EN 31 Design Contest: Base Isolation System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
EN 31 Design Contest: Base Isolation System
Description:
Free vibrations: C. Vibration occurs at the system-dependent natural freqency. ... Typical car: fn=1 Hz; wn=2p radians/sec. Isolates for bump-spacing L v/ meters. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:50
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: EN 31 Design Contest: Base Isolation System
1
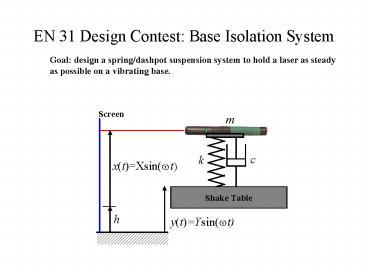
EN 31 Design Contest Base Isolation System
Goal design a spring/dashpot suspension system
to hold a laser as steady as possible on a
vibrating base.
2
Dates
- Friday, November 4 Submit names of group members
and team name on paper before 4pm. Maximum of 5
students per group. - Friday, November 18 Submit design and drawings.
- Monday, November 21 Begin fabrication and
testing. - Friday, December 9 Final demonstration/contest,
Final reports due.
3
Vibration Control Base Isolation
Soft, Springy Mount
4
(No Transcript)
5
The Christchurch Arts CenterWith and Without
Base Isolation
6
Other Suspension Systems (same idea) Keeps
equipment steady while the supports vibrate!
7
Cars
8
Printed Circuit Board Manufacture
9
Everyday examples
10
Free vibrations
C
- Vibration occurs at the system-dependent natural
freqency. - The oscillations decay exponentially (if
) - Initial condidtions x0x(0) and v0 v(0)
determine the amplitude and phase
11
Forced Vibrations Periodic forcing
12
Typical Response
Displacement
Time
Transient vibrations xh(t) at the natural
frequency. Depend on I.C. These decay
exponentially with time.
Steady-state Vibrations xp(t) at the forcing
frequency Independent of I.C. These do not decay.
Total response x(t)xh(t)xp(t)
Amplitude of the steady-state vibrations is
(very) large if the forcing frequency is at or
near the system natural frequency.
13
The Steady State Response Damped
C
Amplitude X/(F0/k)
14
Background Base Excitation
15
Base Excitation
16
Base Excitation
17
Steady state response
Displacement
Time
Transient vibrations xh(t) at the natural
frequency. Depend on I.C. These decay
exponentially with time.
Steady-state vibrations xh(t) at the forcing
frequency Independent of I.C. These do not decay.
Steady state response
18
Amplitude of the steady state response
Isolation
Amplitude X/Y
Amplification
w/wn
Pick a (soft) spring so that (wn)2k/mlt w2/2. Use
light damping
19
Note on the Spring-Mass Frequency
mg
20
Works for any spring system!
21
Car Suspension
- Wheel Motion
- Isolation when (wn)2k/mlt w2/2(2pv/L)2/2
- Typical car fn1 Hz wn2p radians/sec
- Isolates for bump-spacing Lltv/ meters. (v in
meters per second) - If v25mph10m/sec maximum bump spacing is 7
meters