Brain Lesions (Cognitive Neuropsychology) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Brain Lesions (Cognitive Neuropsychology)
Description:
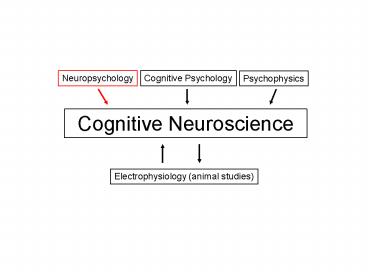
Cognitive Psychology Neuropsychology Psychophysics Cognitive Neuroscience Electrophysiology (animal studies) * * * * Brain Lesions (Chapter 5) (Cognitive ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:168
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Brain Lesions (Cognitive Neuropsychology)
1
Cognitive Psychology
Psychophysics
Neuropsychology
Cognitive Neuroscience
Electrophysiology (animal studies)
2
Brain Lesions (Chapter 5)(Cognitive
Neuropsychology)
- The traditional approach to establishing a
connection between the mind brain. - Limitation of imaging (or any correlational)
methods - Does the activation have anything to do w/
function? - Car analogy
- One way to prove something is necessary
- Take it out
3
History
LANGUAGE
VISION
4
Levels of Analysis
Anatomical
Functional
5
Advancements
- (1) MRI localize brain injury in vivo
- Very precisely locate injury and adapt tests
accordingly - patient populations identify groups of
individuals with common brain injuries
6
Advancement
- The use of control subjects
7
Advancements
- (2) Cognitive psychology paradigms
- Area A is important for reading
- What are the components of reading?
- Perceiving letters
- Letter strings activate corresponding meanings
- Link words coherently
- What specific component is affected by area A
damage?
8
Disengage Shift Engage
XXXX
Disengage Shift Engage
9
Cognitive Psychology Perspective
- Mental processes are composed of elementary
mental operations - These operations are localizable in time
- The operations are localizable in discrete,
contiguous regions of the brain
10
Single and Double Dissociations
- Start with a model/hypothesis
- Facial recognition and emotion recognition (based
on facial features) are different processes
Emotion task
Recognition task
Performance ( Correct)
Region 1 (FFA)
Region Damaged
11
Single and Double Dissociations
- Start with a model/hypothesis
- Facial recognition and emotion recognition (based
on facial features) are different processes
Emotion task
Recognition task
Performance ( Correct)
Performance ( Correct)
Region 1 (FFA)
Controls
Region Damaged
12
Problems with Single Dissociation
- Possible alternative interpretations
- Recognition task might be more difficult
- See task-resource artefact in text (p 82)
13
Single and Double Dissociations
- Start with a model/hypothesis
- Facial recognition and emotion recognition (based
on facial features) are different processes
Emotion task
Recognition task
Performance ( Correct)
Performance ( Correct)
Region 1 (FFA)
Controls
Region 2 (STS)
Region Damaged
14
Double Dissociations (and fMRI)
- Start with a model/hypothesis
- Facial recognition and emotion recognition (based
on facial features) are different processes
Emotion task
Recognition task
fMRI Activation
Region 1 (FFA)
Region 2 (STS)
15
Problems w/ lesions
- A process must be localizable to specific regions
- Compounded by lack of specificity of lesions
- Lesion may disrupt connectivity other
non-damaged areas might be non-functioning. - Assumption that intact regions continue to
function in the same way - No timing information
16
Transient Lesions
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
- Magnetic field induced disruption of neural
activity - A brief pulse is applied that causes neural
activity for 10s ms - If the area is involved in the task, the dual
firing (task and to the TMS pulse) results in
behavioral disruption
17
(No Transcript)
18
Advantageous
- Quickly reversible (no reorganization as w/ true
lesions) - Within-subject designs
- Moveable lesions
- Very focused ( 1 cm resolution)
- Precise timing
19
(No Transcript)