The Theory of Plate Tectonics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
Description:
Title: The Theory of Plate Tectonics Author: Kelly Last modified by: Paulding Created Date: 2/26/2006 9:06:13 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:336
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Theory of Plate Tectonics
1
(No Transcript)
2
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
- Geology Unit
- By
- Mrs.Bartley
3
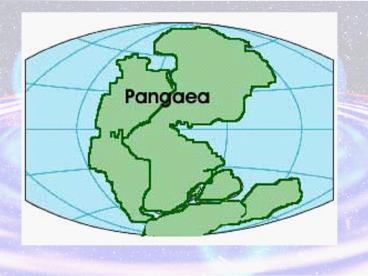
Continental Drift
- Many people have noticed that the edges of the
continents look like they could fit together like
a puzzle. - Alfred Wegener suggested that all the continents
fit together at some point in time. - He designed and proposed the hypothesis of the
continental drift in 1912. - According to his hypothesis, the continents have
moved slowly to their current locations. - He also suggested that all the continents were
connected into a large land mass called Pangaea.
4
Theory Problems
- Alfred Wegener's hypothesis was very
controversial and not accepted until after his
death in 1930. - His original proposal was that the continents
plowed through the ocean floor, driven by the
spin of the Earth. - Many physicists and geologists disagreed with
this idea, however important evidence that came
later eventually supported Wegeners earlier
evidence.
5
Fossil Evidence
- Scientist found fossils of the reptile Mesosaurus
in both South America and Africa. This particular
animal could live on land and in freshwater, but
it could not have swam across the ocean. - There are other reptiles and some plants that
have shown evidence that the continents were
joined together. - Another fossil that supports the hypothesis is
called Glossopteris, which is a plant. The
fossils of this plant have been discovered in
Africa, Australia, India, South America, and
Antartica.
6
The illustration to the left is what a mesosaurus
might look like. It is one of the fossils that
help convince scientist of the possibility of
Pangaea.
This is an illustration of the plant
Glossopteris. The fossils of this plant also help
scientist believe in the idea of Pangaea.
7
Climate Clues
- Wegener used continental drift to explain
evidence of changing climates. - Fossils of warm-weather plants were found on an
island in the Arctic Ocean. Wegener believed this
island drifted from a tropical region to an
arctic region.
8
Rock Clues
- Similar rock structures are found on different
continents. - Parts of the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern
U.S. are similar to those found in Greenland and
western Europe. - South America and Africa also have rock
structures that are similar.
9
Fossil Activity
- Look in your book on page 278.
- Quickly get in groups of 2 or 3.
- Your group will send one person to pick up the
paper and one person to get the colored pencils. - Follow the directions on page 278 under Mini Lab.
- When your group has made 5 land masses, raise you
hand.
10
How could continents drift?
- Wegener may have provided the hypothesis of
continental drift but he could not explain how,
why, and when this would occur. - Wegener had found many clues to support the idea
of continental drift and after he died, even more
clues were found because of advances in
technology. - One of those clues was Seafloor Spreading.
11
Questions
- Who proposed continental drift?
- How do Mesosaurus fossils support the past
existence of Pangaea? - On which continents was the fossil Glossopteris
found?
12
Seafloor Spreading
- Using sound waves, scientists mapped out the
ocean floor. - They found a system of ridges or mountains and
they named it the Mid-Ocean Ridge. - Scientists wanted to know why these ridges were
here because the Mid-Ocean Ridge stretches along
the center of much of the ocean floor.
13
- Scientist Harry Hess suggested an idea of which
he called seafloor spreading - He proposed that hot, less dense material rises
to the surface at the mid-ocean ridges. - As the seafloor spreads apart, magma moves upward
and flows from the cracks. - The magma cools and creates new ocean floor.
14
Questions
- How were mid-ocean ridges discovered?
- How does new seafloor form at mid-ocean ridges?
- Who proposed the idea of seafloor spreading?
15
Plate Tectonics
- Seafloor spreading showed that more than just
continents were moving, as Wegener had thought. - Scientist developed a new theory in the 1960s
that combined continental drift and seafloor
spreading. Its was called Plate Tectonics. - They believed that Earths crust along with the
upper mantle were broken into sections called
plates that float on top of the plastic-like
layer of the mantle. - Plates are made of the crust and upper mantle,
which scientists named Lithosphere. - The plastic-like layer of the mantle was named
the asthenosphere. - The rigid plates of the lithosphere float and
move on top of the asthenosphere.
16
Plate Boundaries
- Plate interaction can occur in different ways.
They can move towards each other, move away from
each other, or slide past each other. - Movement along any plate boundary means that
changes must happen.
17
When plates move apart
- The boundary between 2 plates that are moving
apart is called a divergent boundary. - At a divergent boundary, seafloor spreading
occurs. - The plates are pulled apart and to fill the gap
is cooling magma.
18
When plates come together
- The boundary where 2 plates come together is
called a convergent boundary. - When oceanic plates collide with continental
plates, the oceanic plate sinks beneath the
continental plate creating a subduction zone. - Sometimes volcanoes form above subduction zones.
- When 2 continental plates collide, they form
mountain ranges.
19
When plates slide past each other
- The boundary where 2 plates slide past each other
is called a transform boundary. - The plates can move in the same direction or in
opposite directions. The key is they move at
different speeds. - When a plate slips past another suddenly,
earthquakes occur.
20
What causes plate tectonics?
- It is thought that convection currents cause
plate tectonics. - Convection currents are where hot, dense material
is forced upward by the surrounding cooler
material.
21
Features caused by plate tectonics
- The interaction of plates produces forces that
build mountains, create ocean basins, and cause
volcanoes or earthquakes