Affinity adsorption - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Affinity adsorption
Description:
Affinity adsorption. Stereo-specific recognition of molecules ... Physiological conditions. Conditions that favour. Hydrophobic interactions. Hydrogen bonding ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:236
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Affinity adsorption
1
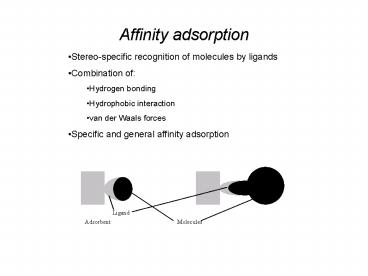
Affinity adsorption
- Stereo-specific recognition of molecules by
ligands - Combination of
- Hydrogen bonding
- Hydrophobic interaction
- van der Waals forces
- Specific and general affinity adsorption
Ligand
Adsorbent
Molecules
2
Affinity adsorbent
- Support material
- Cross-linked dextran
- Cross-linked agarose
- Cross-linked cellulose
- Synthetic resins
- Ligands
- Dye ligands
- Antibodies
- Antigens
- Protein A and protein G
- Substrate analogues
- Enzyme inhibitors
- Complimentary base-pair sequence
- Receptors
- Amino acids
- Lectins
- Concanavalin A
- Immobilized metal ions
3
Affinity binding and desorption
- Binding
- Physiological conditions
- Conditions that favour
- Hydrophobic interactions
- Hydrogen bonding
- Van der Waals forces
- High anti-chaotropic salt concentrations
- Desorption
- pH
- Chaotropic salts
4
Affinity separation Monoclonal antibody
Monoclonal antibody
Impurities
Cell culture supernatant
low pH buffer
Protein-A affinity adsorbent
Protein-A affinity adsorbent
Adsorbent monoclonal antibody
5
Reverse phase adsorption
- Partition type behaviour
- Adsorption of non-polar molecules
- Partition into thin immobilized layer of
hydrocarbon C4 to C18 - Support silica
- Adsorption Polar solvent e.g. water
- Elution Non-polar solvent e.g. acetonitrile and
isopropanol
Polar media
Non-polar media
Adsorbent
Immobilized hydrocarbon layer
Adsorption
Desorption
6
Reverse phase separation Insulin
Insulin
Filtered fermentation media acetonitrile
Impurities
80 acetonitrile 20 isopropanol
C-18 reverse phase adsorbent
C-18 reverse phase adsorbent
Adsorbent Insulin
7
Hydrophobic interaction
- Interaction between the hydrophobic patches on
molecules and those on the adsorbent - Mainly used for protein separation.
- Hydrophobic amino acids shielded by structured
layer of water molecules - Hydrophobic surface shielded by structured layer
of water - Anti-chaotropic salts make water molecules in
bulk solution structured - Less shielding of hydrophobic interactions
Molecule
Structured water layer
Adsorbent
Structured water in bulk solution
Hydrophobic layer
High salt concentration
Low salt concentration
Desorption
Adsorption
8
Hydrophobic interaction Adsorbent, adsorption
and desorption
Adsorbent Support Agarose most widely Groups
Butyl, octyl and phenyl Adsorption High salt
concentrations 1 M or higher Salt concentration
depends on the type of salt Less sodium sulphate
than ammonium sulphate or sodium
chloride Desorption Lowering the salt
concentration pH change
9
Affinity separation rEGF
rEGF
Filtered fermentation media Ammonium sulfate
Impurities
Ammonium sulfate free solution
Hydrophobic interaction adsorbent
Hydrophobic interaction adsorbent
Adsorbent rEGF
10
Adsorption isotherms
- Relationship between bound and free solute
concentrations at equilibrium - Analogous to equilibrium line in extraction
- Data obtained at constant temperature
Linear
Freundlich
Langmuir
Freundlich
CB
Linear
Langmuir
CU
11
Determination of isotherm constants
Linear Determine K from plot of CB versus
CU Freundlich Determine KF and n from plot of
(log CB) versus (log CU) Langmuir Determine
CBmax and KL from plot of (1/CB) versus (1/CU)
Slope n
log CB
log KF
log CU
1/CB
Slope KL/CBmax
1/CBmax
1/CU