Cell Structure of Prokaryotes Bacteria and Eukaryotes Higher Organisms - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Cell Structure of Prokaryotes Bacteria and Eukaryotes Higher Organisms
Description:
Prokaryotes - Single cells without nucleus or other organelles ... Bacteria - Single Chromosome ... Picture of a Centric Diatom (from the protista kingdom) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:77
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cell Structure of Prokaryotes Bacteria and Eukaryotes Higher Organisms
1
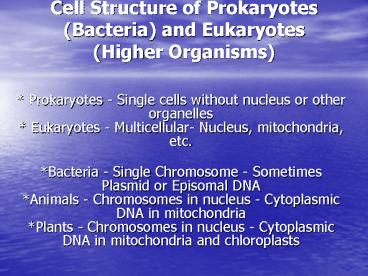
Cell Structure of Prokaryotes (Bacteria) and
Eukaryotes (Higher Organisms)
- Prokaryotes - Single cells without nucleus or
other organelles Eukaryotes - Multicellular-
Nucleus, mitochondria, etc. - Bacteria - Single Chromosome - Sometimes Plasmid
or Episomal DNAAnimals - Chromosomes in nucleus
- Cytoplasmic DNA in mitochondria Plants -
Chromosomes in nucleus - Cytoplasmic DNA in
mitochondria and chloroplasts
2
Prokaryotic cell
- Cells that lack a membrane-bound nucleus are
called prokaryotes (from the Greek meaning before
nuclei). These cells have few internal structures
that are distinguishable under a microscope.
Cells in the monera kingdom such as bacteria and
cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae)
are prokaryotes.
3
(No Transcript)
4
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic
- Prokaryotic cells differ significantly from
eukaryotic cells. They don't have a
membrane-bound nucleus and instead of having
chromosomal DNA, their genetic information is in
a circular loop called a plasmid. Bacterial cells
are very small, roughly the size of an animal
mitochondrion (about 1-2µm in diameter and 10 µm
long). Prokaryotic cells feature three major
shapes rod shaped, spherical, and spiral.
Instead of going through elaborate replication
processes like eukaryotes, bacterial cells divide
by binary fission.
5
Functions that Prokaryotic cell perform
- Bacteria perform many important functions on
earth. They serve as decomposers, agents of
fermentation, and play an important role in our
own digestive system. Also, bacteria are involved
in many nutrient cycles such as the nitrogen
cycle, which restores nitrate into the soil for
plants. Unlike eukaryotic cells that depend on
oxygen for their metabolism, prokaryotic cells
enjoy a diverse array of metabolic functions. For
example, some bacteria use sulfur instead of
oxygen in their metabolism.
6
Evolution of the Eukaryotic cell
7
(No Transcript)
8
Eukaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic cells (from the Greek meaning truly
nuclear) comprise all of the life kingdoms except
monera. They can be easily distinguished through
a membrane-bound nucleus.
9
Eukaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic cells also contain many internal
membrane-bound structures called organelles.
These organelles such as the mitochondrion or
chloroplast serve to perform metabolic functions
and energy conversion. Other organelles like
intracellular filaments provide structural
support and cellular motility. The function of
individual organelles is described in detail in
the Cell Anatomy Section.
10
Another important member of the eukaryote family
is the plant cell. They function essentially in
the same manner as other eukaryotic cells, but
there are three unique structures which set them
apart. Plastids, cell walls, and vacuoles are
present only in plant cells.
11
- Picture of a Centric Diatom (from the protista
kingdom) - Picture of a Bread Yeast - S. cerevisiae (from
the fungi kingdom)
12
Picture of a Bread Yeast - S. cerevisiae (from
the fungi kingdom)
Picture of a Pea Leaf Stomata (from the plantae
kingdom)
Sunflower Petal and Pollen Grains - Helianthus
(from the plantae kingdom)
13
Human Breast Cancer Cell (from the animalia
kingdom)
Human Red Blood Cells, Platelets, and
T-lymphocytes (from the animalia kingdom)