Nebraska - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Nebraska
Description:
Child Care & Development Fund (CCDF) Federal Requirements. Voluntary Early Learning ... Provide adaptive equipment and materials when the child needs support ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:23
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Nebraska
1
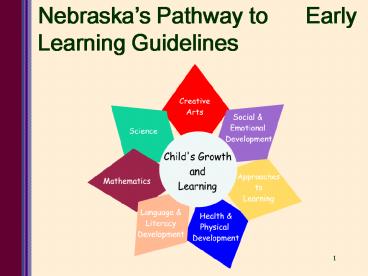
Nebraskas Pathway to Early Learning
Guidelines
2
Child Care Development Fund (CCDF) Federal
Requirements
- Voluntary Early Learning Guidelines
- In early literacy and math
- For ages 3 to 5
- Align with States K-12 standards
- Implement by Fall 2005
3
Nebraska Partnership
- Nebraska Health Human Services
- Nebraska Department of Education
- Nebraska Head Start Association
- Head Start-State Collaboration Office
- Early Childhood Training Center
4
Critical Components of Early Learning
Development
- Safe, supportive environments
- Health nutrition needs met
- Relationships to support positive social and
emotional development
5
Critical Components of Early Learning
Development
- Experiences to support
- -curiosity exploration
- -language, literacy, math plus
- -development across all domains
- Support respect for family and cultural context
6
Early Learning Guidelines Nebraskas Intent
- Resource for planning
- For early childhood caregivers, teachers, parents
and others who work with young children,
including children with disabilities
7
Early Learning Guidelines Nebraskas Intent
- What to expect or look for in the development and
learning of young children - What adults can do to support learning for all
children across domains of development and
learning
8
Early Learning Guidelines Nebraskas Intent
- Include Birth Age 5
- Include Multiple Domains
- Align with Multiple Standards
- Develop comprehensive support system
- Build on current state EC initiatives
9
Birth Age 5
- Important to represent continuum of development
and learning - Broad-based expectations (outcomes)
- Ages 3 to 5 printed January 2005
- Birth to 3 available January 2006
10
Multiple Domains
- Social Emotional Development
- Approaches to Learning
- Health Physical Development
- Language Literacy Development
- Mathematics
- Science
- Creative Arts
11
Elements of each domain
- Introduction Key Elements
- Widely Held Expectations
- Learning in Action Examples for Child and Adult
- The Environment
- Alignments w/Standards
- Strategies to Support Inclusive Environments
12
13
Examples of Strategies to Support Inclusive
Practices
- Divide skills and behaviors into smaller steps
- Provide choices so children have more control
over their environment - Use appropriate verbal, visual, and physical cues
in interactions and activities to meet the
special needs of individual children
14
Examples of Strategies to Support Inclusive
Practices (cont.)
- Use vocabulary and phrases in the childs native
language when introducing new ideas/concepts - Assure that materials in indoor and outdoor
environments are easily accessible (height, size,
location) - Provide physical guidance/support for children
having difficulty with motor tasks
15
Examples of Strategies to Support Inclusive
Practices (cont.)
- Provide good models of communication, including
sign language and other alternative methods - Use special or adaptive devices and/or processes
to increase level of communication and/or
participation - Simplify a complicated task by breaking it into
smaller parts or reducing the number of steps
16
Examples of Strategies to Support Inclusive
Practices (cont.)
- Use shorter but more frequent activities and
routines - Encourage hands-on and sensory experiences such
as touching, holding, exploring, tasting,
smelling, and manipulating - Adapt the environment to promote participation,
engagement, and learning using a variety of
textures
17
Align with Multiple Standards
- Aligns with
- Nebraska State K-12 Standards
- Reading/Writing, Science, Social Studies/History,
Mathematics - Nebraska Rule 11 EC Regulations
- Head Start Outcomes Framework
18
Align with Multiple Standards
- Reflects
- Primary Program Growing and Learning in the
Heartland - Nebraska Rule 51 SPED Regulations
- P-16 Initiative
19
Meeting the DiverseNeeds of All Children
- Individual personality, temperament and learning
style - Experiences and family background, including
language, culture, ethnicity, etc. - Special health considerations
20
Meeting the DiverseNeeds of All Children (cont.)
- Food allergies
- Physical or cognitive disabilities
- Preferences based on child and family interests
21
Strategies to Support Children with
Disabilities
- Provide adaptive equipment and materials when the
child needs support - Provide adult assistance/support as the child
initiates action, then reduce support when the
child shows ability to do some actions
independently - Provide opportunities for interaction with
typically developing peers
22
Strategies to Support Children with Disabilities
(cont.)
- Modify materials and activities so the child can
participate as independently as possible - Utilize peers as models, helpers, and friends to
provide praise and encouragement - Assure that child care homes, centers, and
preschool environments meet the needs of all
children
23
Strategies to Support Children with Disabilities
(cont.)
- Ensure that naturally occurring events, such as
opportunities to use materials both independently
and cooperatively, are purposefully arrange so
the child has learning opportunities - Add new and/or specific activities as needed to
meet individual needs - Provide visual supports (pictures, drawings,
labels, color coding, picture schedules, etc.)
24
Additional Supports
- Print Resources Category Where All
Belong-Celebrating Childrens Diversity and
Special Needs - Early Learning Guidelines Definitions
- Inclusive language/terminology
- Accommodations/modifications
- Adaptations
25
Implementation
- State and local conferences
- Mailing and ongoing distribution beg. Jan.
2005 - Awareness training in regions 2005
- Training of Trainers Fall 2005
- 2- and 6-hour Domain Specific training beg.
Jan. 2006 - Support and resources online and print
26
Implementation Linkages
- Curriculum planning tool for state-funded early
childhood programs - Support document for early childhood outcomes
Results Matter in Nebraska
27
Developing a Comprehensive Support System
- Core Knowledge and Competencies
- Professional Development Support
- Program Practices and Environment
- Parent Involvement and Support
- Public Awareness and Engagement
28
Nebraskas Desired Outcome
- Support learning and development of all young
children - Improve quality of early childhood care and
education in Nebraska
29
For More Information
- Jan Thelen
- jan.thelen_at_nde.ne.gov
- Jeanine Huntoon
- jeanine.huntoon_at_nde.ne.gov



























![[READ DOWNLOAD] Nebraska Pioneer Cookbook PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10075477.th0.jpg?_=202407090310)
![[READ DOWNLOAD] Nebraska Pioneer Cookbook PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10079942.th0.jpg?_=20240717031)
![[READ DOWNLOAD] Nebraska Pioneer Cookbook PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10080147.th0.jpg?_=20240717087)
![[READ DOWNLOAD] Nebraska Pioneer Cookbook PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10082254.th0.jpg?_=20240720044)