Epilepsy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Epilepsy
Description:
Tonic-Clonic Seizure(SGTCS) affect only a small region of the brain ... Divided into two phases, the tonic phase and the clonic phase, preceded by an aura ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:63
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Epilepsy
1
Epilepsy
???
2
What is epilepsy?
- a brain disorder characterized predominantly by
seizures - not a singular disease entity
- May reflect underlying brain dysfunction
3
Epileptic seizures/fits
- sudden, brief periods of unconsciousness or
changes in mental state - often with strange jerking movements
- due to abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal
activity in the brain. - caused by abnormal electric impulses in neurons
in the brain.
4
Common causes
- Injury to the brain
- Meningitis
- In small children common causes of fits are high
fever or severe dehydration. - Epilepsy that steadily gets worse, especially if
other signs of brain damage begin to appear, may
be a sign of a brain tumor. - Hereditary.
5
Triggers
- Can be part of normal daily life.
- Examples are reading, hot water on the head,
hyperventilation, and flashing or flickering
lights. - This last trigger(provocant) is a special type of
reflex epilepsy called photosensitive epilepsy.
6
(No Transcript)
7
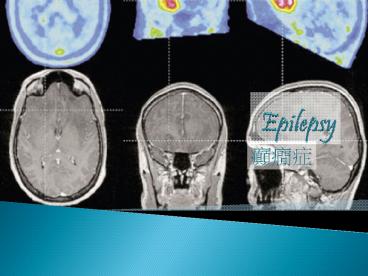
Diagnosis
- Diagnosed by electroencephalography (EEG) or
brain MRI (magnetic resonance image).
MRI Scan for temporal lobe
SPECT -- scan image varies in color depending on
the amount of blood flow
Temporal lobe
8
Normal EEG
9
Generalized 3 Hz spike and wave discharges in EEG
10
Temporal lobe epilepsy
- Simple Partial Seizure(SPS)
- Complex Partial Seizure(CPS)
- Tonic-Clonic Seizure(SGTCS)
11
Simple Partial Seizure(SPS)
- affect only a small region of the brain
- precursors to larger seizures.
- Symptoms vary greatly between people due to
varying locations of the brain the seizures
originate in. - May be unnoticed by others
12
Symptoms
- sudden and unexplainable feelings of joy, anger,
sadness or nausea - unusual feelings or sensations
- hallucinations
- depersonalization feeling as though the
environment is not real or detached from the
environment
13
Complex Partial Seizure(CPS)
- They may then have feelings of fear, as well as
depersonalization. - Vision may be disturbed.
- May display automatisms such as lip smacking,
chewing ,swallowing and undressing.
14
- There may also be loss of memory (amnesia)
surrounding the seizure event. - May not be immediately recognizable to a witness
who may not be aware that there is anything wrong
as the person may still be able to perform
routine tasks such as walking or shopping.
15
Tonic-clonic seizures
- Divided into two phases, the tonic phase and the
clonic phase, preceded by an aura - In the aura, the person may have a simple partial
seizure with a sense of dizziness and unusual
emotions. - Sometimes, the person will lose complete
awareness.
16
- In the tonic phase, the person will fall
unconscious, - muscles will suddenly tense up, causing
extremities(arms and legs) to either pull towards
the body or rigidly pushed away from it. - The person will fall to the ground
- It is the shortest part of the seizure and last
for a few seconds only.
17
- In the clonic phase, the person's muscles will
start to contract and relax rapidly, causing
convulsions. - These may range from exaggerated twitches of the
arms and legs to violent shaking or vibrating of
the stiffened extremities. - They may roll and stretch as the seizure spreads.
18
- Eyes typically roll back, the tongue is often
bitten.
19
Treatment
- Oral medications for treating seizures are termed
as anticonvulsants. - Valproic acid is a commonly used anticonvulsant.
- It can suppress the rapid and excessive firing of
neurons that start a seizure. - A good anticonvulsant would prevent the spread of
the seizure within the brain and offer protection
to prevent brain damage.
20
- It worked by decreasing the excitation of neurons
(e.g., by blocking sodium or calcium channels) or
by enhancing their inhibition. - For some patients, surgery is the primary
alternative. - It may produce many side effects such as mild
coordination problems, dizziness, sinus pain,
indigestion, heartburn and etc.
21
What should we do when someone is under the tonic
clonic seizure attack?
22
- Put them into the recovery position, and remove
any dangerous objects. - Once convulsion started, we should not try to
stop them, instead we should ensured they do not
injure themselves by placing something soft under
their head, and their limbs and body don't bump
any objects.
23
Should we put something into their mouth like
what weve seen in some films or tv programmes?
24
- NO!
- Nothing should ever be placed into the person's
mouth, as this can cause the person to bite their
tongue or choke.