Convective Clouds - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Convective Clouds
Description:
Convective Clouds – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:42
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Convective Clouds
1
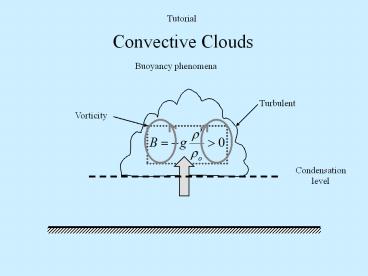
Tutorial
Convective Clouds
Buoyancy phenomena
Condensationlevel
2
Cumulus
Fair weather type
3
Cumulus congestus
4
Cumulus congestus
5
Cumulonimbus
6
Cumulonimbus
7
Mesoscale Convective System
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
(No Transcript)
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
(No Transcript)
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
1458GMT 13 May 2004
45
Mesoscale Convective Systems Robert
Houze Department of Atmospheric
Sciences University of Washington
Nebraska
Kansas
Oklahoma
Seminar, Georgia Tech, Atlanta, 19 November 2004
46
Figure CONVSF
Precipitation in a Mesoscale Convective System
Houze 1997
Houze 1997
47
Heating Cooling Processes in an MCS
Houze 1982
48
Idealized Heating Profiles of MCSs
Non-dimensional Heating
Houze 1982
49
Circulation Pattern of an MCS, ca 1989
Mesoscale circulation features identified, but
suggests air enters updraft from thin surface
layer
Houze et al. 1989
50
Parcel Model of Convection
51
Layer lifting
52
Layer Model of Convection
Moncrieff 92
53
TOGA COARE Airborne Doppler Observations of MCSs
25 convective region flights Show deep layer of
inflow to updrafts
Kingsmill Houze 1999
54
Bryan and Fritsch 2000Analysis and simulation of
midlatitude continental convection
Slab or Layer Overturning
55
Mechem, Houze, Chen 2000Simulation of tropical
oceanic convection
56
Pandya Durran 1996
Mean heating in convective line
Horizontal wind
57
Simulation of an MCS over the tropical ocean,
near Kwajalein Courtesy Professor Rob Fovell
Gentle, persistent lifting ahead of line
Lower troposphere above boundary layer cooler,
more moist, and less stable
58
Discrete Propagation
59
Loop showing tropical discrete propagation in an
MCS over Oklahoma
Courtesy Professor Rob Fovell
60
Loop showing tropical discrete propagation in an
MCS over the Bay of Bengal
61
Midlevel Inflow
62
Heating Cooling Processes in an MCS
Houze 1982
63
Figure CONVSF
Midlevel inflow can come from any direction
Houze 1997
rear inflow
Houze 1997
64
TOGA COARE Airborne Doppler Observations of MCSs
25 Stratiform region flights
Kingsmill Houze 1999
65
Heating, PV generation, upscale feedbacks
66
Sizes of MCSs observed in TOGA COARE
Chen et al. 1996
67
Divergence Profiles of MCSs over West Pacific
Courtesy Brian Mapes
68
PV Generation by an MCS
Fritsch et al. 1994(based on Raymond Jiang
1990)
69
Vortex Spinup by an MCS
Chen Frank 1993
70
Development of a Tropical Cyclone from an MCS
Bister and Emanuel 1997
71
Idealized Heating Profiles of MCSs
Non-dimensional Heating
Houze 1982
72
Interaction of MCSs with Synoptic-scale Easterly
Wave
From AMMA Science Plan Thorncroft et al. 2004
73
MCSs in tropical cyclone genesis
Ritchie et al. 2003
74
What about momentum feedbacks?
75
Buoyancy Produced Pressure Minimum in an MCS
LeMone 1983
76
Perturbation pressure field in a simulated MCS
Yang Houze 1996
77
Momentum changes produced by different parts of
simulated MCS
Yang Houze 1996
78
Stratiform region momentum transport in TOGA
COARE MCS of 11 February 1993 As seen by ship
radar
reflectivity
stratiformecho
SW
NE
Doppler velocity
midlevel inflow
Downward momentumtransport
Houze et al. 2000
79
Stratiform region momentum transport in TOGA
COARE MCS of 15 December 1992 As seen by ship
radar
0.5 km
Houze et al. 2000
80
TOGA COARE Ship and aircraft radar data relative
to Kelvin-Rossby wave structure
Low-level flow
strong westerly region
westerlyonset region
Houze et al. 2000
81
Mesoscale model simulation of MCS in westerly
onset regime Perturbation momentum structure
Mechem et al. 2004
82
Mesoscale model simulation of MCS in strong
westerly regime Perturbation momentum structure
Mechem et al. 2004
83
Flux Convergence
Strong Westerly Case
Momentum fluxes and flux convergences for
simulated cases
feedback
Westerly Onset Case
- feedback
Mechem et al. 2004
84
Global satellite observations Global variability
of MCS structure
85
TRMM Precipitation Radar Schumacher Houze 2003
86
Large-scale response to precipitation heating
Hartmann et al. 1984Schumacher et al. 2004
400 mb heating
200 mb stream function
4 month El Nino season 1998
Most realistic when horizontal distribution of
vertical profile of heating is correct
Most realistic when horizontal distribution of
vertical profile of heating is correct
87
Zonal cross section 8.5 N 8.5 S Vertical
motion (hPa/h) Zonal wind (m/s) Schumacher et
al. 2004
Stratiform rain fraction varies according to TRMM
obs.
Stratiform rain fraction assumed 40 everywhere
88
The variation of stratiform and convective
structure of MCSs is most pronounced between
land ocean
89
TRMM view of Africa vis a vis the Atlantic AMMA
Science Plan, Thorncroft 2004
Rain
Stratiform Rain Fraction
MCSs with large 85GHz ice scattering
Lightning
90
India Another example of continental MCS
91
(No Transcript)
92
The End
93
(No Transcript)
94
Layer lifting