Using enzymes in facial treatments - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 33
Title: Using enzymes in facial treatments
1
Using enzymes in facial treatments
- Michael Q. Pugliese
2
Topics we will cover in this portion
- Enzymes in the treatment of acne, rosacea,
enviornmentally damaged, and aging skin. - The use of enzymes and oxygen together in the
treatment of acne and rosacea. - The use of enzymes and chemical peels for
treatment of pigmentation dissorders.
3
Enzymes and Acne
- First lets take a look at acne as a condition.
4
What is Acne?
- Acne is the term used for a plugged pore, usually
manifested in the form of a blackhead (open
comedones), or whitehead (closed comedones). - It is primarily an abnormality of the sebaceous
follicle.
5
What causes acne?
- There are five main factors that play a part in
the formation of Acne - 1.Hormones
- 2.Excess sebum
- 3.Follicle fallout
- 4.Bacteria
- 5.Inflammation
6
Anatomy of the an Acne Lesion
Impacted follicle
Normal Skin
Infundibulum
- Comedo
7
Open comedones (blackheads)
Open comedo
8
Closed Comedones
Histological cross section of a closed comedo.
9
How do we classify Acne?
- Dermatologists generally classify acne into four
grades - Grade I Blackheads and milia
- Grade II Papules and pustules
- Grade III Nodules
- Grade IV Cysts
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
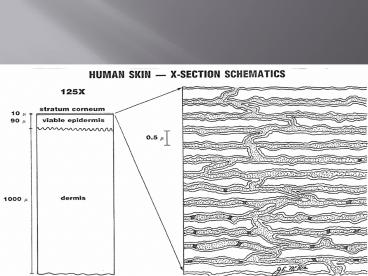
So how can we use enzymes to treat acne?
- Enzymes can exofliate the top layers of the
straum corenum to remove devitalized tissue. - This can help remove the keratin plug or black
head. - Helps to soften the cells around the comedo
aiding in the penetration of other theraputic
agents. - Other actives can be added to the enzyme
combination for additional benefits.
15
Anatomy of the an Acne Lesion
Impacted follicle
Normal Skin
Infundibulum
- Comedo
16
Addition of Oxygen Rx in treating acne
- Using an enzyme and oxygen together can be a
potent combination in the treatment of acne. - Newly exfoliated skin will allow for deeper
penetration of actives particularly oxygen. - This combo provides a strong germacidal action to
aid in killing bacteria as well as
vasoconstrictiog action to reduce the visible
appearance of redness often associated with acne.
17
Enzymes and Rosacea
- Although the condition of rosacea is not fully
understood, certain treatment combinations can
help to provide relief for often socially
debilitating symptoms. - First lets a look at what we know about the
condition of rosacea.
18
What is Rosacea?
- Rosacea is a chronic (long-term) disease that
affects the skin and sometimes the eyes. Rosacea
usually affects the face. - The disorder is characterized by
- 1. Diffused Redness
- 2. Pimples and pustules
- 3. In advanced stages, thickened skin.
19
Who Gets Rosacea?
Approximately 14 million people have
Rosacea. Women are more often afflicted than
men. Peak age of onset is between 30-60. More
cases after menopause.
20
Classification of Rosacea
- The condition of Rosacea can differ
significantly from person to person, but
generally is divided into four Subtypes based on
the severity of the symptoms. - Subtype 1 Facial Redness (Erythematotelangiectati
c Rosacea) - Subtype 2 Bumps and Pimples (Papulopustlar
Rosacea)
21
Classification of Rosacea (cont.)
- Subtype 3 Enlargement of the Nose (Phymatous
Rosacea) - Subtype 4 Eye Irritation (Ocular Rosacea)
- (National Rosacea Society)
22
Clinical Picture
The Many Faces of Rosacea
Erythema
Mild Papules
23
Telangiectasia in natural light.
Augmentation of red areas.
24
The Many Faces of Rosacea
Severe Erythema
Pustules and Papules
25
The Many Faces of Rosacea
Marked hypertrophic scarring
26
Very severe rhinophyma
Note involvement in areas of sebaceous gland
activity.
27
So what causes Rosacea?
- Even though the pathology of Rosacea is not
fully understood, many theories and connecting
factors are shedding light on the subject.
28
The cause of rosacea is unknown. There are
several theories There may be genetic
factors. It may be environmental. There may be
an allergic component. There may be a vascular
etiology. There are inflammatory factors.
(bacteria, fungus, mites)
29
Environmental Triggers
- Non-specific stimuli such as ultraviolet
radiation, heat, cold, chemical irritation,
strong emotions, alcoholic beverages, hot drinks,
and spicy foods can trigger flares. Tea and
coffee are not precipitants, but heat is.
30
What on Earth is that?
Living within a hair follicle
Crawling on skin surface
Front view with eight legs
31
So How do we use Enzymes to treat Rosacea?
- Well we treat it much the same way we treat acne.
Again Cocoa enzyme is a good choice. - Because Rosacea is an inflamatory condition,
enzymes are a much better choice than peels to
exfoliate. - The use of Oxygen Rx will also help to kill
bacteria associated with rosacea, as well as
constrict blood vessels while reducing the
visible signs of redness.
32
Enzymes and Aging Skin
- Removes dead skin cells.
- Prepares skin for subsequent treatment.
- Helps to smooth fine facial lines.
- Stimulates both dermis and epidermis with
associated ingredients.
33
Enzymes and Chemical Peels in Disorders of
Pigmentation
- Hyperpigmentation is excessive melanin.
- Melanin is reduced by 1.removal of stratum ,
- 2. stopping melanin production, 3. preventing
- Melanosome s from entering keratinocytes. 4.
killing the melancyte.