DNA Replication: copying DNA during cell division - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
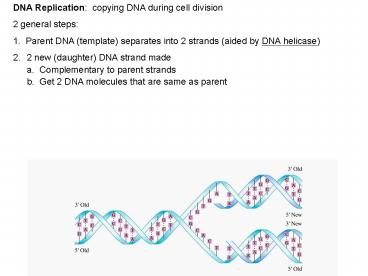
DNA Replication: copying DNA during cell division
Description:
Begins at initiation codon (AUG) also codes for met ... complementary to codon for the amino acid on the tRNA stem. UUC complementary to codon AAG, which gives ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:106
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: DNA Replication: copying DNA during cell division
1
- DNA Replication copying DNA during cell
division - 2 general steps
- 1. Parent DNA (template) separates into 2
strands (aided by DNA helicase) - 2 new (daughter) DNA strand made
- a. Complementary to parent strands
- b. Get 2 DNA molecules that are same as parent
2
Replication occurs at several sites on parent DNA
3
- DNA polymerase elongates chainadds nucleotides
- 5 to 3 direction only
- 3 to 5 strand made as Okazaki fragments
DNA ligase joins ends Okazaki fragments and
pieces from different origins of replication
4
22.41 In the replication of a DNA molecule, 2
daughter molecules, Q and R, are formed. The
following sequence is part of the newly formed
strand in daughter molecule Q. 5 A C T T A G
3 Indicate the corresponding sequence in a. The
newly formed strand in daughter molecule R
5
- The parent strand in daughter molecule Q
- The parent strand in daughter molecule R
6
- Protein Synthesis making protein
- uses information carried in DNA
- General process
- DNA RNA protein
- 4 steps
- Transcription
- Editing
- Transfer to cytoplasm
- Translation
transcription
translation
in nucleus
in cytoplasm
7
- Transcription making an RNA copy of the DNA,
called heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) - also called primary transcript RNA (ptRNA)
- Made like replication, but only 1 strand copied
hnRNA complementary to DNA but A paired with U
instead of T
8
- genes information on DNA for making proteins
- 2 parts exons sequences for making protein
- introns extra sequences, probably
for regulation - Editing removing the introns from hnRNA to make
messenger RNA (mRNA) just exons - Done by enzymes with the help of small nuclear
RNA (snRNA) (100-200 nucleotides)
exon
intron
exon
intron
exon
hnRNA
Editing by enzymes snRNAs
mRNA
exon
exon
exon
9
- Transfer to cytoplasm. mRNA carries the message
from the nucleus to the cytoplasmto ribosomes - Ribosomes made of protein and ribosomal RNA
(rRNA) - Ribosomes are free in cytoplasm and on
endoplasmic reticulum - 4. Translation reading of mRNA by ribosomes
10
Begins at initiation codon (AUG) also codes for
met Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings in appropriate
amino acid, where it starts or adds to a protein
chain Genetic Code language of RNA. Made of
codons. Codon a set of 3 nucleotides that
specifies a particular amino acid
11
Genetic Code
Only 1 amino acid per codon reads 5 to
3 degenerate more than 1 codon for some amino
acids, usually varies in 3rd position universal
most living things use the same genetic code 1
start codon AUG (met) 3 stop codons UAA, UAG,
UGA
22.79 Predict the amino acid sequence coded by
the mRNA 5- A U G A A A G A A G A C C U A -3
12
Ribosomes move along mRNA, tRNA brings in amino
acids, enzymes (peptidyl transferases) move amino
acid from tRNA to growing protein chain
13
Structure of tRNA cloverleaf with 3 hairpin
loops and a stem where amino acid
attaches Anticodon set of 3 nucleotides
complementary to codon for the amino acid on the
tRNA stem
UUC complementary to codon AAG, which gives
lysine upon translation
14
Alternative views of tRNA structure
15
Determine the amino acid sequence specified by
the following DNA sequence, showing all
intermediate steps. 3- GCGCATTTGCACCTTGGCACG -5
exon
exon
intron