Doppler Ultrasound - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 40
Title:
Doppler Ultrasound
Description:
fluid layers over one another. central portion of fluid moves at ... Distensible. Expands & contracts with. pressure changes. Changes over cardiac cycle ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:5333
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Doppler Ultrasound
1
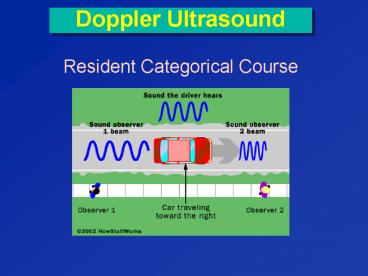
Doppler Ultrasound
- Resident Categorical Course
2
Laminar Flow
- also called parabolic flow
- fluid layers slide over one another
- central portion of fluid moves at maximum speed
- flow near vessel wall hardly moves at all
- friction with wall
3
Turbulent Flow
- random chaotic
- individual particles flow in all directions
- net flow is forward
- Often occurs beyond obstructionsuch as plaque on
vessel wall
4
Flow, Pressure Resistance
- Quantity of flow is function of
- Pressure
- Resistance
- Pressure
- Heart provides pulsating pressure
5
Flow and Pressure
6
Resistance to Flow
- more resistance lower flow rate
- resistance affected by
- fluids viscosity
- vessel length
- vessel diameter
7
Resistance to Flow
Less Viscosity More Flow
More Viscosity Less Flow
8
Resistance to Flow
Longer Vessel Less Flow
Shorter Vessel More Flow
9
Resistance to Flow
Larger Diameter More Flow
Smaller Diameter Less Flow
10
Flow Variations
- Large fluctuation in pressure flow in arteries
with pulse - Less fluctuation in pressure flow in veins
- pulse variations dampened by arterial system
11
Normal Vessel
- Distensible
- Expands contracts with
- pressure changes
- Changes over cardiac cycle
- Vessel expands during systole
- Vessel contracts during diastole
12
Flow Rate Measurements
- Volume flow rate
- Volume of liquid passing a point per unit time
- Example
- 100 ml / second
13
Flow Rate Measurements
- Linear flow rate
- Distance liquid moves past a point per unit time
- Example
- 10 cm / second
14
Flow Rate Measurements
- Volume Flow Rate Linear flow rate X Cross
Sectional Area
15
Flow Rate Measurements
- Volume Flow Rate Linear flow rate X
Cross-sectional Area
High Velocity Small Cross-section
Low Velocity Large Cross-section
Same Volume Flow Rate
16
Volume Flow Rates
- constant volume flow rate in all parts of closed
system
Any change in flow rate would mean youre gaining
or losing fluid.
17
Stenosis
- narrowing in a vessel
- fluid must speed up in stenosis to maintain
constant flow volume - no net gain or loss of flow
- turbulent flow common downstream of stenosis
18
Stenosis
- If narrowing is short in length
- Little increase in flow resistance
- Little effect on volume flow rate
- If narrowing is long
- Resistance to flow increased
- Volume flow rate decreased
19
Doppler Shift
- difference between received transmitted
frequency - caused by relative motion between sound source
receiver - Frequency shift indicative of reflector speed
OUT
IN
20
Doppler Angle
- angle between sound travel flow
- 0 degrees
- flow in direction of sound travel
- 90 degrees
- flow perpendicular to sound travel
21
Doppler Angle
- Angle between direction of sound and direction of
fluid flow
q
22
Doppler Sensing
- Flow vector can be separated into two vectors
- Only flow parallel to sound sensed by scanner!!!
- Sensed flow always lt actual flow
Flow parallel to sound
Flow perpendicular to sound
23
Doppler Sensing
- cos(q) SF / AF
Actual flow (AF)
q
Sensed flow (SF)
q
24
Doppler Equation
2 X fo X v X cosq f D fe
- fo -------------------------
c
q
v
- fD Doppler Shift in MHz
- fe echo of reflected frequency (MHz)
- fo operating frequency (MHz)
- v reflector speed (m/s)
- q angle between flow sound propagation
- c speed of sound in soft tissue (m/s)
25
Relationships
2 X fo X v X cosq f D fe
- fo -------------------------
c
- Positive Doppler shift
- reflector moving toward transducer
- echoed frequency gt operating frequency
- Negative Doppler shift
- reflector moving away from transducer
- echoed frequency lt operating frequency
q
q
26
Relationships
2 X fo X v X cosq f D fe
- fo -------------------------
c
q
- Doppler angle affects measured Doppler shift
- Larger angle
- Smaller cosine
- Small Doppler shift
27
Simplified (?) Equation
2 X fo X v X cosq f D fe
- fo -------------------------
c
77 X fD (kHz) v (cm/s)
-------------------------- fo
(MHz) X cosq
Simplified
- Solve for reflector velocity
- Insert speed of sound for soft tissue
- Stick in some units
28
Doppler Relationships
Constant
77 X fD (kHz) v (cm/s)
-------------------------- fo
(MHz) X cos?
?
- higher reflector speed results in greater Doppler
shift - higher operating frequency results in greater
Doppler shift - larger Doppler angle results in lower Doppler
shift
29
Continuous Wave Doppler
- Audio presentation
- 2 transducers used
- one continuously transmits
- one continuously receives
30
Continuous Wave DopplerReceiver Function
- receives reflected sound waves
- Subtract signals
- detects frequency shift
- typical shift 1/1000 th of source frequency
- usually in audible sound range
- Amplify subtracted signal
- Play directly on speaker
31
Pulse Wave vs. Continuous Wave Doppler
32
Doppler Pulses
- Different Imaging Doppler pulses
- short pulses required for imaging
- Accurate echo timing
- minimizes spatial pulse length
- optimizes axial resolution
- longer pulses required for Doppler analysis
- reduces bandwidth
- provide purer transmitted frequency
- important for accurate measurement of frequency
differences needed to calculate speed
33
Color-Flow Display Features
- Imaged electronically scanned twice
- imaging scan processes echo intensity
- Doppler scan calculates Doppler shifts
- Reduced frame rates
- only 1 pulse required for imaging
- additional pulses required when multiple focuses
used - several pulses may be required along a scan line
to determine Doppler shift
34
Duplex Doppler Gates
- operator defines active Doppler region (gate)
- only sound in gate analyzed
35
Spectral Display
- Displays real-time range of frequencies received
- amplitude of each frequency indicated by
brightness - display indicates range of frequencies received
- corresponds to range of speeds of blood cells
- indicative of type of flow
- laminar, turbulent
36
Absolute Speed Measurement
- Absolute speed measurements must include Doppler
angle - angle between flow sound propagation
- Indicated by operator
- Accuracy affects flow speed accuracy
37
Relative Speed Measurement
- relative measurements can be useful
- Doppler angle not required
- indications of spectral broadening do not require
absolute measurements - ratio of peak-systolic to end-diastolic relative
flows independent of angle
38
Color Doppler
- User defines window superimposed on gray scale
image - For each location in window scanner determines
- flow direction
- mean value
- Variance
- window size affects frame rate
- larger window slower scanning
- more Doppler pulses required
39
Spectral vs. Color-Flow
- spectral Display shows detailed frequency data
for single location - Color Dopplers color represents complete
spectrum at each location in window
40
Power Doppler
- AKA
- Energy Doppler
- Amplitude Doppler
- Doppler angiography
- Magnitude of color flow output displayed rather
than Doppler frequency signal - flow direction or different velocities not
displayed
"Color Power Angio" of the Circle of Willis