Figure 7.1 The basic MOS differential-pair configuration. - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Figure 7.1 The basic MOS differential-pair configuration.
Description:
Figure 7.7 The linear range of operation of the MOS differential pair can be ... at the gates and with vid applied in a complementary (or balanced) manner. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:65
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Figure 7.1 The basic MOS differential-pair configuration.
1
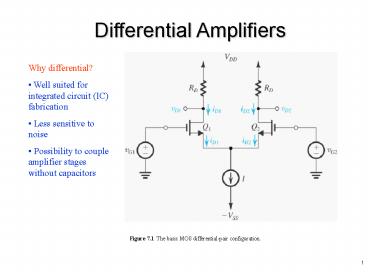
Differential Amplifiers
Why differential? Well suited for integrated
circuit (IC) fabrication Less sensitive to
noise Possibility to couple amplifier stages
without capacitors
Figure 7.1 The basic MOS differential-pair
configuration.
2
Operation with a Common-Mode Input Voltage
Figure 7.2 The MOS differential pair with a
common-mode input voltage vCM.
3
Operation with a Differential Input Voltage
Figure 7.4 The MOS differential pair with a
differential input signal vid applied. With vid
positive vGS1 gt vGS2, iD1 gt iD2, and vD1 lt vD2
thus (vD2 - vD1) will be positive. With vid
negative vGS1 lt vGS2, iD1 lt iD2, and vD1 gt vD2
thus (vD2 - vD1) will be negative.
4
Large-Signal Operation
Figure 7.5 The MOSFET differential pair for the
purpose of deriving the transfer characteristics,
iD1 and iD2 versus vid vG1 vG2.
5
Figure 7.6 Normalized plots of the currents in a
MOSFET differential pair. Note that VOV is the
overdrive voltage at which Q1 and Q2 operate when
conducting drain currents equal to I/2.
6
Figure 7.7 The linear range of operation of the
MOS differential pair can be extended by
operating the transistor at a higher value of VOV.
7
Small-Signal Operation of The MOS Differential
Pair
Differential Gain
Figure 7.8 Small-signal analysis of the MOS
differential amplifier (a) The circuit with a
common-mode voltage applied to set the dc bias
voltage at the gates and with vid applied in a
complementary (or balanced) manner. (b) The
circuit prepared for small-signal analysis.
8
Common-Mode Gain and Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
Figure 7.10 (a) The MOS differential amplifier
with a common-mode input signal vicm. (b)
Equivalent circuit for determining the
common-mode gain (with ro ignored). Each half of
the circuit is known as the common-mode
half-circuit.
9
The BJT Differential Pair
Figure 7.12 The basic BJT differential-pair
configuration.
10
Figure 7.14 Transfer characteristics of the BJT
differential pair of Fig. 7.12 assuming a . 1.