EIM Overview - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
EIM Overview
Description:
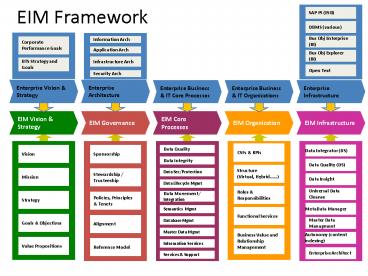
EIM Framework SAP PI (ESB) DBMS (various) Bus Obj Enterprise (BI) Information Arch Corporate Performance Goals Application Arch Bus Obj Explorer (BI) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:37
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: EIM Overview
1
EIM Framework
SAP PI (ESB)
DBMS (various)
Bus Obj Enterprise (BI)
Information Arch
Corporate Performance Goals
Application Arch
Bus Obj Explorer (BI)
Infrastructure Arch
BTS Strategy and Goals
Open Text
Security Arch
Enterprise Vision Strategy
Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise Business IT Core Processes
Enterprise Business IT Organizations
Enterprise Infrastructure
EIM Vision Strategy
EIM Governance
EIM Core Processes
EIM Organization
EIM Infrastructure
CSFs KPIs
Data Integrator (DS)
Vision
Sponsorship
Data Quality
Data Integrity
Data Quality (DS)
Structure (Virtual, Hybrid)
Mission
Data Sec/Protection
Stewardship / Trusteeship
Data Insight
Data Lifecycle Mgmt
Roles Responsibilities
Universal Data Cleanse
Strategy
Data Movement/ Integration
Policies, Principles Tenets
MetaData Manager
Semantics Mgmt
Functional Services
Goals Objectives
Alignment
Database Mgmt
Master Data Managment
Master Data Mgmt
Business Value and Relationship Management
Autonomy (content indexing)
Value Propositions
Reference Model
Information Services
Enterprise Architect
Services Support
2
EIM Definition
- Enterprise information management (EIM) is an
integrative discipline for structuring,
describing and governing information assets,
regardless of organizational boundaries or
technologies.
- EIM strives to improve operational efficiency,
promote transparency and enable business insight.
- The broad scope of EIM requires a level of
organizational commitment to improve the
accuracy, integrity, accessibility and security
of information assets.
- The objective of EIM is to resolve data
definition, format and content issues across
applications and document stores.
3
EIM Mission Statement
To provide integrated enterprise level data and
information, managed as a corporate asset, within
a standardized and shared infrastructure to
facilitate and support integrity of data for
daily operations and fact based decision making.
4
EIM Scope
- All Consumers Energy data and information assets
including structured data and unstructured
content. - The organization, processes, infrastructure and
standards governing management of the enterprise
information and content. - Cross organizational roles and responsibilities
related to management of the information assets. - Management of information assets through the
entire information life cycle from creation
through disposal.
5
EIM Benefits
- Business Value
- Ensures that the CEA investment in common data
and process is leveraged for future projects and
the business value is maximized thru data
governance. - Strives to provide a single version of the truth
supporting business insight. - Enables better business decisions and
responsiveness to change by making timely,
consistent and accurate information readily
available. - Efficiency
- Enables faster and lower cost information
delivery by shortening development times and
repurposing proven information services. - Supports development collaboration thru a shared
central metadata repository. - Provides a stable data foundation for system
integration transparency based on standards and
best practices. - Data Quality
- Increases data quality thru ongoing data quality
assessments and exception monitoring. - Improves the ability to derive consistent
information providing the foundation for
actionable and timely business intelligence. - Builds confidence in the accuracy and relevance
of information provided with data lineage
traceability. - Transparency
- Promotes common understanding and sharing of
information across the enterprise. - Instills business ownership and stewardship of
the critical information resources. - Improves communication and reduces ambiguity
within the organization by promoting consistent
data definition, format and usage standards.
6
EIM Vision (2015)
- Data and information is recognized and managed as
a valuable corporate resource across
organizational and technology boundaries. - Information assets are managed through the entire
information life cycle (creation, maintenance,
access, archive and disposal) using well defined
processes. - Consistent data definition and understanding
provides a common vocabulary for the business. - Information is managed and utilized to maximize
its benefit in support of the goals of the entire
organization.
- A standardized information infrastructure and
processes are implemented supporting data sharing
and process integration. - Information is readily available through common
services on a need to know basis and is secured
from unauthorized access. - Current, complete and consistent information is
readily available providing a single version of
the truth enabling business insight and fact
based business decisions. - Consumers Energy Executive management recognizes
and embraces the role of EIM in achieving the
corporate objectives.
7
Gartner - Data Management and Integration
Maturity Assessment