Mendelian Genetics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title:
Mendelian Genetics
Description:
Mendelian Genetics AP Biology Unit 3 Mendel s Experiments Crossbred Pea Plants P, F1, F2 generations Alleles Alleles are different (alternate) forms of a gene How ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:39
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Mendelian Genetics
1
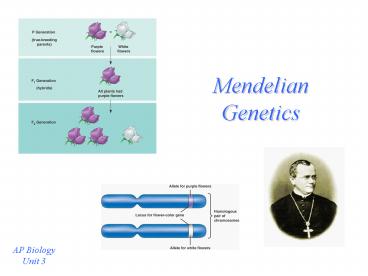
Mendelian Genetics
AP Biology Unit 3
2
Mendels Experiments
- Crossbred Pea Plants
- P, F1, F2 generations
3
Alleles
- Alleles are different (alternate) forms of a gene
- How do alleles relate to homologous chromosomes?
- Homologous chromosomes may contain different
alleles
4
Yeast Complementation Alleles
- How did alleles play a role in the yeast
complementation experiment? - Strains of yeast have different alleles
- When mated, the a normal allele could complement
a mutated allele - HA1 mutated ade 1 allele , normal trp allele
- HBT normal ade1 allele, mutated trp allele
5
Dominant vs. Recessive Alleles
- Dominant Allele
- Determine phenotype if there is a copy present
- Recessive Allele
- Need 2 copies to determine phenotype
6
Law of Segregation
- Two alleles for a trait separate during gamete
formation - Gametes can have different alleles
7
(No Transcript)
8
Punnett Squares
- Allow you to predict possible genotypes of
offspring if parental genotypes are known - Phenotypes can be deduced from the genotypes
9
Phenotype Ratios
- Characteristic possible phenotype ratios always
occur - 22 (11)
- 31
- 40 (10)
10
Test Cross
- Suppose you have an organism with a dominant
phenotype - You want to determine its genotype PP or Pp?
- Cross with a recessive phenotype to determine
genotype test cross
11
(No Transcript)
12
Law of Independent Assortment
- Pairs of alleles for a given trait segregate
independently of other pairs of alleles for
another trait - Ex. YyRr can result in YR, Yr, yR, or yr
- This only applies to two traits on different
chromosomes (NOT LINKED)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Blood Type Alleles
- Codominance both IA and IB alleles are dominant
- Multiple alleles (more than 2 alleles)
15
Practice Problem 1
- The Huntingtons disease allele is dominant
(represented as H). - A husbands genotype is Hh a wifes genotype is
hh - Which of them will develop Huntingtons disease
- What are the possible genotypes for their
children? What are the chances their child will
have Huntingtons Disease?
16
Answer
- The husband will develop Huntingtons Disease
- Children could be Hh (50 chance) or hh (50
chance) - So there is a 50 chance their child will have
Huntingtons disease.