M E T H O D S - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
M E T H O D S
Description:
Among the composite hydrogels, those bearing ionic groups occupy a special place, ... from polyacrylonitrile by the aminolysis-hydrolysis reaction, was used as ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:57
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: M E T H O D S
1
COVALENT CROSSLINKED COMPOSITE POLYELECTROLYTE
HYDROGEL
ECATERINA STELA DRAGAN, MARIA MARINELA PERJU
Petru Poni Institute of Macromolecular
Chemistry, Iasi, Romania, email sdragan_at_icmpp.ro
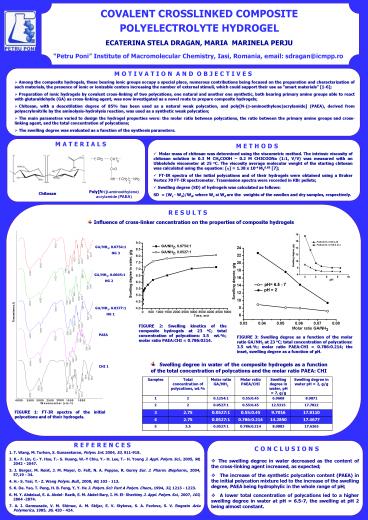
M O T I V A T I O N A N D O B J E C T I V E S
- Among the composite hydrogels, those bearing
ionic groups occupy a special place, numerous
contributions being focused on the preparation
and characterization of such materials, the
presence of ionic or ionizable centers increasing
the number of external stimuli, which could
support their use as smart materials 1-6 - Preparation of ionic hydrogels by covalent
cross-linking of two polycations, one natural and
another one synthetic, both bearing primary amine
groups able to react with glutaraldehyde (GA) as
cross-linking agent, was now investigated as a
novel route to prepare composite hydrogels - Chitosan, with a deacetilation degree of 85 has
been used as a natural weak polycation, and
polyN-(?-aminoethylene)acrylamide (PAEA),
derived from polyacrylonitrile by the
aminolysis-hydrolysis reaction, was used as a
synthetic weak polycation - The main parametres varied to design the
hydrogel properties were the molar ratio between
polycations, the ratio between the primary amine
groups and cross-linking agent, and the total
concentration of polycations - The swelling degree was evaluated as a function
of the synthesis parameters.
M A T E R I A L S
M E T H O D S
- Molar mass of chitosan was determined using the
viscometric method. The intrinsic viscosity of
chitosan solution in 0.3 M CH3COOH 0.2 M
CH3COONa (11, V/V) was measured with an
Ubbelohde viscometer at 25 oC. The viscosity
average molecular weight of the starting chitosan
was calculated using the equation ? 1.38 x
10-4 MV0.85 7 - FT-IR spectra of the initial polycations and of
their hydrogels were obtained using a Bruker
Vertex 70 FT-IR spectrometer. Trasmission spectra
were recorded in KBr pellets - Swelling degree (SD) of hydrogels was calculated
as follows - SD (Ws - Wd)/Wd, where Ws si Wd are the
weights of the swollen and dry samples,
respectively.
PolyN-(?-aminoethylene) acrylamide (PAEA)
Chitosan
R E S U L T S
- Influence of cross-linker concentration on the
properties of composite hydrogels
GA/NH2, 0.07541 HG 3
GA/NH2, 0.06051 HG 2
GA/NH2, 0.03771 HG 1
FIGURE 2 Swelling kinetics of the composite
hydrogels at 23 oC total concentration of
polycations 3.5 wt. molar ratio PAEACHI
0.7860214.
PAEA
FIGURE 3 Swelling degree as a function of the
molar ratio GA/NH2 at 23 oC total concentration
of polycations 3.5 wt. molar ratio PAEACHI
0.7860.214 the inset, swelling degree as a
function of pH.
- Swelling degree in water of the composite
hydrogels as a function of the total
concentration of polycations and the molar ratio
PAEA CHI
CHI 1
FIGURE 1 FT-IR spectra of the initial
polycations and of their hydrogels.
R E F E R E N C E S
C O N C L U S I O N S
1. T. Wang, M. Turhan, S. Gunasekaran, Polym.
Int. 2004, 53, 911-918. 2. K.- F. Lin, C.- Y.
Hsu, T.- S. Huang, W.-Y Chiu, Y.- H. Lee, T.- H.
Young J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2005, 98, 2042 -
2047. 3. J. Berger, M. Reist, J. M. Mayer, O.
Felt, N. A. Peppas, R. Gurny Eur. J. Pharm.
Biopharm., 2004, 57,19 - 34. 4. H.- S. Tsai, Y.-
Z. Wang Polym. Bull., 2008, 60, 103 - 113. 5. K.
De. Yao, T. Peng, H. B. Feng, Y, Y. He J. Polym.
Sci Part A Polym. Chem., 1994, 32, 1213 -
1223. 6. M. Y. Abdelaal, E. A. Abdel- Razik, E.
M. Abdel-Bary, I. M. El- Sherbiny J. Appl. Polym.
Sci., 2007, 103, 2864 -2874. 7. A. I. Gamzazade,
V. M. Shimac, A. M. Skljar, E. V. Stykova, S. A.
Pavlova, S. V. Rogozin Acta Polymerica, 1985, 36,
420 - 424.
- The swelling degree in water decreased as the
content of the cross-linking agent increased, as
expected - The increase of the synthetic polycation
content (PAEA) in the initial polycation mixture
led to the increase of the swelling degree, PAEA
being hydrophylic in the whole range of pH - A lower total concentration of polycations led
to a higher swelling degree in water at pH
6.5-7, the swelling at pH 2 being almost constant.