The Nervous System - Lab Exercise 5 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
The Nervous System - Lab Exercise 5
Description:
The Nervous System - Lab Exercise 5 Central nervous system (CNS) brain & spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) cranial nerves & spinal nerves Divisions ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:100
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Nervous System - Lab Exercise 5
1
The Nervous System- Lab Exercise 5
2
Divisions of the Nervous System
- Central nervous system (CNS) brain spinal
cord - Peripheral nervous system (PNS) cranial nerves
spinal nerves
3
The Central Nervous System
CNS well protected by bones (cranial
vertebrae), CT meninges, cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF)
Meninges Connective tissues that surround and
protect the brain and spinal cord (CNS)
- 3 layers
- Dura Mater
- Arachnoid
- Pia Mater
4
Meninges
Dura Mater tough, fibrous outer layer
- 2 layers thick around brain with creation of
dural sinuses between layers
- 1 layer around spinal cord with epidural space
external
5
Meninges
Arachnoid spidery web-like middle layer
Pia Mater delicate, thin inner layer adhered
to brain cord extension of pia mater (filum
terminale) extends from tip of cord to coccyx to
anchor cord in place
Subarachnoid space between arachnoid pia
mater contains cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
6
Superior sagittal sinus
Dura mater (gray color)
Arachnoid (orange color)
Subarachnoid space (blue color)
Pia mater (red color)
7
The Brain
- Brain stem
- medulla oblongata (M.O.)
- pons
- midbrain
- Diencephalon
- thalamus
- hypothalamus
- mamillary bodies
- epithalamus (pineal gland)
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
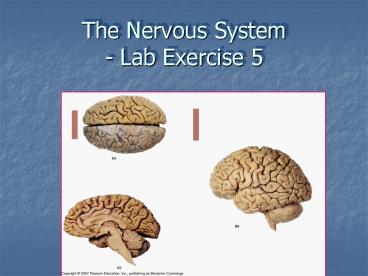
Cerebrum
T
P
P
H
midbrain
M
Cerebellum
pons
m.o.
8
Cerebrum
T
P
H
midbrain
M
pons
Cerebellum
m.o
Spinal cord
9
The Brainstem
- medulla oblongata (M.O.)
- pons
- midbrain
- cerebral peduncle
- cerebral aqueduct of midbrain
- corpora quadrigemina
- superior colliculi
- inferior colliculi
pons
Cerebral peduncle
m.o.
Cerebral aqueduct of midbrain
10
Cerebral aqueduct of midbrain
Superior colliculus
Inferior colliculus
Cerebral peduncle
11
The Diencephalon
- thalamus
- intermediate mass
- hypothalamus
- mamillary bodies
- connects to pituitary gland via infundibulum
- epithalamus (pineal gland)
M
12
(No Transcript)
13
Cerebrum
convolutions
gyrus
sulcus
4 lobes per hemisphere- frontal, parietal,
temporal, occipital
14
The Cerebrum
15
The Cerebellum
- gray matter folia
- white matter arbor vitae
- separated from cerebrum by transverse fissure
Transverse fissure
16
(No Transcript)
17
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- clear, colorless fluid formed by filtration of
blood plasma by choroid plexuses within
ventricles of the brain.
- functions in protection of CNS, support,
nutrient supply, waste removal
18
(No Transcript)
19
CSF Circulation
Lateral ventricles (in cerebral hemispheres) ?
interventricular foramen ? third ventricle (in
diencephalon around thalamus) ? cerebral aqueduct
of midbrain ? fourth ventricle (between
pons/cerebellum) ? subarachnoid space central
canal of SC
Lateral ventricle (behind septum pellucidum)
Third ventricle
Aqueduct of midbrain
Fourth ventricle
20
Reabsorption of CSF through arachnoid
granulations (arachnoid villi) of dural sinuses
(superior sagittal sinus) ? into cerebral veins
21
Superior sagittal sinus
Arachnoid granulation (villus)
22
Cranial Nerves
- 12 pairs of nerves that connect to the brain
provide motor, sensory /or autonomic
(parasympathetic) function
23
I (olfactory bulb)
Olfactory tract
Optic chiasm
Optic tract
II
III
IV
V
VII
VI
VIII
IX
X
XII
XI