Chechnya - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Chechnya
Description:
... from groups such as Human Rights Watch over killings and kidnapping incidents ... This step requires a certain stability so that foreign workers are not kidnapped ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:255
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chechnya
1
Chechnya
2
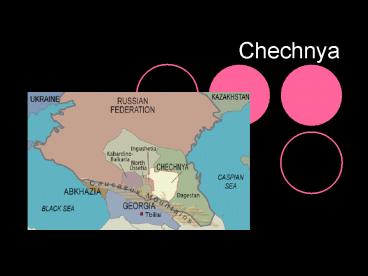
Origins/Background
- In the 19th century The region of the North
Caucasus was incorporated into the Russian
empire following border conflicts with the
existing Ottoman Empire. - Numerous Islamic peoples, the Ingush, Dagestani
and the Chechen were settled in the region. - Resistance to foreign authority and russification
was present from the beginning. - Following the Bolshevik revolution
Chechnya-Ingushetia gained the status of an
autonomous republic (ASSR). - During World War II like most western soviet
ethnic groups about 400,000 Chechens were
deported to Siberia by Stalin, under the
accusation of being Nazi collaborators. - In 1957 under Khrushchev these people were
allowed to return to their homeland. - The deportation remains the central grievance
for Chechens and looms heavy in their collective
memory. Ironically, it was during the hard years
they spent away from their land that a
distinctive Chechen identity appears to have
taken form. - http//worldconflictstoday.com/index.php?page_id1
60menu_id230
3
First Chechen War
- In 1994 Russian troops attacked the Chechen
capital city of Grozny and sought to displace the
pro-independence government. The ranks of Chechen
pro-independence fighters quickly swelled and the
war dragged on for 2 more years, ending with
recapture of Grozny by the Chechen rebels in
1996. Dudayev was killed and was succeeded by
Aslan Maskhadov the Chief commander of the
Chechen army. - The dismaying recapture of Grozny as well as the
overall unpopularity of the war brought the
Russians around to the peace table. The
devastation of the region and mounting civilian
casualties were enough for the Chechens. - The officially accepted death toll was around
- 2,500 Chechen fighters, 6,000 Russian troops, and
50,000 civilians - http//worldconflictstoday.com/index.php?page_id1
61menu_id230
4
Independence
- Following the collapse of the Soviet Union and
the withdrawal of the 15 republics Chechen
independence sentiments were reinvigorated. - In 1991 The National Congress of the Chechen
People was formed a - political party led by
Dzhokhar Dudayev. The party, through the use of
militants, dissolved the old governing body of
the Chechn-Ingush ASSR and declared independence
from the Russian Federation. Elections were
held and Dudayev became president. Ingushetia
voted to remain part of the Russian federation - Yeltsin did not recognize the illegitimate
government. However between 1991-94 some
attempts were made to strike a deal to keep
Chechnya a relatively autonomous region within
the confines of the Russian federation.
Communication eventually broke down and Russia
began to support coup detat attempts on
Dudayevs government. - Towards 1994 Dudayevs policies had transformed
Chechnya into a mafia haven and crime and
lawlessness were on the rise. Added to that there
was strong opposition against him within the
provisional council.
Dudayev
5
Lead up to renewed hostilities
- Following the cease-fire Chechnyan autonomy was
recognized and Maskhadov was elected president of
Chechnya. - The man however could not control the numerous
militant groups that took root in the region.
Added to that the governing judicial body was
weakened due to the rise of Islamic Sharia law.
Crime and lawlessness continued to be a problem.
- In August 1999, Shamil Baseyev a militant
commander during the first Chechen war led
several hundred soldiers over the Chechen border
in to the neighbouring Russian republic of
Dagestan. Russian troops drove the invaders back
and began bombing southern Chechnya. Vladimir
Putin annulled the 1996 cease-fire agreement and
the Second Chechen war began.
6
Second Chechen War
- Began by the Russians in retaliation in response
to the Islamic International Peacekeeping
Brigades invasion of Dagestan in 1999, and the
bombing of various places in Russia blamed on the
Chechens (it is never proved the bombings were
the work of the Chechens) - Starting with an air campaign and followed by a
land invasion, Russia, under Putin, attacks
Chechnya - Massive amounts of refugees flee to neighboring
countries, who then appeal to the UN for help - Aslan Maskhadov is elected leader of the Chechen
government - In return, Putin declares Aslan Maskhadov and his
government illegitimate - In an attempt to make peace, Maskhadov offers to
get rid of the warlords responsible for the
invasion of Dagestan but this is rejected by
Russia - Maskhadov declares a holy war against the
Russians who begin the siege of Grozny (capital
of Chechnya) - Russia gains control of Grozny in February 2000,
but most of Grozny has been destroyed and over
200,000 people have fled - Direct rule is established by Putin after Aslan
Maskhadov is assassinated in May 2000 and Akhmad
Kadyrov is elected head of the new Chechen
government in a fixed election
7
After the Second Chechen War
- In March 2003 a new constitution is put in place,
which grants Chechnya some independence in return
for Chechnyas surrender of claims for complete
independence - Suicide bombings ensue
- In 2005 Ramzan Kadyrov becomes caretaker prime
minister, later appointed president in 2007 who
is criticized for being head of a private militia
group (Kadyrovtsy) which has garnered warnings
from groups such as Human Rights Watch over
killings and kidnapping incidents - High levels of unemployment (an estimate 70)
still reign in Chechnya despite the 2 billion
put in by the Russian government to rebuild the
economy (an estimated 350 million has actually
gone where its supposed to) - Guerilla warfare still continues and despite a
recent 2007 poll in which 70 of Russians want
talks with the separatists instead of a military
response
8
Stalingrad
Grozny
9
Shamil Basayev
10
Proposed Solution - Military
- Secure the region by increasing Russian troop
presence - -Extremely high levels of violence, corruption
in both the Russian and Chechen government and
crime must be reduced as a foundation of
improvement - -Increasing international pressure/economic
incentive for Russia to minimize human rights
violations - -Continue operations to root out terrorist
militants political negotiations are dead-ends
with radical extremists
11
Proposed Solution Political
- Keep Chechnya in the Russian Federation for the
short term with long-term possibility of
separation Russia will not tolerate a radical
state as a neighbour. - An unstable Chechnya caused by Russian
withdrawal ruled by militants is unfavorable
because as in 1996-1999, a state of lawlessness
or radical Taliban like Islamic power will
prevail - Once Chechnya is stable in the future, allow
separation to free up Russian resources, and the
Russians should be given a portion of Chechnyas
economic resources as a incentive to let go of
Chechnya - Once security is achieved, gradually move towards
a Chechen elected leader free of Moscow
interference - The new Chechen leadership enters a regional
security alliance with Russia to secure
Chechnyas strategic importance
12
Proposed Solution Economic
- Increasing oil output to create enough capital to
spur industrialization projects - Appeal to foreign and Russian investments as a
source of reducing the unemployment rate - This step requires a certain stability so that
foreign workers are not kidnapped - Request humanitarian aid for the region







![[PDF] Putin's Wars: From Chechnya to Ukraine PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10135114.th0.jpg?_=20240922074)






















