Geographic Regions of Georgia - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Geographic Regions of Georgia
Description:
Coastal Plain There are two parts to Georgia s coastal plain: The Inner Coastal Plain The Outer Coastal Plain Which color do you think represents the Inner ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:283
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Geographic Regions of Georgia
1
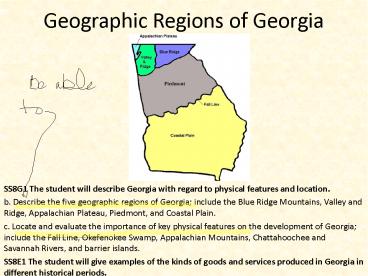
Geographic Regions of Georgia
- SS8G1 The student will describe Georgia with
regard to physical features and location. - b. Describe the five geographic regions of
Georgia include the Blue Ridge Mountains, Valley
and Ridge, Appalachian Plateau, Piedmont, and
Coastal Plain. - c. Locate and evaluate the importance of key
physical features on the development of Georgia
include the Fall Line, Okefenokee Swamp,
Appalachian Mountains, Chattahoochee and Savannah
Rivers, and barrier islands. - SS8E1 The student will give examples of the kinds
of goods and services produced in Georgia in
different historical periods.
2
- Compare and Contrast these pictures. What do
these pictures tell you about the different
physiogeographic regions of Georgia?
3
Terms to Know
- Physiogeographic
- Region
- Precipitation
- Wetland
- Barrier Island
- Continental Shelf
- Fall Line
4
Georgia has 5 physiogeographic regions.
- Appalachian Plateau
- Ridge and Valley
- Blue Ridge
- Piedmont
- Coastal Plain
- The characteristics of each region make unique
contributions to our state.
5
Appalachian Plateauaka Cumberland Plateau/ TAG
corner
- Our smallest physiogeographic region
- From Lookout Mt. to Sand Mt. with ridges of
limestone a long narrow valley in between - Soil of limestone, shale sandstone hardwoods
and pastureland - Our only significant coal deposits.
- Economy tourism and forestry
6
Ridge and Valley
- Lower elevation than Appalachian Plateau
- Low open valleys and narrow ridges
- Soil good for forests, pastures, and crops such
as grain and apples - Industry includes textiles and carpet (Dalton,
GA. is the carpet capital of the world)
7
Blue Ridge
- Highest mts. in the state including Brasstown
Bald- Georgias highest point. - Sandy loam and clay soil good for hardwoods,
vegetable farming and apples - Beginning of Appalachian Trail, home to Amicalola
Falls, Tallulah Gorge, and Helen, GA - Highest percent of rainfall is in the Blue Ridge
8
Blue Ridge
Brasstown Bald You can see 3 states from this
point.
Amicalola Falls
Helen, Georgia has a strong German influence.
Why do you think that is? How does the town of
Helen contribute to our state?
Ga. Fruits Vegetables
9
Piedmont Foot of the mountain
- Begins in the mountain foothills of N. Georgia
and goes to the central part of the state. - Most of Georgias population live in the Piedmont
region. - Granite based foundation (Whats our largest
granite outcropping?) - Soil is sandy loam and red clay suitable for
growing hardwoods, pine, and agriculture. - Cotton belt before the Civil War, now wheat,
soybeans, corn, poultry, and cattle. - Some of the most densely populated cities and
crossed by Chattahoochee, Flint, Ocmulgee, and
Oconee rivers.
10
Piedmont
Georgias Flint River starts in Clayton County.
Why do you think most of Georgias major cities
are located in the Piedmont region?
Sandy loam and red clay are make good soil for
agriculture.
Why do you think most of Georgias rivers start
in the Piedmont region?
11
Coastal Plain
- There are two parts to Georgias coastal plain
- The Inner Coastal Plain
- The Outer Coastal Plain
- Which color do you think represents the Inner
Coastal Plain and which color represents the
Outer Coastal Plain? Why?
12
The Inner Coastal Plain
- Good supply of underground water
- Major agricultural region Vidalia Onions,
peanuts, pecans, and corn - Why do you think President Jimmy Carter was known
as The Peanut Farmer from Georgia during his
campaign?
13
The Outer Coastal Plain
- Soil not good for agriculture but trees provide
naval stores and pulp production - Deep harbors and barrier islands also provide for
tourism/recreation, fishing industry, and ports
for importing/exporting goods. - Location of the earliest visits by explorers,
first forts for protection, and Georgias first
settlements.
14
Outer Coastal Plain
Why do you think a British flag flies over Fort
Frederica?
Trees are used to produce pulp and naval stores.
The processed goods are then shipped from our
shores.
Our shores continue to bring visitors to our
state.
Early map of Savannah
15
Other Important Coastal Plain Features
- Okefenokee Swamp
- Covers 681 square miles making it the largest
freshwater swamp in North America
16
Another type of wetland
- Salt Marshes
- A wetland that is influenced by tides
- Georgia ranks 4th in the nation in wetland acres
- A marsh at low tide. The same
marsh at high tide.
17
Georgias Barrier IslandsIslands of Gold
- Barrier islands protect the mainland from wind,
sand, and water that cause erosion. - Georgia has 18 barrier islands.
- These islands are tourist destinations but 2/3 of
the land remains wilderness sanctuaries. - During colonial times grew indigo and rice
18
Other Georgia Geographic Features
- Continental Shelf
- Where the land meets the sea
- The Fall Line
- Where hilly land meets the coastal plain
- Runs from Columbus through Macon to Augusta
- Prevented exploration but provided for
settlements
19
Rivers
- Chattahoochee River Borders Georgia and Alabama.
Mainly used as a water source for millions of
Georgians. It also is used for industry and
recreational purposes. - Savannah River Borders Georgia and South
Carolina. The river is navigable between
Savannah and Augusta. The river is used for
shipping, a source of drinking water, and to cool
off two nuclear power plants, and to generate
hydroelectric power.