Insecticidal Control of Caterpillar Pests of Cole Crops - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Insecticidal Control of Caterpillar Pests of Cole Crops
Description:
Insecticidal Control of Caterpillar Pests of Cole Crops Alton N. Sparks, Jr. and David G. Riley, University of Georgia, Tifton, Georgia RESULTS AND DISCUSSION – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Insecticidal Control of Caterpillar Pests of Cole Crops
1
Insecticidal Control of Caterpillar Pests of Cole
Crops
Alton N. Sparks, Jr. and David G. Riley,
University of Georgia, Tifton, Georgia
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
ABSTRACT Diamondback moth has been the target of
many of the most recently registered insecticides
for cole crops. While this pest is of primary
concern, other Lepidopterous pests do occur and
require control. A series of small plot trials
were conducted to evaluate the efficacy of these
insecticides against other common caterpillar
pests of cole crops. Avaunt, Intrepid, SpinTor,
Rimon and Warrior (used as a standard) provided
the most consistent control of cabbage looper,
imported cabbageworm and cross-striped
cabbageworm larvae. BAS 320I appeared to provide
good control of all three species, but showed
indications of shorter residual activity.
Proclaim and Tesoro provided good control of both
cabbageworm species, but showed less activity
against cabbage loopers as compared to the other
insecticides.
INTRODUCTION Cole crops in Georgia may be
attacked by a wide variety of insect pests
including aphids, whiteflies, thrips and beetles.
However, caterpillars are the key pests of this
crop group. Of the various caterpillars that
attack cole crops, the diamondback moth has
generally been of greatest concern because of
difficulty of control and its potential for
development of resistance to insecticides. Most
of the recently developed insecticides for this
crop group target this pest and have generally
shown excellent efficacy against diamondback
moth. However, diamondback moth is not the only
caterpillar that attacks cole crops, is seldom
the only species in an infested field, and has
actually been less pestiferous in the last two
years than several other caterpillar species.
Thus, efficacy data against these other species
of caterpillars is needed to aid producers in
pesticide selection decisions. This poster
presents results of small plot studies conducted
to evaluate the efficacy of newer insecticides
against common caterpillar pests of cole crops in
Georgia. Species targeted in these tests included
the cabbage looper and imported cabbageworm which
are common pests throughout Georgia and can occur
in damaging populations throughout the year in
south Georgia. Cross-striped cabbageworm, which
is a problem in the fall in north Georgia, was
targeted in one test.
MATERIALS AND METHODS Four of the tests were
conducted at University of Georgia research farms
in Tifton, Georgia (south Georgia). The fifth
test was conducted at the Georgia Mountain
Research and Education Center in Blairsville,
Georgia (north Georgia). Plot size and
application dates were as follows Test Plot
Size Application dates Cabbage, 2004 2 rows
(16 in centers) by 24 feet 1, 8, 16, 28 Oct., 6
Nov. Collards, 2004 2 rows (36 in centers) by
21 feet 29 Sept., 8, 16 Oct. Cabbage, 2005 2
rows (36 in centers) by 40 feet 17, 25 April, 2,
13, 20 May Collards, 2005 1 row (35 in) by 25
feet 5, 19, 29 July Collards, 2005,
Blairsville 1 row (36 in) by 20 feet 1, 16
Aug. Treatments were applied with a CO2
pressurized backpack sprayer (60 PSI) in a total
volume of 30 GPA. The Cabbage, 2004 test was
treated with 2 hollow cone nozzles per bed. All
other tests were treated with 3 hollow cone
nozzles per row, with one nozzle over-the-top and
one on each side of the row on drops.
Insecticides evaluated were Trade Name Common
name Rate per acre (formulated / lb
AI) Manufacturer Avaunt 30WDG indoxacarb 3.5
oz/ 0.065 DuPont Intrepid 2F methoxyfenozide
8 oz / 0.125 Dow AgroSciences Proclaim
5SG emamectin benzoate 3.2 oz /
0.01 Syngenta SpinTor 2SC spinosad 4 oz /
0.0625 Dow AgroSciences Tesoro
4EC pyridalyl 6.4 oz / 0.2 Valent Rimon
0.83EC novaluron 9-12 oz / 0.058-0.078 Chemtur
a Warrior 1CS lambda-cyhalothrin 3.84 oz /
0.03 Syngenta (BAS 320 I) 2SC metaflumizone 1
3.7 oz / 0.214 BASF All tests were visually
sampled, with caterpillars per plant counted on 5
randomly selected plants per plot. In two tests,
number of plants damaged were counted in each
plot. Plants were classified as minor damage
(outter leaves with feeding damage) or severe
damage (large sections of leaves or terminal of
plant damaged). In the Cabbage, 2005 test a final
efficacy rating was conducted with a 1
excellent control, 2 good control, 3 obvious
control but not acceptable, 4 poor control but
some suppression, and 5 no control. Data were
analyzed with the PROC ANOVA procedure of PC-SAS.
Where significant differences were detected
(Plt0.05), means were separated with LSD (P0.05).
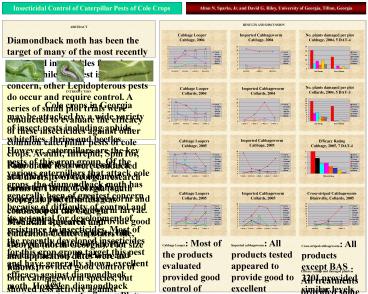
Cabbage Looper Most of the products evaluated
provided good control of cabbage looper, with the
exceptions of Proclaim and Tesoro. This weakness
was most evident in the Cabbage, 2004 trial.
Although not consistently statistically
different, the same trends appeared in both 2005
trials. SpinTor and BAS 320I both showed high
looper densities at 9 days after treatment in the
Collards, 2005 trial however, it appears that
this likely resulted from shorter residual
control rather than poor control.
Imported cabbageworm All products tested
appeared to provide good to excellent control of
imported cabbageworm. Minor statistical
differences that occurred among insecticide
treatments were likely a result of different
residual control levels rather than efficacy. At
9 days after the first treatment in the Collards,
2005 trial BAS 320I and Proclaim failed to
separate from the check (a similar trend occurred
in the Cabbage, 2005 trail at 10 DAT-3), but
provided good control on dates nearer application
dates.
Cross-striped cabbageworm All products except
BAS 320I provided similar levels of control. BAS
320I failed to separate from the check at 7 DAT-1
and was not in the lowest statistical rating at 6
DAT-2, but provided excellent control at 4 DAT-1.
As with the previous pests, this may have
resulted from short residual control.
Efficacy ratings and damaged plants All
treatments provided some level of damage
reduction as compared to the check. General
trends across all three tests with ratings
indicate increased level of damage with BAS 320I,
Tesoro, and Proclaim. This damage most likely
resulted from a slight weakness on loopers with
Tesoro and Proclaim and a shorter residual
control with all three products.