With Applicator - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 53
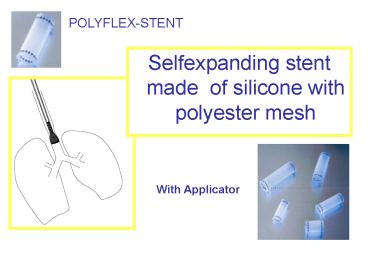
Title:
With Applicator
Description:
compression or stricture due to tumours (trachea and main bronchus) ... of the particular material characteristics of the netting material (squashing) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: With Applicator
1
With Applicator
- Selfexpanding stent made of silicone with
polyester mesh
2
Indications
- stenosis of the central airways (trachea and main
bronchus) - compression or stricture due to tumours (trachea
and main bronchus) - esophagotracheal/-bronchial fistulas
3
Stenosis
4
new POLYFLEX-Stent
5
Contraindications
- none in the case of vital indication
- obstruction to passage at laryngeal level
- bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve paresis
6
Relative Contraindications
- tracheomalacia
- benign operable stenosis
7
Applicator System
- Introducer sleeve
- Stent loader/positioner
- blue/white stopper
8
Available Sizes
9
Sizes DUMON-Stent
10
Characteristics
- Silicone coating throughout
- prevents ingrowth of tumour tissue
- closes tracheo-oesophageal and broncho-oesophageal
fistulae
11
Characteristics
- Mesh structure of the outer surface of the
- stent
- increases security against dislocation
12
Characteristics
- Smooth inner surface
- hinders encrustation with secretions
13
Characteristics
- Uniform gentle resilience
- adapts elastically to the anatomy of the airways
- for inner support of the trachea and bronchi
- reduces tissue compression to a minimum
14
Characteristics
- Reduction of cross section when stretched
lengthwise - allows simple change of stent
15
Characteristics
- Thin wall
- suitable for stent-in-stent insertion
16
Characteristics
- Broad range of widths and lengths
- can be coordinated for each indication and
anatomical situation
17
Characteristics
- Radiopaque insertion set
- facilitates precise positioning and monitoring of
use
18
THE IMPROVED POLYFLEX-STENT
- Silicone reinforcement protects the edges
- less stimulation for granulation
19
THE IMPROVED POLYFLEX-STENT
- X-ray marker
- improved visibility during placement and
post-operative follow-up
20
THE IMPROVED POLYFLEX-STENT
- Modified mesh geometry
- optimized radial force
- easier application of the stent
21
Biomechanics tracheobronchial Stents
22
Biomechanics tracheobronchial Stents
23
- Dumont Stent
Noppent Stent
POLYFLEX Stent (first version)
POLYFLEX Stent (new version)
24
- Ultraflex Stent
Gianturco Stent
Wallstent
New Nitinol Stent
25
TYPES OF STENOSIS (1/8)
- exophytic tumor
26
TYPES OF STENOSIS (2/8)
- granulation
27
TYPES OF STENOSIS (3/8)
- floppy membrane
28
TYPES OF STENOSIS (4/8)
- compression
29
TYPES OF STENOSIS (5/8)
- hour glass
30
TYPES OF STENOSIS (6/8)
- scabbard trachea
31
TYPES OF STENOSIS (7/8)
- stricture
32
TYPES OF STENOSIS (8/8)
- web stenosis
33
Patient preparation
- The patient must be adequately anaesthetized with
an appropriate degree of relaxation - The position is the same as for conventional
intubation
34
Selection of Polyflex stent size - Diameter
- The inner diameter of the Polyflex stent should
be about 2 mm bigger than the main bronchus and
about 4 mm bigger in the tracheal area than the
measured diameter of the lumen of the healthy
bronchus or trachea!
35
Selection of Polyflex stent size - Length
- The Polyflex stent must extend beyond the
stenosis at both ends by up to 10 mm. - Please note that the stent is longer when
compressed than when completely stretched! - Do not shorten the Polyflex stent!!
36
Preparation of the stent 1
- Moisten the outer surface of the Polyflex stent
with commercially available aqueous lubricant - Do not use mineral oil-based lubricants, silicone
oils, silicone sprays or other silicone-containing
agents!
37
Preparation of the stent 2
- To insert the stent in the introducer sleeve,
stretch the stent loader by pushing it back - Insert the stent about halfway into the basket
38
Loading the Stent (1)
- Pull the stent with the basket into the
introducer sleeve, guiding in the stent without
pressure
39
Loading the Stent (2)
- Pull the stent in until only about 2 mm of it
projects from the transparent introducer sleeve
40
Loading the Stent (3)
- Use the blue stopper to secure the stent in the
introducer sleeve so that it cannot be inserted
any further
41
Loading the Stent (4)
- Pull the loader off the stent by pulling it
backwards - The stent must be pushed fully into the
introducer sleeve after the loader is removed
42
Loading the Stent (5)
- Remove the loader and reinsert its other end in
the introducer
43
Insertion of stent (1)
- The introducer sleeve holding the Polyflex stent
can be advanced through the rigid bronchoscope
(without distal light source) as far as the
distal end of the stenosis - The Polyflex stent and the distal end of the
positioner can be seen radiographically
44
Insertion of stent (2)
- The transparent introducer sleeve is held at its
upper end where it is reinforced with netting and
is withdrawn over the positioner
45
Insertion of stent (3)
- The positioner must be held in position!
46
Insertion of stent (4)
- Kleinsasser technique
- The Kleinsasser operating laryngoscope is an
alternative to the rigid bronchoscope (continuous
ventilation)
47
Insertion of stent (5)
- This illustration shows the correct position of
the stent - The released stent can be moved proximally if
necessary using an atraumatic grasping forceps
48
BENIGN TRACHEAL STENOSISsplinted with
POLYFLEX-STENT
49
Removal of the Polyflex stent
- The Polyflex stent narrows when under traction.
- Because of this, the stent can be removed with an
atraumatic foreign body forceps by pulling it
back slowly and carefully
50
Questions and Answers 1
- The POLYFLEX-STENT is placed too distally...
- The POLYFLEX-STENT can be withdrawn proximally
under careful traction using an atraumatic
foreign body forceps (universal jaws).
51
Questions and Answers 2
- The POLYFLEX-STENT is placed too proximally ...
- Pushing the POLYFLEX-STENT distally is not
advisable because of the particular material
characteristics of the netting material
(squashing). - Remove it and place it once more.
52
Questions and Answers 3
- Can I shorten the POLYFLEX-STENT?
- NO! Do not shorten the POLYFLEX-STENT.(risk of
mucosal damage by projecting netting fibres).
53
Questions and Answers 4
- Can I use laser while the POLYFLEX-STENT is in
place?
- NO! Protect POLYFLEX-STENT from direct laser
bombardment. - Magnetic resonance imaging and CT are possible