Economic Fluctuation and the Business Cycle - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Economic Fluctuation and the Business Cycle
Description:
Economic Fluctuation and the Business Cycle The business cycle is up-and-down movement in production and jobs. A business cycle has two phases, expansion and ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:243
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Economic Fluctuation and the Business Cycle
1
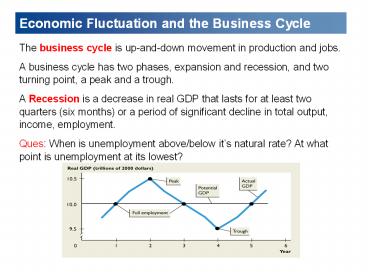
Economic Fluctuation and the Business Cycle
- The business cycle is up-and-down movement in
production and jobs. - A business cycle has two phases, expansion and
recession, and two turning point, a peak and a
trough. - A Recession is a decrease in real GDP that lasts
for at least two quarters (six months) or a
period of significant decline in total output,
income, employment. - Ques When is unemployment above/below its
natural rate? At what point is unemployment at
its lowest?
2
Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
- Recall- We covered models determining real
output, the market for loanable funds, and the
money market. - (can someone comment on some major aspects of
these models?) - We need a model to analyze economic fluctuation.
- The AS-AD model is one that helps explain
economic fluctuation, the business cycle, and the
aim of government policy. - AS-AD prices and money supply does affect real
GDP.
3
AGGREGATE SUPPLY
- Aggregate supply is the relationship between the
quantity of real GDP supplied and the price level
when all other influences on production plans
remain the same. - -a change in the price level changes the quantity
of real GDP supplied. - n.B There is a 1) short run AS curve that slopes
upward. - Shifters- Changes in firms cost of production
- (i.e wages , rent , interest rates, corporate
tax rates). - 2) Long run AS curve, that identifies the level
of potential GDP. ( the idea is the output will
always return to its long run potential. - Shifters- Factors that change potential GDP.
(recall) - n.b- A shift of the long run AS curve also shifts
the short run curve.
4
(No Transcript)
5
AGGREGATE DEMAND
- Aggregate demand is the relationship between the
quantity of real GDP demanded and the price level
when all other influences on expenditure plans
remain the same. - A change in price impacts the quantity of AD via
three effects. - Wealth Effect, Interest Rate Effect, Exchange
Rate effect. - Can you think how they work.
- Recall- Y CIG(N-X)
- Shifters
- Expectations on future income, profits.
- Government and Fed policy
- Overseas economies.
6
AGGREGATE DEMAND
- Government can use fiscal policy to influence
aggregate demand. - Fiscal policy is changing taxes, transfer
payments, and government expenditure on goods and
services. - The Federal Reserve can use monetary policy to
influence aggregate demand. - Monetary policy is changing the quantity of money
and the interest rate.
7
13.4 UNDERSTANDING BUSINESS CYCLES
Three possible macroeconomic equilibriums are
1. Below full-employment equilibrium, when
potential GDP exceeds equilibrium real GDP.
2. Full-employment equilibrium, when equilibrium
real GDP equal potential GDP.
3. Above full-employment equilibrium, when
equilibrium real GDP exceeds potential GDP.
8
Analysis of the Business Cycle Fluctuation
- 4 step analysis.
- Decide if there is a shift in AS, AD or both.
- Decide which direction
- Describe how output, prices, and wages are
affected. - Keep track of short-run and long-run equilibrium.
- Describe how the economy transitions to long
run. - Example. New technology is created increasing the
profitability of firms. Analyse the possible
economic fluctuation that may occur.
9
UNDERSTANDING BUSINESS CYCLES
- Ex. 2 Analyze the short run and long run impact
of a global rise in oil prices. - What we see occur is called stagflation/stagnation
. - Stagflation is a combination of recession
(falling real GDP) and inflation (rising price
level).
10
(No Transcript)
11
- Definitions
- Inflationary gap is a gap that exists when real
GDP exceeds potential GDP and that brings a
rising price level. - Recessionary gap is a gap that exists when
potential GDP exceeds real GDP and that brings a
falling price level.
12
- Figure 13.12 shows adjustments toward full
employment.
Real GDP exceeds potential GDP there is an
inflationary gap and the price level rises.
As the money wage rate gradually rises, aggregate
supply decreases, real GDP decreases, and the
price level rises farther.
13
- Potential GDP exceeds real GDPrecessionary gap
and the price level falls.
Eventually, the money wage rate starts to fall,
aggregate supply increases, real GDP increases,
and the price level falls farther.
14
Additional Questions
- Use the AS-AD model to describe how Real GDP and
prices are impacted in the short-run and long run
if there is a - An increase in the corporate tax rate
- A reduction in wages
- A increase in the average education level.
- 2) Use the AS-AD model to identify a
- Fed policy that may remove a recessionary gap.
- Fiscal policy that may combat an inflationary
gap. - 3)Use the AS-Ad model to analyze the business
cycle created by the wall street crisis. - Analyze the policy tools used to shorten the
recessionary period.