Maxwell - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 32
Title:
Maxwell
Description:
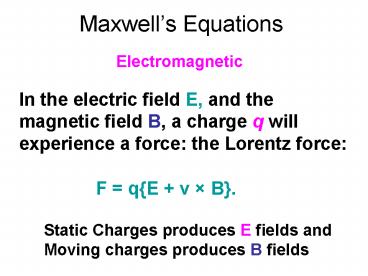
Maxwell s Equations Electromagnetic In the electric field E, and the magnetic field B, a charge q will experience a force: the Lorentz force: F = q{E + v B}. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:412
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Maxwell
1
Maxwells Equations
- Electromagnetic
In the electric field E, and the magnetic field
B, a charge q will experience a force the
Lorentz force
F qE v B.
Static Charges produces E fields and Moving
charges produces B fields
2
Maxwells Equations
- Electromagnetic
The effects may be summarized in the expressions
for the divergence and the curl of E and B
divE ?/?,
curlE 0 ,
divB 0 ,
curlB µ0J
3
Maxwells Equations
- Electromagnetic
Equations without divergence and curl express
passive aspects, while with curl and divergence
express active aspects.
A field with a curl but no divergence is called a
solenoidal field, while one with a divergence but
no curl is called an irrotational field.
4
Electrostatic Field Potential Distribution.
5
Electrostatic Field
Equipotentials and Electric Field Vectors
of Electrostatic Field.
6
(No Transcript)
7
Electric Field Vectors
Equipotentials and Electric Field Vectors of
aMicrostrip Line.
8
Potential Distribution
Potential Distribution associated with a
Corner Resistor.
9
Electric Field Magnitude
Logarithmic scaled Electric Field Magnitude
10
Electrodynamics
- A Charged Particle
If a charged particle is set free in an electric
field, it is accelerated by a force proportional
to the field and charged particle
F eE
Where F is Force e is a charge, and E is electric
Field Intensity
11
Electrodynamics
- Newtons Second Law
d(mv)
dv
dm
F
m
v
dt
dt
dt
Where m mass of particle, kg V velocity of
particle, m-1
12
Electrodynamics
- Newtons Second Law
- F m
dv
ma
dt
ma eE
- Velocity is very small as compared to
velocity of light - Mass is essentially constant
13
Electrodynamics
- Energy
Integrating the force over the distance traveled
by charged particle is
2
2
W m ? a dL e? E dL
1
1
While the Integral of E between points of 1 and 2
is a potential difference V
2
W m? v dv eV
1
W ½ m( v22 v12) eV
14
Electrodynamics
- Particle Energy
- W eV ½ mv2
- where
- W energy acquired by particle, J
- v2 velocity of particle at point 2, or final
velocity, ms-1 - V1 velocity of particle at point 1, or initial
velocity, ms-1 - e charge on particle, C
- m mass of particle, kg
- V magnitude of potential difference between
points 1 2, V
15
Electrodynamics
- Final velocity
Considering a charged particle e starting from
rest and passing through a potential of V, will
attain the final velocity of ?-
? ? 2eV/m
16
Electrodynamics
- Final velocity
- While
- e 1.6 x 10-19C falling through
- V 1 volt
- Energy 1.6 x 10-19 Joules
- m mass of 0.91 x 10-30kg, will attain Velocity
v 5.9 x 105? V
at 1 volt the charge attains 590 kms-1
17
Electrodynamics
eVd
eVdL
- ay
vy
vy ayt
? tan-1
vx
md
mvxd
L
Vd
y
v
vy
Ed
?
vx
d
18
Electrodynamics
- Problem-
- A CRT with Va 1500V,
- Deflecting space d 10mm,
- Deflecting plate length 10mm,
- Distance x 300mm,
- Find Vd to deflection of 10mm-
- Deflection y VdLx/2Vad
- Vd 2Vady/Lx 100 V
19
Electrodynamics
- Moving particle in static magnetic field
- Force on a current element dL in a magnetic field
is given by - dF (I x B)dL (N) Motor equation
- I q/t
- IL qL/t qv
- IdL dqv
- dF dq(v x B)
- F e(v x B) Lorentz force
20
Electrodynamics
- Moving conductor in a magnetic field
- E F/e v x B
- V12 ? E dL ? (v x B) dL
2
2
1
1
1
Generating Equation
?
?
?
?
?
B
dL
v
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
2
E v x B
21
Electrodynamics
- Magnetic Brake
22
Electrodynamics
- Magnetic Brake
I, B, PUSH Therefore F due to I is opposing to
PUSH
Conductive Plate
Magnet Assembly
23
Electrodynamics
- Magnetic Levitation
24
How does the LEVITRON work?
When the top is spinning, the torque acts
gyroscopically and the axis does not overturn but
rotates about the (nearly vertical) direction of
the magnetic field.
25
How does the LEVITRON work?
- levitionta
26
Electrodynamics
- levitation
27
Electrodynamics
- levitation
- "We may perhaps learn to deprive large masses of
their gravity and give them absolute levity, for
the sake of easy transport." - - Benjamin Franklin
28
Electrodynamics
- Maglev Trains
29
Electrodynamics
- Maglev Train
A maglev train floats about 10mm above the
guidway on a magnetic field. It is propelled by
the guidway itself rather than an onboard engine
by changing magnetic fields (see right). Once the
train is pulled into the next section the
magnetism switches so that the train is pulled on
again. The Electro-magnets run the length of the
guideway
30
Electrodynamics
- Maglev Train Track
31
Maglev Train
- Aerodynamics Brakes
32
Electrodynamics
- Advantages
- no components that would wear out
- there is no friction. Note that there will still
be air resistance. - less noise
- The final advantage is speed








![⚡Read✔[PDF] Amy Maxwell's 6th Sense: An Amy Maxwell Cozy Mystery (Amy Maxwell Series Book 3) PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10066060.th0.jpg?_=202406270410)





















