ProtoLanguage - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
ProtoLanguage
Description:
a3 e = a4 (1/16a, 1/16b, 1/8c, 1/4d, 1/2e) a4 f = a5 (1 ... history of Eurasia was largely. caused by nomadic migration. Asian languages. Eurasian languages ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:84
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: ProtoLanguage
1
2
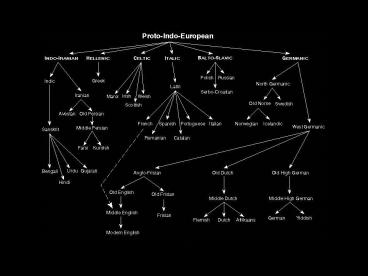
Modern Languages
Language family
Proto-Language
3
Sino-Tibetan
Kadai Group
Protolanguage
Protolanguage
Austronesian
4
Ancestress
Ancestor
Ancester 2
Ancester 3
Ancester 4
Ancester 5
5
Modern Languages
Language family
Proto-Language
6
Proto-Language
7
Language family
Language family
Proto-Language
8
Modern Languages
Modern Languages
Modern Languages
Proto-Language
9
Descendant?
Ancestor?
10
Ancestor?
Descendant?
11
Interaction and Interrelation
12
ancestor
spouse
descendant
Characteristics of descendant
a b a1 (1/2a, 1/2b)
a1 c a2 (1/4a, 1/4b, 1/2c)
a2 d a3 (1/8a, 1/8b, 1/4c, 1/2d)
a3 e a4 (1/16a, 1/16b, 1/8c, 1/4d, 1/2e)
a4 f a5 (1/32a, 1/32b, 1/16c, 1/8d, 1/4e,
1/2f)
an g a?
How many traits have been kept after so many
generations?
13
The Replacement Assumption (or the Out of
Africa Model)
This assumption proposes a single origin of Human
beings
14
The Replacement Assumption (or the Out of
Africa Model)
Homo sapiens
All the Homo erectus in Europe and Asia were
replaced by the Homo sapiens from Africa
15
The Continuity Assumption (or the Regional
Model)
This assumption insists that evolution occurred
in multiple regions
16
Historical sound reconstruction method
labial is deemed as the common property
Labiodental fricative /f/
labial /p/
Bilabial voiced non-aspirated plosive /b/
Bilabial voiceless aspirated plosive /ph/
17
Interaction and Interrelation
18
Ancient Eurasia nomadic society migration was
common
Ancient Asia slow agricultural interactions
Ancient Chinese dictionaries have many words
about pigs, but very few words about sheep.
Words and legends about sheep or shepherd are
common in European languages.
19
Language development in early history of Eurasia
was largely caused by nomadic migration
Eurasian languages
Asian languages
Language changes in Asia were mainly caused by
multilateral and slow linguistic interactions.