Atoms and Molecules - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Atoms and Molecules
Description:
Plasma Physics and the Earth Ranges of Plasma Plasma Propulsion for Deep Space Exploration Plasma is a partially ionized gas. Electrons are ripped from their atoms. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:47
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Atoms and Molecules
1
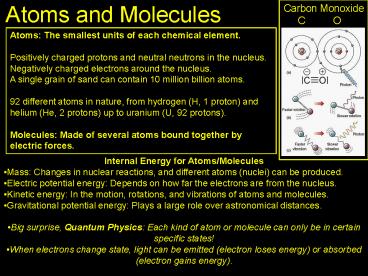
Atoms and Molecules
Carbon Monoxide C O
Atoms The smallest units of each chemical
element. Positively charged protons and neutral
neutrons in the nucleus. Negatively charged
electrons around the nucleus. A single grain of
sand can contain 10 million billion atoms. 92
different atoms in nature, from hydrogen (H, 1
proton) and helium (He, 2 protons) up to uranium
(U, 92 protons). Molecules Made of several
atoms bound together by electric forces.
- Internal Energy for Atoms/Molecules
- Mass Changes in nuclear reactions, and different
atoms (nuclei) can be produced. - Electric potential energy Depends on how far the
electrons are from the nucleus. - Kinetic energy In the motion, rotations, and
vibrations of atoms and molecules. - Gravitational potential energy Plays a large
role over astronomical distances. - Big surprise, Quantum Physics Each kind of atom
or molecule can only be in certain specific
states! - When electrons change state, light can be emitted
(electron loses energy) or absorbed (electron
gains energy).
2
UNR is Plasma Physics Central!!
- Plasma is a partially ionized gas. Electrons are
ripped from their atoms. - Some electrons are free rather than being bound
to an atom or molecule. - Positive and negative charges move somewhat
independently. Plasma is electrically conductive
so that it responds strongly to electromagnetic
fields. - Plasma has properties quite unlike those of
solids, liquids or gases and is considered to be
a distinct state of matter. - Plasmas are the most common phase of matter in
the universe, by mass and volume. - All stars are made of plasma.
- Colors are from electrons relaxing to lower
energy states when they recombine with ions. - Light color is characteristic of the atoms or
molecules in the gas.
3
Plasma Physics and the Earth
Photo of aurora borealis
As the speeding solar wind hits the Earth's
magnetic field, it creates a shock wave,
compresses the forward side of the field, and
stretches the far side into a long magnetotail.
The field traps particles into the donut-shaped
Van Allen radiation belts, which then protect the
Earth against the wind. The interaction of the
wind and the Earth's field generate two rings of
electrical current that flow around the magnetic
poles (which are offset relative to the rotation
axis) and that in turn create the aurora
borealis. (From Stars, J. B. Kaler, Scientific
American Library, Freeman, NY, 1992.)
www.astro.uiuc.edu/kaler/aurora.html
4
Ranges of Plasma
5
Plasma Propulsion for Deep Space Exploration
Plasma Propulsion Engine
- Ion thruster uses plasma in some part of the
thrust generation process. - Much less powerful than conventional rocket
engines. - Very efficient, good for long-distance
Interplanetary space travel missions. - First developed by Russia during 1963-1965 to
propel spacecraft to Mars. Now in common use!