Practical taxonomy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
Practical taxonomy
Description:
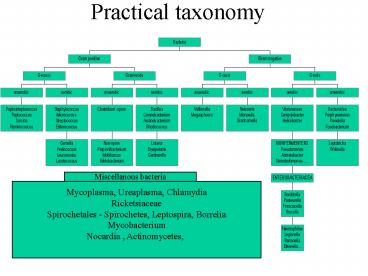
Miscellanous bacteria Mycoplasma, Ureaplasma, Chlamydia Ricketsiaceae Spirochetales - Spirochetes, Leptospira, Borrelia Mycobacterium Nocardia , Actinomycetes, – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:234
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Practical taxonomy
1
Practical taxonomy
Miscellanous bacteria
Mycoplasma, Ureaplasma, Chlamydia Ricketsiaceae Sp
irochetales - Spirochetes, Leptospira,
Borrelia Mycobacterium Nocardia , Actinomycetes,
2
GenusBacillus - Gsporeforming bacilli, aerobic
and facultatively anaerobic
- Bacillus anthracis,Bacillus
cereus,Other Bacillus sp. - Bacillus cereus - 2 enterotoxins
-
heat stable - emetic form - contaminated rice -
heat resistant spores survive initial cooking
that kills vegetative cells, germinate, multiply
and toxin is not destroyed by reheting
- heat labile - diarrheal form
- adenylcyclase-cAMP system stimulation in
intestinal cells - fluid accumulation
-contaminated meat and vegetable - toxin is
produced in situ, longer incubaion - Panophthalmitis - traumatic eye infection (soil,
penetrating object), complete loss, massive
destruction
- toxins - necrotic - heat labile
enterotoxin
- cereolysin - hemolysin
-
phospholipase C - lecithinase - Ubiquitous, isolation witout symptoms
contamination - Other Bacillus - immunosupressed patients - shunt
and catheter inf.
3
Bacillus antracis
4
Bacillus anthracis
- Spore and capsule (protein) not seen in clinical
specimens - Antrax toxin - 3 antigenically distinct
components -protective Ag, lethal factor, edema
factor - not active separately, - Pathogenesis capsule - antiphagocytic, Ab are
not protective, toxins are active in cooperation
of protective lethal or edema f. - Cultivation - on nonselective media, rapidly
growing adherent colonies, no hemolysis, Non
motility,liquifaction of agar
Microscopy caput medusae
serpentine like chains,
5
Bacillus anthracis
- Human diseases - cutaneous - inoculation -
painless papule, ulcer, necrosis
- respiratory -
inhalation - rapid progresive diffuse pulmonary
involvement - respiratory failure - 95 mortality
-
gastrointestinal - ingestion - rare - mesenteric
adenopathy, hemorrhage, ascites, 90 mortality - Therapy - PNC (TTC, CMP)., control of animal
antrax, vaccination.
6
Bacillus antracis
7
Non sporeforming G bacilli - heterogenous group
- Corynebacterium - coryneforms, diphtheroids- C.
diphteriae (diphtheria), C. jeikeium
(oportunistic). C. urealyticum(urinary tranct
inf.), C. pseudodiphthericum (endocarditis), C.
ulcerans (pharyngitis) - Arcanobacterium haemolyticum - pharyngitis
- Actinomyces - granulomatous ulcerative inf.
- Rhodococcus - suppurative pneumonia,
opportunistic - Listeria - meningitis, septicemia, granulomatosis
infantiseptica - Erysipelothrix - erysipeloid, septicemia,
endocarditis - Gardnerella - bacterial vaginosis
8
Corynebacterium
- Pleoimorphia, Grods, forming short chains, china
letters, or letter Y,V - forms - Metachromatic granuls resulting colour differs
from the colour of the used one - Special cell wall structure mesodiaminopimelic
acid, arabinogalactan, mycolic acid with short
chains taxonomic neighbour to mycobacteria - C. diphtheriae preventabil disease diphthteria
- asymptomatic carriage in pharynx droplet
transmission - C. jeikeium - JK - oportunistic patogen in
immunocompromised - hematological disorders - Others - transmitted from annimals
9
Corynebacterium- patogenesis and immunity
- Diphtheric exotoxin - tox gen can be transmitted
to bacteria (C. diftérie, C. ulcerans,
C.pseudotuberculosis via bacteriophage
lysogenic conversion - A-B protein B phragment binding on the cell
surface enable enter of A phragment to the cell.
A phragment is enzymatically active - blocking
synthesis of proteins prolngation of peptid
chain on ribosomes - Skin test detection of neutralising antibodies
in vivo - i.d. application of diphtheric toxin
10
- Phospholipase D - dermonecrotic toxin enable
spread by increasing vascular permeability .
ulcerans, C. pseudodiphthericum - Urease - C. urealyticum alkalinisation of urine
and urine calculi forming - ATB resistence selection of resistent strains -
C. urealyticum, C. jeikeium resistent to
commonly used ATB in UT infection
11
Diphtheria
- Clinical presentation depends on state of
immunity and place of infection - asymptomatic
colonisation, mild respiratory infection,
fulminant diphtheria - Difphtheria URT infectionwith low grade fever,
toxin induce local damage adherent pseudomembrane
on tonsils, pharynx, nose and general symptoms of
intoxication. Myocarditis. - Skin diphtheria transmission via skin contact
from infected persons, colonisation and enter via
small injurie - papules and chronic ulcers with
membrane and general signs of intoxication, less
sever,
12
Diphtheria
13
Laboratory diagnosis
- Microscopy detection of metachromatic granules
methylen blue staining not important - Cultivation on common media (blood agar),
special media Loffler
medium,
- tellurit agar gray
brown colonies - 3 types of colonies - gravis (big, irregular,
gray), mitis (small, convex,round, black),
intermedius (small, plate, gray) connected with
importance and virulence not considered more - Biochemical identification
- Detection of toxigenicity - Eleks test -
immunodiffusion, - antitoxic test on annimal
model.,
14
Arcanobacterium
- A.haemolyticum - colonise human, responsible for
pharyngitis (/- scarlet fever-like rash),
cutaneusinf., endocarditis, meningitis - in older
patients - Missdiagnosed as Str. pyogenens, grows slowly,
weak hemolysis - 2 toxins - hemolysin and phospholipase D
- enzymes neuraminidase
15
Erysipelotrix
- E. rusiopathiae G non spore forming facultative
anaerobic bacillus, worldwide distribution in
animals - Cultivation in reduced oxygen athmosphere, small
grayish, alfa hemolytic colonies, 2-3 days,
sample from deep tissue or deep aspirates. - Erysipeloid - occupational disease (butchers,
meat processors) after subcutaneous innoculatio
-localised skin infection
-generalised
cutaneous forme
-septicaemia - associated with endocarditis
(undamaged heart valve - aortic) - Therapy PNC, ERY,CLI (sulfonamids, vancomycin,
aminoglycosides - resistent)
16
Listeria
- 7 species, most important L. monocytogenes
facultatively anaerobe neonporeforming G rod - meningoencephalitis, bacteraemia, endocarditis
- New borne, older gravid women, immunocompromised
patients (after transplantation - Frequently transfer via milk and row milk
products, row vegetable - Able to grow in wide range of pH a and low
temperature 22C , faible beta hemolysis, motile
in liquid media
17
Clinical syndroms
- Newborne listeriosis - infection in utero -
granulomatosis infantiseptica, devasting disease,
diseminated abscesses and granulomes multiorgan
involvement
- late listeriosis - 2-3 weaks after delivery -
meningitis, septicaemia - Meningitis of adults in immunocompromised,after
transplantation - Bacteraemia, Endocarditis
- Dg. Microckopy of CSF usually negat.- few
bacteria, Cultivation and indentification - Therapy - penicillin /- combination with
aminoglycosids
18
Rhodococcus
- G, obligate aerobic, red-pigmented, acid fast,
mycolic acid. Veterinary pathogen. Present in
soil - Intracellular - surviving in macrophages
- Granulomatous inflammation with abscess formation
(lung,lymph nodes, menings, pericardium, skin) -
immnosupressed - Cultivation - nonselected media, aerobically,
pigmented colonies after 4 and more days - Therapy prolonged - multiple ATB able to
penetrate into macrophages
19
Gardnerella
- Morphologically resembles gram negative bacilli,
has cell wall structure of gram , nonmotile, not
capsule - part of normal vaginal flora
- present in bacterial vaginosis together with
obligate anaerobes - Mobiluncus,
Peptostreptococcus,absence of Lactobacillus.
Present in postpartum bacteremia, endometritis,
vaginal abscesses - Lab. dg. - simple isolation is not prooving,
importance of microscopic examination - clue
cells - epitelial cells covered with G variable
bacilli (Gardnerella) and G- small curved bacilli
(Mobiluncus), absence of G bacilli
(Lactobacilli) - Therapy ampicilin, metronidasol
20
Actinomyces
- G filamentous rods, 5-10CO2,
- Actinomyces israeli, A. meyeri, A. naeslundii,
A.odontolyticus - chronical disease with abscess, tissue
destruction and sulphur granules in tissue (mass
of mycelia surrounded by protein, polysaccharide
and bacteria) - cervicofacial forme(endogenous, after tooth
extraction) - abdominal,( starting in appendix
and diverticules) -pelvic forme (from
IntraUterinDevices) - hematogenous disemination
- Lab. Dg. - pus with sulphur granuls - Ziehl
Neelsen - microscopy, cultivation - agar with
heart brain infusion - 10 days, colony shape -
mollar tooth
21
Nocardia
- Gstrictly aerobe rods. Similar to quickly
growing mycobacteria, saprophytes in environment.
Acid fast., Mycolic acid - Nocardia asteroides, N. brasiliensis, N. madurae
- pneumonia - with confluent abscess formation,
exogenous inhalation - skin infection - Actinomyces brasilinensis -
localised celulitis, purulent sinuses with
chronical granulomatous inflamation - mycetoms - Madurmycosis - chronical granulomatous infection
of bone and soft tissue, deformations, (Sudam,
Northern Africa, East India) - diseminated - CNS - brain abscesses, in
immunocompromised - Lab. Dg. - microscopy - modified Ziehl Neelsen,
Gram , cultivation - standard media -2-30 days,
colonies adherent to agar, cream, orange rose
color, chalky consistence - Therapy surgeryATB 3 months sulphonamids,
amikacin, imipenem, broad spectrum to be
effective if fungal ethiology
22
Anaerobic bacteriae
- Gcocci
polymicrobial - G-cocci
endogenouse - G-rod
mixture - Grod nonspores forming fac.patogenic
-
- sporeforming patogens,
-
clinical units
23
Gcocci anaerobic
- Peptostreptococcus, -Peptococcus,- Sarcina (fac.
anaerobic) -
Coprococcus, - Ruminococcus
-
colonisation of the skin and mucouse membrane
GIT, UGT, -
oportunistic patogens in connection with foreign
bodies cultivation require special grow
conditions, slowly growing
Clinical symptoms - pleuropneumonia
following aspiration, sinusitis, brain absces
spreading from oropharynx or lung,
- intraabdominal infection and sepsis
spreading from colon,
- pelvic infections (endometritis, absces,
puerperal sepsis, bacterial vaginosis)
- infection of soft tissue (celulitis),
endocarditis, osteomyelitis - Laboratory diagnosis colonising bacteria or
ethiological agent, sampling and transport under
anaerobic conditions, prolonged cultivation on
enriched media - Th - PNC, cefalosporins, imipenem, CMP -
polymicrobial ethiology.
24
G-cocci
- anaerobic
- Veillonella, Megasphera present in oropharynx,
low virulence, in cultivation usually part of
polymicrobial mixture
25
G-rod anaerobic
- Bacteroides fragilis
obligatory anaerobic rod, not sporeforming,
- most important part of
fysiological flora in oropharynx, UGT, GIT.
- Clinical symptomes - pleuropneumonia,
intraabdominal abscess, genital infections.
- Endogenous and polymicrobial infections,
absceses after break down of physiological
barieres. - Lab.dg. strictly anaerobic sampling, transport
and cultivation
stimulation of the growth by 20 cholic
acid.
- Th surgery intervention ATB, - B.producesa
betalactamase, Metronidasol - B(G). stearothermophilus- spores used for testing
efficiency of sterilisation devices - Prevotella, Porphyromonas, Fusobacterium,
Leptotricha, Wolinella colonisation of
orofarynx, GIT, UGT, part of physiological flora,
pathogenic after the breakdown of natural
barieresr e.g.. Surgical intervention - They produce histolytical enzymes,
- absceses and polymicrobial infection (CNS,
UGT,intraabdominal) - Production of betalaktamase resistente to
PNC. - Lab. dg. Anaerobic sampling and transport,
prolonged cultivation
26
Grods aerobic
- Spores forming
- Bacillaceae - Bacillus cereus,
B. antracis - flagella, facultative anaerobes or
strict aerobes. Production of toxins. - Nonsporesforming
- Listeria
monocytogenes - motile, aerobic, surviving 22C
and broad interval of pH, infecting annimals
-
Corynebacteriaceae -aerobic nonmotile slightly
curved, forming picture of alphabet letters,
irregularly stainable Containing metachromatic
granules, production of toxin -
lysogenic conversion - toxigenicita of strains
- Eleks test.
Corynebacterium diphtheriae, C.
pseudodiphtericum,
Erysipelotrix rusiopathiae - facult. anaerobic,
transmission from annimals, grey colonies, alfa
hemolysis,
Nocardiaceae Nocardia asteroides
contain lipid in the cell wall modified Ziehl
Neelsen staining, nonmotil, filamentous form in
microscopy, prolonged cultivation
27
Grods anaerobic nonsporesforming
- - Actinomycetaceae Actionomyces israeli,
A.naeslundii - Clinical signs cerebral, cerevicofacial,
abdominal, thoracal actinomycosis, - chronical pyogenic infection with absceses.
- Lab.dg. Sampling from the depth of sinus or
abscess containing sulphur granules, typical
colonies looking like tooth molar, requiring,
long cultivation.
- Th surgery ATB prolonged PNC
-Propionibacteriaceae
Propionibacterium acnes
- colonisation of skin, external ear, conjunctiva,
orofarynx, female external genital tract. - Clinical symptomes Acne and opportunistic
infections in patients with foreign bodies. - Lab. dg. On common media, prolonged cultivation
- Mobiluncus
---gram variable, structue of G, curved, growth
reqirements, colonisation of fem.external genital
in case of dysmicrobia - vaginosis
-Bifidobacteriaceae, Eubacteriaceae,-
Lactobacillaceae . part of physiological flora
28
Anaerobic Gram sporesforming rodsClostridium
sp.
- strictly anaerobic, spores typically localised in
the cell enlarging the body, proteolytical
ensymes, production of toxins, - C. tetaní tetanus traumatic
- - newborne
- C. botulinum - botulizmus newborne
- -
wound
- - food
borne - C. septicum - nontraumatic myonecrosis, patients
immunocompromised - Ca of colon
- breakdown of the integrity of colon, spread of
clostridia in tissues, hyperacute course - C. difficile - pseudomembranouse colitis
connected with broad spectrum ATB therapy,
produces 2 toxins, part of FF,
exposition to ATB taht eliminate colon bacterial
flora overgrowth of C. difficile and its spores
29
Anaerobic gram spores forming rodsClostridia
of anaerobic traumatoses
- Clostridia - 100 species, some of them can be
aerotolerantné
- C. histolyticum can looks like gram
negatívne, spores not constantly detectable.
Commonly present in soil, water, GIT of annimal
and human. - C. perfringens - Bacteraemia, myonecrosis gas
gangrene, infection of soft tissue, necrotising
enteritis
30
Clostridium tetani
- Motile rod, spores forming, spores enlarging
cell,squash rocket, transiently gram negative.
Very sensitive to oxygen, metabolically very
active. - Produces 2 toxins - Termolabil neurotoxin-
tetanospasmin released from lysing cells. AB
toxin - blocking neurotransmitters in CNS on na
inhibation synapsesh nonregulation of
excitation synaptic activity - spastic paraysis,
convulsions.
-
tetanolysin - Present in soil and GIT of annimal. Vegetative
formes are very sensitive on oxygen. Spores are
surviving years - Generalised tetanus, - localised tetanus, -
nexborne tetanus, - tetanus of drug abusers - Therapy - PNC, antitoxin, - toxin bound on
synapses is not neutralisable and ATB are active
agains viable cells (not toxin) Symptomatic - Vaccination
31
(No Transcript)
32
Clostridium botulinum
- Heterogennous group, nutritionnaly requiring
spores forming rods. 4 groups I
- IV based on proteolytical aktivity a type of
toxin. - Producing 7 antigenically different botulotoxines
A,B,C alfa, D, E, F, G - A,B,E most frequent. AB
toxin , termolabil toxin - 20minutes/80C - Blocking transmission on nervemuscular platelet
on synapses of periferic nerves. - Food borne, wound botulisme, infant botulisme
- Blurred vision, dilatation of pupils, dry tongue,
constipation, bilateral muscular weakness
complete restoration after months or years
- Wound botulisme very rare
- Infant botulisme - 1976 - in vivo production of
neurotoxin in colon colonising clostridia (age of
6mnth - 1 y) progresive paralysis, respiration
failure - mortality 1 - frequently cause of SIDS - Dg. - clinical, detection of clostridium or toxin
- Th. lavage of stomach antitoxin,
- PNC, destruction of spores and
prevention of spores germination
33
Clostridium botulinum
34
Clostridium perfringens
- Colonisation or sever disease, spores are seen
scarecely, hemolysis, metabolic aktivity. - Production of letal toxins (alfa, beta, epsilon,
iota, termolabil enterotoxin) with sever life
threating biological activity, ensymes. Types
A-E A in environment, B-E in colon,
A gas
gangrene and intoxication, C necrotizing
enteritis - Microscopy - Grods without leu in clinical
samples Th
surgery in traumatoses, high doses of PNC,
antitoxin, hyperbaric room for oxygen therapy
35
Clostridium perfringens
- Bacteraemia usually not significant, transient
from skin contaminant. - Gas gangrene life threating, histotoxic
clostridia, after injury, devitalised tissue
gas production. (C. septicum, histolyticum,
novyi)
- Celulitis, fasciitis after colonisation of the
wound, oftently not important or rapidly
progressing destruction of tissue (C. septicum)
- Necrotizing enteritis small intestine, typ C,
50 letality
Food borne intoxication short
incubation time, spasmes, watery diarrhoe
ingestion of contaminated food, toxin -
termolabil protein