Introduction to Lab 6: Ex. Protozoa - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Introduction to Lab 6: Ex. Protozoa
Description:
Introduction to Lab 6: Ex. Protozoa Introduction to Lab 6: Ex. Protozoa This lab exercise introduces a group of microorganisms that are called the Protozoa (proto ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:24
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Introduction to Lab 6: Ex. Protozoa
1
Introduction to Lab 6 Ex. Protozoa
2
- Introduction to Lab 6 Ex. Protozoa
- This lab exercise introduces a group of
microorganisms that are - called the Protozoa (proto primitive zoa
animal). - Characteristics of Protozoa are
- -unicellular (one-celled) organisms,
- -aquatic habitats
- Eukaryotic
- lack a cell wall,
- -may have specific structures to help in
movement - (pseudopodia, flagella, cilia)
- -aerobic,
- -holozoic nutrition (ingest food particles).
- -some are parasitic and cause diseases in humans
and animals.
3
Protozoa are classified into different groups
based on the presence and type of locomotory
organelle they possess Sarcodina - pseudopodia
(false feet cytoplasmic outflowings that help
the organism move and to obtain food)
Mastigophora have whip-like structures called
flagella, move by undulations) Ciliophora
have short hair-like structures distributed over
the surface to help in locomotion. Organisms
will be studied by making wet mounts. Methyl
cellulose (protoslo) will be added to slow down
highly motile organisms.
4
Specific organisms to be studied in lab Amoeba
proteus (wet mount) Amorphous structure changing
shape due to formation of pseudopodia
5
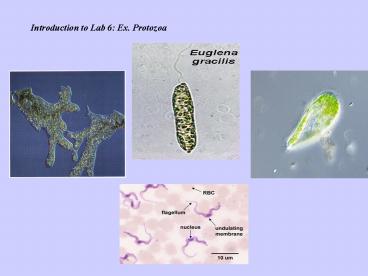
Euglena (wet mount) Elongated shape with
flagella protruding out of one end green due
to presence of chloroplast (able to
photosynthesize)
6
Trypanosoma (stained slide) Elongated with a
single flagella out of one end. Causes
Sleeping sickness in humans transmitted to
humans by the bite of vector the tse tse fly.
Infection found in the blood and affects the
nervous system resulting in loss of muscle
control and gives the appearance of sleeping.
Found in Africa and South America
7
Paramecium (wet mount) Slipper shaped cell with
many cilia distributed over the entire surface
of the organism.