MSR Image based Reality Project - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
MSR Image based Reality Project
Description:
Title: Computer Vision: Photometric Stereo Author: Steve Seitz Last modified by: Li Zhang Created Date: 5/10/1998 5:20:27 PM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:95
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: MSR Image based Reality Project
1
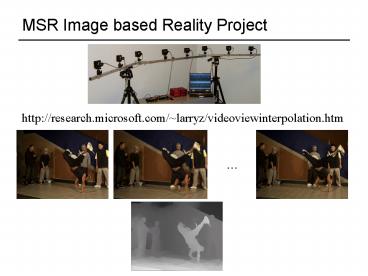
MSR Image based Reality Project
http//research.microsoft.com/larryz/videoviewint
erpolation.htm
2
The visibility problem
Which points are visible in which images?
3
Volumetric stereo
Scene Volume V
Input Images (Calibrated)
Goal Determine occupancy, color of points in V
4
Discrete formulation Voxel Coloring
Discretized Scene Volume
Input Images (Calibrated)
Goal Assign RGBA values to voxels in
V photo-consistent with images
5
Complexity and computability
Discretized Scene Volume
3
N voxels C colors
6
Issues
- Theoretical Questions
- Identify class of all photo-consistent scenes
- Practical Questions
- How do we compute photo-consistent models?
7
Voxel coloring solutions
- 1. C2 (shape from silhouettes)
- Volume intersection Baumgart 1974
- For more info Rapid octree construction from
image sequences. R. Szeliski, CVGIP Image
Understanding, 58(1)23-32, July 1993. (this
paper is apparently not available online) or - W. Matusik, C. Buehler, R. Raskar, L. McMillan,
and S. J. Gortler, Image-Based Visual Hulls,
SIGGRAPH 2000 ( pdf 1.6 MB ) - 2. C unconstrained, viewpoint constraints
- Voxel coloring algorithm Seitz Dyer 97
- 3. General Case
- Space carving Kutulakos Seitz 98
8
Reconstruction from Silhouettes (C 2)
Binary Images
- Approach
- Backproject each silhouette
- Intersect backprojected volumes
9
Volume intersection
- Reconstruction Contains the True Scene
- But is generally not the same
- In the limit (all views) get visual hull
- Complement of all lines that dont intersect S
10
Voxel algorithm for volume intersection
- Color voxel black if on silhouette in every image
- for M images, N3 voxels
- Dont have to search 2N3 possible scenes!
O( ? ),
11
Properties of Volume Intersection
- Pros
- Easy to implement, fast
- Accelerated via octrees Szeliski 1993 or
interval techniques Matusik 2000 - Cons
- No concavities
- Reconstruction is not photo-consistent
- Requires identification of silhouettes
12
Voxel Coloring Solutions
- 1. C2 (silhouettes)
- Volume intersection Baumgart 1974
- 2. C unconstrained, viewpoint constraints
- Voxel coloring algorithm Seitz Dyer 97
- For more info http//www.cs.washington.edu/homes
/seitz/papers/ijcv99.pdf - 3. General Case
- Space carving Kutulakos Seitz 98
13
Voxel Coloring Approach
Visibility Problem in which images is each
voxel visible?
14
Depth Ordering visit occluders first!
Scene Traversal
Condition depth order is the same for all input
views
15
Panoramic Depth Ordering
- Cameras oriented in many different directions
- Planar depth ordering does not apply
16
Panoramic Depth Ordering
Layers radiate outwards from cameras
17
Panoramic Layering
Layers radiate outwards from cameras
18
Panoramic Layering
Layers radiate outwards from cameras
19
Compatible Camera Configurations
- Depth-Order Constraint
- Scene outside convex hull of camera centers
20
Calibrated Image Acquisition
Selected Dinosaur Images
- Calibrated Turntable
- 360 rotation (21 images)
Selected Flower Images
21
Voxel Coloring Results (Video)
Dinosaur Reconstruction 72 K voxels colored 7.6
M voxels tested 7 min. to compute on a 250MHz
SGI
Flower Reconstruction 70 K voxels colored 7.6 M
voxels tested 7 min. to compute on a 250MHz SGI
22
Limitations of Depth Ordering
- A view-independent depth order may not exist
p
q
- Need more powerful general-case algorithms
- Unconstrained camera positions
- Unconstrained scene geometry/topology
23
Voxel Coloring Solutions
- 1. C2 (silhouettes)
- Volume intersection Baumgart 1974
- 2. C unconstrained, viewpoint constraints
- Voxel coloring algorithm Seitz Dyer 97
- 3. General Case
- Space carving Kutulakos Seitz 98
- For more info http//www.cs.washington.edu/homes
/seitz/papers/kutu-ijcv00.pdf
24
Space Carving Algorithm
Image 1
Image N
...
- Space Carving Algorithm
25
Which shape do you get?
V
True Scene
- The Photo Hull is the UNION of all
photo-consistent scenes in V - It is a photo-consistent scene reconstruction
- Tightest possible bound on the true scene
26
Space Carving Algorithm
- The Basic Algorithm is Unwieldy
- Complex update procedure
- Alternative Multi-Pass Plane Sweep
- Efficient, can use texture-mapping hardware
- Converges quickly in practice
- Easy to implement
Results
Algorithm
27
Multi-Pass Plane Sweep
- Sweep plane in each of 6 principle directions
- Consider cameras on only one side of plane
- Repeat until convergence
True Scene
Reconstruction
28
Multi-Pass Plane Sweep
- Sweep plane in each of 6 principle directions
- Consider cameras on only one side of plane
- Repeat until convergence
29
Multi-Pass Plane Sweep
- Sweep plane in each of 6 principle directions
- Consider cameras on only one side of plane
- Repeat until convergence
30
Multi-Pass Plane Sweep
- Sweep plane in each of 6 principle directions
- Consider cameras on only one side of plane
- Repeat until convergence
31
Multi-Pass Plane Sweep
- Sweep plane in each of 6 principle directions
- Consider cameras on only one side of plane
- Repeat until convergence
32
Multi-Pass Plane Sweep
- Sweep plane in each of 6 principle directions
- Consider cameras on only one side of plane
- Repeat until convergence
33
Space Carving Results African Violet
Input Image (1 of 45)
Reconstruction
Reconstruction
Reconstruction
34
Space Carving Results Hand
Input Image (1 of 100)
Views of Reconstruction
35
Properties of Space Carving
- Pros
- Voxel coloring version is easy to implement, fast
- Photo-consistent results
- No smoothness prior
- Cons
- Bulging
- No smoothness prior
36
Alternatives to space carving
- Optimizing space carving
- recent surveys
- Slabaugh et al., 2001
- Dyer et al., 2001
- many others...
- Graph cuts
- Kolmogorov Zabih
- Level sets
- introduce smoothness term
- surface represented as an implicit function in 3D
volume - optimize by solving PDEs
37
Alternatives to space carving
- Optimizing space carving
- recent surveys
- Slabaugh et al., 2001
- Dyer et al., 2001
- many others...
- Graph cuts
- Kolmogorov Zabih
- Level sets
- introduce smoothness term
- surface represented as an implicit function in 3D
volume - optimize by solving PDEs
38
Level sets vs. space carving
- Advantages of level sets
- optimizes consistency with images smoothness
term - excellent results for smooth things
- does not require as many images
- Advantages of space carving
- much simpler to implement
- runs faster (orders of magnitude)
- works better for thin structures, discontinuities
- For more info on level set stereo
- Renaud Kerivens page
- http//cermics.enpc.fr/keriven/stereo.html
39
References
- Volume Intersection
- Martin Aggarwal, Volumetric description of
objects from multiple views, Trans. Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 5(2), 1991,
pp. 150-158. - Szeliski, Rapid Octree Construction from Image
Sequences, Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image
Processing Image Understanding, 58(1), 1993, pp.
23-32. - Matusik, Buehler, Raskar, McMillan, and Gortler ,
Image-Based Visual Hulls, Proc. SIGGRAPH 2000,
pp. 369-374. - Voxel Coloring and Space Carving
- Seitz Dyer, Photorealistic Scene
Reconstruction by Voxel Coloring, Intl. Journal
of Computer Vision (IJCV), 1999, 35(2), pp.
151-173. - Kutulakos Seitz, A Theory of Shape by Space
Carving, International Journal of Computer
Vision, 2000, 38(3), pp. 199-218. - Recent surveys
- Slabaugh, Culbertson, Malzbender, Schafer, A
Survey of Volumetric Scene Reconstruction Methods
from Photographs, Proc. workshop on Volume
Graphics 2001, pp. 81-100. http//users.ece.gatec
h.edu/slabaugh/personal/publications/vg01.pdf - Dyer, Volumetric Scene Reconstruction from
Multiple Views, Foundations of Image
Understanding, L. S. Davis, ed., Kluwer, Boston,
2001, 469-489. ftp//ftp.cs.wisc.edu/computer-vis
ion/repository/PDF/dyer.2001.fia.pdf
40
References
- Other references from this talk
- Multibaseline Stereo Masatoshi Okutomi and
Takeo Kanade. A multiple-baseline stereo. IEEE
Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence (PAMI), 15(4), 1993, pp. 353--363. - Level sets Faugeras Keriven, Variational
principles, surface evolution, PDE's, level set
methods and the stereo problem", IEEE Trans. on
Image Processing, 7(3), 1998, pp. 336-344. - Mesh based Fua Leclerc, Object-centered
surface reconstruction Combining multi-image
stereo and shading", IJCV, 16, 1995, pp. 35-56. - 3D Room Narayanan, Rander, Kanade,
Constructing Virtual Worlds Using Dense Stereo,
Proc. ICCV, 1998, pp. 3-10. - Graph-based Kolmogorov Zabih, Multi-Camera
Scene Reconstruction via Graph Cuts, Proc.
European Conf. on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2002. - Helmholtz Stereo Zickler, Belhumeur,
Kriegman, Helmholtz Stereopsis Exploiting
Reciprocity for Surface Reconstruction, IJCV,
49(2-3), 2002, pp. 215-227.
41
So far
- Passive Stereo
- Spacetime Stereo
- Multiple View Stereo
42
Next
- Structure from Motion
- Given pixel correspondences,
- how to compute 3D structure and camera motion?
Slides stolen from Prof Yungyu Chuang
43
Epipolar geometry fundamental matrix
44
The epipolar geometry
- What if only C,C,x are known?
45
The epipolar geometry
epipolar geometry demo
- C,C,x,x and X are coplanar
46
The epipolar geometry
- All points on ? project on l and l
47
The epipolar geometry
- Family of planes ? and lines l and l intersect
at e and e
48
The epipolar geometry
epipolar pole intersection of baseline with
image plane projection of projection center in
other image
epipolar geometry demo
- epipolar plane plane containing baseline
- epipolar line intersection of epipolar plane
with image
49
The fundamental matrix F
R
C
C
50
The fundamental matrix F
51
The fundamental matrix F
R
C
C
52
The fundamental matrix F
53
The fundamental matrix F
R
C
C
54
The fundamental matrix F
- The fundamental matrix is the algebraic
representation of epipolar geometry - The fundamental matrix satisfies the condition
that for any pair of corresponding points x?x in
the two images
55
The fundamental matrix F
F is the unique 3x3 rank 2 matrix that satisfies
xTFx0 for all x?x
- Transpose if F is fundamental matrix for (P,P),
then FT is fundamental matrix for (P,P) - Epipolar lines lFx lFTx
- Epipoles on all epipolar lines, thus eTFx0, ?x
?eTF0, similarly Fe0 - F has 7 d.o.f. , i.e. 3x3-1(homogeneous)-1(rank2)
- F maps from a point x to a line lFx (not
invertible)
56
The fundamental matrix F
- It can be used for
- Simplifies matching
- Allows to detect wrong matches
57
Estimation of F 8-point algorithm
- The fundamental matrix F is defined by
for any pair of matches x and x in two images.
- Let x(u,v,1)T and x(u,v,1)T,
each match gives a linear equation