Oxidation-Reduction Reactions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Description:
Oxidation half-reaction (lose e-) Reduction half-reaction (gain e ... hydrogen is 1 except when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds (hydride) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:60
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
1
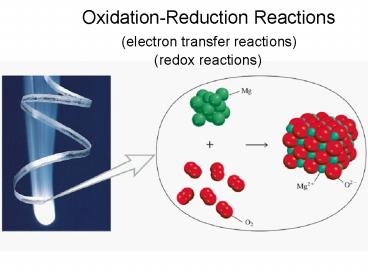
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
(electron transfer reactions)
(redox reactions)
2
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
(electron transfer reactions)
(redox reactions)
Oxidation half-reaction (lose e-)
Reduction half-reaction (gain e-)
3
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
(electron transfer reactions)
Oxidation half-reaction (lose e-)
Reduction half-reaction (gain e-)
L E O G E R
4
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
(electron transfer reactions)
Oxidation half-reaction (lose e-)
Reduction half-reaction (gain e-)
?
?
?
?
Reducing agent causes oxidation Oxidizing agent
causes reduction
5
Oxidation number
The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or
an ionic compound) if electrons were completely
transferred.
- Free elements (uncombined state) have an
oxidation number of zero.
Na, Be, K, Pb, H2, O2, P4 0
- In monatomic ions, the oxidation number is equal
to the charge on the ion.
Li 1 Fe3 3 O2- -2
- The oxidation number of oxygen is usually 2. In
H2O2 and O22- it is 1. Dont forget the free
element rule for O2.
6
- The oxidation number of hydrogen is 1 except
when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds
(hydride). In these cases, its oxidation number
is 1.
- Fluorine is always 1. (except elemental F2),
Other halogens have negative numbers when
occurring as halides (eg Cl-). In oxoacids and
oxoanions, they have positive numbers.
6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the
atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to the charge
on the molecule or ion.
7. Oxidation numbers do not have to be integers
(but they usually are in this class). One common
example is the oxidation number of O -1/2 in
superoxide, O2-.
7
Figure 4.10 The oxidation numbers of elements in
their compounds
8
Oxidation Number
0
0
2
-2
- Rules
- Elements zero
- Sum of oxidation numbers charge on molecule
- Sum of oxidation numbers reactants sum of
oxidation numbers products
9
Harder examples
IF7
F -1
?
?
?
7x(-1) ? 0
I 7
K2Cr2O7
NaIO3
O -2
O -2
K 1
Na 1
3x(-2) 1 ? 0
7x(-2) 2x(1) 2x(?) 0
I 5
Cr 6