Calculating branch lengths from distances. - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Calculating branch lengths from distances.
Description:
NJ is based on minimum evolution principle (sum of branch length should be minimized) ... Orangutan. Gorilla. Chimpanzee. Human. Fixation of mutations. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:70
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Calculating branch lengths from distances.
1
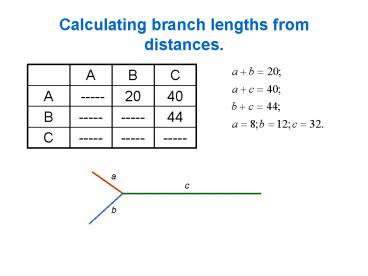
Calculating branch lengths from distances.
A B C
A ----- 20 40
B ----- ----- 44
C ----- ----- -----
a
c
b
2
1.1 Distance methods Neighbor-joining method.
- NJ is based on minimum evolution principle (sum
of branch length should be minimized). - Given the distance matrix between all sequences,
NJ joins sequences in a tree so that to give the
estimate of branch lengths. - Starts with the star tree, calculates the sum of
branch lengths.
C
B
b
c
D
a
d
e
A
E
3
1.2 Neighbor-joining method.
- 2. Combine two sequences in a pair, modify the
tree. Recalculate the sum of branch lengths, S
for each possible pair, choose the lowest S.
C
B
c
b
d
D
a
e
A
E
3. Treat cluster CDE as one sequence X,
calculate average distances between A and X,
B and X, calculate a and b. 4. Treat AB
as a single sequence, recalculate the distance
matrix. 5. Repeat the cycle and calculate the
next pair of branch lengths.
4
2.1 Maximum parsimony definition of informative
sites.
- Maximum parsimony tree tree, that requires the
smallest number of evolutionary changes to
explain the differences between external nodes. - Site, which favors some trees over the others.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
- A A G A C T G
- A G C C C T G
- A G A T T T C
- A G A G T T C
- Site is informative if there are at least two
different kinds of letters at the site, each of
which is represented in at least two of the
sequences.
5
2.2 Maximum parsimony.
Site 3
1.G
3.A
1.G
2.C
2.C
1.G
G
A
A
A
A
A
2.C
4.A
3.A
4.A
4.A
3.A
Tree 1.
Tree 2.
Tree 3.
Site 3 is not informative, all trees are realized
by the same number of substitutions. Advantage
deals with characters, dont need to compute
distance matrices. Disadvantage
- multiple substitutions are not
considered - branch
lengths are difficult to calculate
- slow
6
2.3 Maximum parsimony method.
- Identify all informative sites in the alignment.
- 2. Calculate the minimum number of
substitutions at each informative site. - 3. Sum number of changes over all informative
sites for each tree. - 4. Choose tree with the smallest number of
changes.
7
Maximum likelihood methods.
- Similarity with maximum parsimony
- - for each column of the alignment all
possible trees are calculated - - trees with the least number of
substitutions are more likely - Advantage of maximum likelihood over maximum
parsimony - - takes into account different rates of
substitution between different amino acids and/or
different sites - - applicable to more diverse sequences
8
Molecular clock.
- First observation rates of amino acid
substitutions in hemoglobin and cytochrome c are
the same among different mammalian lineages. - Molecular clock hypothesis rate of evolution is
constant over time in different lineages
proteins evolve at constant rates. - This hypothesis is used in estimating divergence
times and reconstruction of phylogenetic trees.
9
Estimation of species divergence time.
- Assumption rate constancy, molecular clock.
- Find T1 if T2 is known.
T1
T2
A
B
C
10
Classwork phylogeny of humans and apes.
Human Chimpanzee Gorilla Orangutan Rhesus monkey
Human
Chimpanzee 1.45
Gorilla 1.51 1.57
Orangutan 2.98 2.94 3.04
Rhesus monkey 7.51 7.55 7.39 7.10
11
Fixation of mutations.
- Not all mutations are spread through population.
Fixation when a mutation is incorporated into a
genome of species. - Fixation rate will depend on the size of
population (N), fitness (s) and mutation rate (µ)
12
Neutral theory of evolution.
- Kimura in 1968 majority of molecular changes in
evolution are due to the random fixation of
neutral mutations (do not effect the fitness of
organism. - As a consequence the random genetic drift occurs.
- Value of selective advantage of mutation should
be stronger than effect of random drift.
13
Classwork maximum marsimony.
- Search the NCBI Conserved Domain Database for
pfam00127. - Construct maximum parsimony tree using MEGA3.
- Analyze this tree and compare it with the
phylogenetic tree from the research paper.