 756 - 1031, Cordoba was a political and
cultural center for the Muslims.
34
Muslim Art Architecture
- The Muslim religion prohibited the picturing of
human and natural forms. - Muslim art was thus channeled into artistic
displays of great geometric complexity and
abstract ornamentation.
Arabesque- flowery designs That go on for
infinity
35
Muslim Art Architecture
- This Muslim mosque in Seville, was built in 1172.
- It was converted to a Chrisitan Cathedral in
1248.
36
Why it Matters
- Preserved Western (Greek and Roman knowledge)
- Brought together the best minds from India,
China, Africa, Europe, Persia
- Improved on medicine, math, astronomy, chemistry
- Helped launch the European Renaissance
- Spread Islam to ½ of the world.
37
Ottoman Empire (1300-1918)
- The Ottoman Empire would rival that of China in
size and economic power. - But over time the Ottoman Empire would be
weakened until the twentieth century. - Yet under Suleiman the Magnificent (1520-1566)
the Ottoman Empire expanded into North Africa and
Syria.
38
F320Ottoman Map
39
Growth of the Ottoman Empire
- For nearly 300 years the Ottomans expanded into
the Balkans and to Persia. - By 1683 the Turks controlled Hungary in Europe to
the Persian Gulf. - Initial Ottoman conquest and expansion was
under their able leader Osman (1299-1326). - Osman was a ghazi, or warrior, who was
determined to spread the faith.
40
Why Did The Ottomans Succeed?
- Ottomans tolerated other faithsdidnt fight wars
of religious exclusivism - Many in Old Byzantine Empire were weary of
corruption in Byzantine state
41
Key Events of the Ottoman State
- 1389 Defeat the Serbs at Battle of Kosovo.
- 1396 Crushed the Hungarians and foreign knights
at Nicopolis. - 1402 Tamerlane defeats the Ottomans near
Ankara. - 1453 Turks capture Constantinople by Mohammed
II. - 1517 Turks captured Cairo.
- 1529 First siege of Vienna.
- 1683 Second siege of Vienna.