Biosynthesis of Macromolecules - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 25
Title:
Biosynthesis of Macromolecules
Description:
Biosynthesis of Macromolecules Anabolism - use energy (ATP) from catabolism - use carbon from sugars, lipids, proteins, or any other carbon source (xenobiotics) to ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1193
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Biosynthesis of Macromolecules
1
(No Transcript)
2
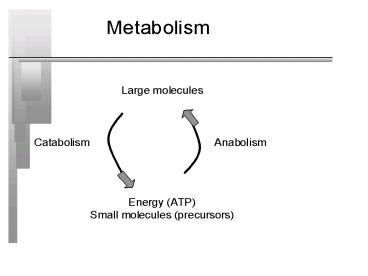
Biosynthesis of Macromolecules
- Anabolism- use energy (ATP) from catabolism
- - use carbon from sugars, lipids, proteins, or
any other carbon source (xenobiotics) to build
cellular components
3
(No Transcript)
4
Key Intermediates
- Located in the glycolytic pathway
- Ex. Glucose-6-phosphate, pyruvic acid, etc.
- Located in the TCA cycle
- Ex. Oxaloacetic acid, ketoglutaric acid
5
Central Metabolic pathway
- Catabolism and anabolism are interconnected due
to amphibolic pathways
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Lipid Biosynthesis
- Fatty acid biosynthesis- Acetyl-CoA---gtfatty acid
(cell structure) - Poly-ß-hydroxybutyric acid- Acetyl-CoA---gt Poly.
(storage) - Phospholipid- Glycolytic intermediate---gt lipid (
membrane) - Sterols- eukaryotic cell membrane
9
(No Transcript)
10
Amino Acid Biosynthesis
- Amination addition of an amine group (N
containing) to a critical intermediate - Transamination - new amino acids are made from
the amine group from old amino acids
11
(No Transcript)
12
Nucleotide Biosynthesis
- N molecule (amino acid), five carbon sugar,
phosphate combine gtnucleotides (DNA, RNA) - Five carbon sugar
- Pryrimidines- cytosine, thymine
- Purines- adenine, guanine
13
(No Transcript)
14
Polysaccharide Biosynthesis
- Peptidoglycan- Glycolytic intermediates,
nucleotides ---gtPEG - Lipopolysaccharide- Glycolytic intermediates,
other sugars ---gt LPS, teichoic acid, mycolic
acid, glycogen, etc.
15
(No Transcript)
16
Photosynthetic microbes
- Carbon dioxide fixation
- Inorganic CO2 is incorporated into the cellular
structure (Calvin cycle)
17
(No Transcript)
18
Metabolic diversity
- Different sources of carbon and energy exist for
various microbes, plants, and animals.
19
Metabolic diversity
- Four main groups of microbes
- 1.) chemoheterotrophs
- 2.) chemoautotrophs
- 3.) photoautotrophs
- 4.) photoheterophs
20
Chemoheterotrophs
- Many medically important microbes are in this
category (E. coli, B. anthrasis, etc.) - Carbon source organic molecules (carbohydrates,
proteins, lipids, xenobiotics) - Energy sourceorganic molecules (carbohydrates,
proteins, lipids, xenobiotics)
21
Chemoautotroph
- Many soil microbes
- Source of carbon inorganic molecule (ex. CO2)
- Source of energy electrons from inorganic
compounds (ex. S, H2S, NO2)
22
Photoautotroph
- Photosynthesis (green sulfur bacteria, etc.)
- Source of carbon CO2
- Source of energy light
23
Photoheterotroph
- photosynthesis (green nonsulfur bacteria, etc.)
- Source of carbon organic molecule ( ex. Fatty
acids, alcohol, etc.) - Source of energy light
24
Summary of Anabolism
- Use ATP (energy) from catabolism for biosynthesis
- Build small molecules into larger molecules or
cell structures (ex. Glucose, amino acids, fatty
acidsgtlipid, PG) - Diversity of metabolic systems (chemoheterotrophs,
etc.) - Cell division (binary fission)anabolism
25
- Catabolism and anabolism are integrated
- (amphibolic pathways)