Xray generation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Xray generation
Description:
Individual crystals are randomly oriented. Fe2S04. Neutron diffraction. Orthorhombic crystal. Examples of ... For example for KBr (200) (020) (002) coincide. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:61
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Xray generation
1
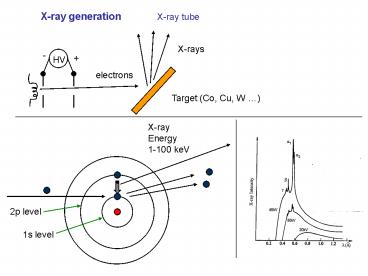
X-ray generation
X-ray tube
X-rays
-
HV
electrons
Target (Co, Cu, W )
X-ray Energy 1-100 keV
2p level
1s level
2
Synchrotron radiation
electrons
- Advantages
- High luminosity
- Arbitrary wavelength
- 3) Polarized x-ray if needed
3
Powder X-ray diffraction
detector
2J
J
X-ray
source
sample
Individual crystals are randomly oriented
4
Examples of powder diffraction data
Orthorhombic crystal
For crystals with high Symmetry many x-ray
diffraction peaks coincide in x-ray diffraction
pattern. For example for KBr (200) (020) (002)
coincide.
Fe2S04
Neutron diffraction
5
Apparatus for the single crystal x-ray
diffraction Four axis diffractometer
6
Neutron diffraction
Neutrons interact with nuclei of atoms (capture
and re-emission)
Neutron has a spin and may interact with other
unpaired spins (electron spin of atom) Production
nuclear reactors, spoliation sources.
Thermal neutrons
7
Summary of statistical physics
or
Quantum state of a single particle
Quantum state of the system of particles
Energy level of a particle and of a system
H
H
H
Degeneracy (multiplicity) number of different
quantum states of the system with the same energy
Entropy
definition
8
Combined multiplicity of two non interacting
systems?
We need to find all possible arrangements of spins
9
1) Fundamental assumption of the statistical
mechanics The closed system is equally likely
to be found in any of the quantum state
accessible to it
A closed system is isolated from environment and
has constant energy, constant number of particles
and constant external parameters.
Example spin system in zero magnetic field
The system is likely to be found in one of this
states
Any of these states has equal probability to
occur.
10
The second law of the thermodynamics The entropy
of the closed system takes maximum value allowed.
The combined system is closed
System 1
System 2
Energy exchange
Example two spin systems in magnetic field
Energy exchange