Basic Anatomy of a Crossbow Node - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Basic Anatomy of a Crossbow Node
Description:
128 kB of Flash for program memory. 4 kB of SRAM for data and variables ... Antenna. MMCX connector. LEDs. Now FCC/ARIB certified. TinyOS Platforms Panel: MICAz. 5 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:178
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Basic Anatomy of a Crossbow Node
1
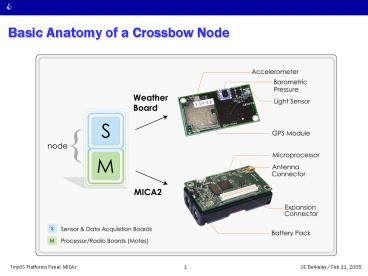
Basic Anatomy of a Crossbow Node
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
MICAz Platform
Now FCC/ARIB certified
- Microprocessor Atmel ATmega128L
- 7.3728 MHz clock
- 128 kB of Flash for program memory
- 4 kB of SRAM for data and variables
- 2 UARTs (Universal Asynchronous Receive and
Transmit) - Serial Port Interface (SPI) bus
- Dedicated hardware I2C bus
- Radio Chipcons CC2420
- External serial flash memory 512 kB
- 51-pin expansion connector
- Eight 10-bit analog I/O
- 21 general purpose digital I/O
- User interface 3 programmable LEDs
- JTAG port
- Powered by two AA batteries
- 1850 mAh capacity
5
Microcontrollers and the ATMega128
- Careful consideration required when comparing
different processor cores on systems performance - Wake up from sleep ?1 ?sec.
- With the ATMega internal oscillator enabled
XMesh does this automatically. - Wake up gt 200 ?sec when using the external
oscillator. - Sleep current of ?10 to 15 ?A
- Battery performance in a Mesh is not limited by
this difference - Operating voltage
- Minimum input voltage specified at 2.7 V
- Most sensors and I/O devices wont operates to
2.5 V - Practical experience shows ATMega128 operates to
2.3 V - Note Chipcon radio typically doesn't operate
below 2.1 V
6
MICAz Roadmap
- 8 kB SRAM
- Further reduction in sleep current
- MICAz Postage Stamp
- July 05 release date
- Significantly reduced cost
- Surface mount (SMT) package
7
Sensor and Data Acquisition Boards
8
Typical Solution
- Select Sensor type based on Application
- Temp/Humidity/Light
- Security
- Industrial .
Xlisten PostgreSQL Database
MICAz Mote network w/ XMesh Routing
Mote-VIEW Client Tools
9
Software Architecture
10
Deployment Overview
Remote Database Use Mote-VIEW to view data
logged at a remote location
Proxy Logging Use serial forwarder to log
readings from a remote gateway in locally.
Local Logging Store data from local gateway to a
local database and view it all on one machine.
Gateway Forwards data from sensor network to
server.
11
Data Visualization with MOTE-VIEW