DIURETICS: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
DIURETICS:
Description:
Davidoff 09 DIURETICS: (know those used to Tx hypertension and HF) Thiazide diuretics: hydrochlorothiazide Loop diuretics: furosemide, ethacrynic acid – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:314
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: DIURETICS:
1
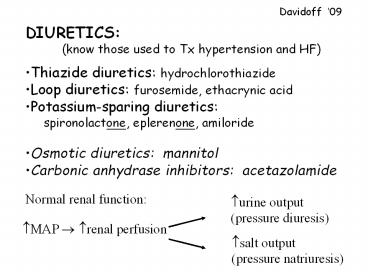
Davidoff 09
- DIURETICS
- (know those used to Tx hypertension and HF)
- Thiazide diuretics hydrochlorothiazide
- Loop diuretics furosemide, ethacrynic acid
- Potassium-sparing diuretics
- spironolactone, eplerenone, amiloride
- Osmotic diuretics mannitol
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors acetazolamide
2
Rationale for using diuretics
For heart failure ?Blood volume ? ?preload
(?cardiac work) ?congestion (?edema)
For hypertension ? Blood volume and peripheral
resistance ? ? preload (ventricular filling) ?
? CO ? ? BP
- Diuretics promote natriuresis (Na excretion)
- Water tends to follow Na (diuresis)
- Relative potencies of diuretics
- Loops gtgt Thiazides gtgtgtgtgtgt K sparing
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
Na
Ca2
reabsorption
Thiaz
filtration
K sparing
Na
secretion
Na
ALD
Loops
K H
ADH
Katzung Fig 15-1
6
- Thiazides hydrochlorothiazide
- Most commonly used class of diuretics
- Differ in their pharmacokinetics
- Indicated for mild hypertension
- short-term effects ? ?blood volume
- long-term effects ? ?TPR (lose their diuretic
effects) - For moderate or severe hypertension,
- used in combination with other antihypertensive
drugs - Flat dose-response curve
- (i.e., increasing dose does not make them more
effective)
7
Brenner Fig 10-2
8
- Thiazides (cont)
- ?Na reabsorption by inhibiting Na/Cl
co-transport in the distal - convoluted tubule
- Modest effect because only 5-10 of Na is
reabsorbed there - Must be filtered or secreted to work, therefore
ineffective - in patients with renal insufficiency/failure
- Require renal prostaglandins to work, therefore
NSAIDs can - interfere with diuresis
- Side effects
- Hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis
- ?Blood glucose, lipids, and uric acid
Bonus ?Blood Ca2 (via ?Ca2 reabsorption) useful
for osteoporosis ? Urine Ca2 useful for
kidney stones
9
How do thiazides (and loops) promote K loss?
Na
?tubular Na
collecting duct
Na
K H loss
?Na/K exchange
urine
urine
10
Loop diuretics furosemide, ethacrynic acid
- High ceiling diuretics - work in a
dose-dependent manner - Ethacrynic acid is an alternative if patient has
sulfonamide allergy - Extremely effective, rapid onset
- Indicated for severe edema (e.g., pulmonary
edema, CHF) - not typically used for hypertension
- Inhibit Na/K/2Cl transport in ascending loop of
Henle - normally responsible for 35 Na reabsorption
- Are filtered and secreted
- Directly increase renal blood flow, therefore
effective with renal insufficiency
11
'high ceiling diuretics'
Diuresis
'flat D-R curve'
Dose of diuretic
Brenner Fig 13-3
12
Like Thiazides Loops require renal
prostaglandins to work, therefore NSAIDs can
interfere with diuresis
- Side effects include
- Hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis and hyperuricemia
- Hypovolemia
- Ototoxicity
Loops greater incidence of adverse side effects
than thiazides
13
Na
Ca2
reabsorption
Thiaz
filtration
K sparing
Na
secretion
Na
ALD
Loops
K H
ADH
Katzung Fig 15-1
14
Potassium sparing diuretics Spironolactone,
Eplerenone, Amiloride
- Weak diuretics
- used in combination with other diuretics
- Antagonize aldosterone effects
- Aldosterone is a steroid
- binds to mineralocorticoid receptors in tubular
epithelial cells - stimulates the synthesis of Na/K/H pumps
- promotes Na reabsorption, K/H secretion
- Prevents hypokalemia from thiazide and loop
diuretics - Must be cautious of hyperkalemia
15
- Spironolactone
- Competitively binds to aldosterone receptors -
nonselective - (mineralocorticoid, androgenic and progesterone
receptors) - Inhibits aldosterone-induced synthesis of pumps
- Slow onset (WHY?), long duration (active
metabolites) - Weak naturiuretic effects, but lowers BP in some
patients with mild/moderate hypertension - Also indicated for hyperaldosteronemia
- Shown to improve morbidity and mortality in
patients with end-staged heart failure (Pitt et
al., NEJM, 1999) - Side effects include
- Men gynecomastia and erectile dysfunction
because of anti-androgenic actions - Women menstrual irregularities, hirsutism
16
- Eplerenone
- More specific for aldosterone receptors than
spironolactone therefore avoids side effects - (but really expensive)
- Currently approved hypertension and post-MI LV
dysfunction - CYP450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin,
verapamil, and grapefruit juice) can elevate
blood levels of eplerenone - Aldosterone is also associated with endothelial
dysfunction and fibrotic effects in hypertension,
HF and atherosclerosis - (mechanism underlying ACE-I cardioprotection???
) - Cardioprotective effects appear similar to
spironolactone
http//www.jaapa.com/issues/j20040201/articles/020
4wcardiomeds.html
17
- Amiloride
- Directly inhibits pumps in distal tubules and
collecting ducts - therefore independent of aldosterone
- (blocks Na selective channels in apical
membrane) - Onset of action much faster than spironolactone
- does not involve gene expression
- Relatively few side effects (caution about
hyperkalemia)
18
JNC VII Compelling Indications for Drug Classes
Clinical-Trial Basis
Compelling Indication
Initial Therapy Options
MERIT-HF, COPERNICUS, CIBIS, SOLVD, AIRE, TRACE,
Val-HeFT, RALES
Diuretic, BB, ACEI,ARB, Aldo Ant
Heart Failure
ACC/AHA Post-MI Guideline, BHAT, SAVE, Capricorn,
EPHESUS
BB, ACEI, Aldo Ant
Post-MI
ALLHAT, HOPE, ANBP2,LIFE, CONVINCE
High CAD Risk
Diuretic, BB, ACEI, CCB
NKF-ADA Guideline,UKPDS, ALLHAT
Diuretic, BB, ACEI,ARB, CCB
Diabetes Mellitus
NKF Guideline, Captopril Trial, RENAAL, IDNT,
REIN, AASK
Chronic Kidney Disease
ACEI, ARB
Recurrent Stroke Prevention
PROGRESS
Diuretic, ACEI
ACEIAngiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor,
Aldo AntAldosterone antagonist, ARBAngiotensin
receptor blocker, BBb-blocker, CADCoronary
artery disease, CCBCalcium channel blocker,
MIMyocardial Infarction
Chobanian AV et al. JAMA. 20032892560-2572