Pr - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title: Pr
1
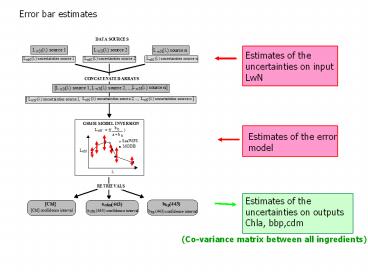
Error bar estimates
2
Derivation of the uncertainties on nLw used as
inputs of the GSM retrieval procedure
- Two sources of uncertainties
- Statistical errors between satellite observations
and in-situ measurements - Statistical errors of the semi-analytical model
3
Derivation of the uncertainties on nLw used as
inputs of the GSM retrieval procedure
- Two sources of uncertainties
- Statistical errors between satellite observations
and in-situ measurements - Statistical errors of the semi-analytical model
The sensor observations nLw (l) are compared to
values extracted from the NOMAD in-situ database
4
Derivation of the uncertainties on nLw used as
inputs of the GSM retrieval procedure
- Two sources of uncertainties
- Statistical errors between satellite observations
and in-situ measurements - Statistical errors of the semi-analytical model
The radiances from the NOMAD database have been
used as input for the GSM model in order to get
Chla, bbp and aCDM. These quantities have been
used to rebuild the values of radiances nLw(l)
and then compared with original radiances
values. The discrepancies have been quantified in
terms of statistical quantities(RMS, bias,
etc).
5
Final uncertainties are computed as the quadratic
sum of the satellite vs in-situ data RMS and of
the GSM model characterisation RMS. The net
result has been divided by two, considering as a
preliminary assumption that the error on
measurements used for characterization counts for
half of the final uncertainties levels.
Error bars used as inputs in GlobColour
6
Weakness and limitation of current approach
- A constant absolute value of the uncertainty is
used instead of a varying one (relative) - The observations are implicitly considered as
unbiased.
Assessment of the quality of the error budget in
GlobColour v1.1
- Computation of chi-2 (should be close to 1 if
error budget is correct). - Computation of residuals (residual is the
difference between observed LwN and modeled nLw
rebuilt with GSM direct model) - rms of residuals
should be comparable with error budget, assuming
no bias (cf. limitation 2). - Computation of covariance matrix of retrieved
parameters (diagonal of the matrix should compare
well with uncertainty estimates derived from
statistical analysis with in situ off-diagonal
terms give an indication of the correlation of
retrieved parameters - the lower the better).
7
Cost function Full covariance matrix of errors
CtotCnoiseCmod Maximum likelihood solution
minimize
- Currently we do not consider the covariance
terms, neither on the model nor on the
measurements, so that the cost function reduces
to
where si,j correspond to the square root of the
diagonal terms of C,tot
8
Background
- Full Nomad-2 is used for matchups with
- SeaWiFs and/or MODIS-Aqua and/or MERIS
- GSM versions (all with red bands)
- with no error on nLw no reliable error budget
- with error on nLw reliable error budget ?
- with error on nLw with a new parameters tuning
(GSM08) - Taking into account the uncertainties on nLw
error model for item 2 and 3
9
With and without uncertainties Impact on the
retrieved quantity
GlobColour/GSM
GSM - no error on nLw
10
With and without uncertainties Impact on the
retrieved quantity
GlobColour/GSM with red bands
GSM - no error on nLw
11
With and without uncertainties Impact on the
retrieved quantity
GlobColour/GSM with red bands
GSM - no error on nLw
12
Analysis of the retrieval quality Chi-2
GlobColour/GSM with red bands
GlobColour/GSM with red bands
13
Analysis of the retrieval quality Residual on the
nLw after inversion
GlobColour/GSM with red bands SeaWiFS
residuals
Orange dots are the a priori uncertainties
(inputs of GSM) no bias
14
Conclusions Input uncertainties on nLw are
consistent with residual However, a bias is
observed for 443 and 490. As similar bias exists
for MERIS and MODIS this points towards a
weakness in the reflectance model
GlobColour/GSM with red bands MERIS residuals
GlobColour/GSM with red bands MODIS residuals
15
Analysis of the retrieval uncertainties What is
the quality of final error bars?
GlobColour/GSM with red bands Chla uncertainty
estimates
Final uncertainties (outputs of GSM)
Actual difference (absolute) between observed and
retrieved
16
Analysis of the retrieval uncertainties What is
the quality of final error bars?
GlobColour/GSM with red bands CDM uncertainty
estimates
Final uncertainties (outputs of GSM)
Actual difference (absolute) between observed and
retrieved
17
Analysis of the retrieval uncertainties What is
the quality of final error bars?
GlobColour/GSM with red bands Bbp uncertainty
estimates
Final uncertainties (outputs of GSM)
Actual difference (absolute) between observed and
retrieved
Hair-splitting plots How to quantify the quality
of the result ?
If the orange dots are reliable standard
deviation there should be, statistically, about
68 of blue points below the corresponding orange
points (/-1s)
18
Analysis of the retrieval uncertainties What is
the quality of final error bars?
Transition from (X,s) couple to reduced variable
X/s If everything went well and there is no
bias, the X/s distribution should follow
a standard normal distribution (centered).
19
Analysis of the retrieval uncertainties What is
the quality of final error bars?
GlobColour/GSM with red bands Normalised error
distribution (Chla, CDM, bbp)
These error bars are available in GlobColour
daily products
Excellent behaviour of Chla AND bbp error
estimates Suspect behaviour for CDM error
estimates
20
Example of products uncertainties - daily
21
Example of products uncertainties