Function of the Kidney - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Function of the Kidney
Description:
All 3 laminae contain collagen. Laminae rarae contain laminin molecules to ... Laminae rarae contain heporan sulfate proteolycate which. has a negative charge ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:35
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Function of the Kidney
1
Function of the Kidney
- Physics of Circulation and Respiration
- Maartje Dekker
- December 2004
2
Function of the Kidney
- Outline
- What does it do?
- How does it work?
- Dialysis machines
3
Function of the Kidney Function overview
- What does the kidney do?
- Remove undesirable substances from the blood
plasma - Toxins
- Metabolism wastes
- Excess of ingested water
- Excess of mineral salts
- Regulate the acidity of blood
- 25 of the blood flows through
- the kidneys (1,2 l/min)
- 130 ml/min is concentrated into
- ultra filtrate
4
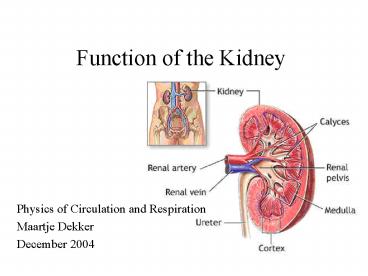
Function of the Kidney Terminology
- Blood is filtered in the nephrons
- The cortex of each kidney contains 1,2 million
nephrons - The nephron consists of a renal corpuscle and a
renal tubule - The renal tubule consists of the convoluted
tubule and the loop of Henle - The main filter of the nephron is glomerulus
which is located within the Bowman's capsule
5
Function of the Kidney The glomerulus
- The glomerulus consists of a network of parallel
capillaries. - It is a filter made up from different layers
- Endothelium cells containing pores in their
cytoplasm of radius 25-50nm - The basal membrane
- Lamina rara interna
- Lamina densa
- Lamina rara externa
- Epithelium cells
6
Function of the Kidney The basal membrane
- Flitration based on size
- All 3 laminae contain collagen
- Laminae rarae contain laminin molecules to bind
the collagen to the endo-, epithelium cells - The collagen network acts as a filter
- Molecules with 6 nm lt r lt 1,8 nm can pass the
filter - Filtration based on charge
- Laminae rarae contain heporan sulfate
proteolycate which - has a negative charge
- Cell membranes of endo-, epithelium cells are
charged negatively - Negatively charged proteins are hindered in their
passing
7
Function of the Kidney The glomerulus
- Filtration depends on
- Plasma flow through glomerulus, Qa
- Hydrostatic pressure Pgc
- Colloid osmotic pressure at begin (pa ) and end
(pe ) of filtration - Filtration capacity of the capillaries, S
- Fluctuations in blood pressure have little effect
due to auto regulation of the blood pressure in
the glomular vessel - Filtration stops if blood pressure drops below 36
nmHg
8
Function of the Kidney Transport in the
tubular apparatus
- Filtrate produced per day 180 l
- Urine production 1,5 l
- Water reabsorbed in proximal tubulus (80)
- Active transport of minerals
- Water transport by osmotic pressure difference
- Urine concentrated in loop of Henle (6)
- Another 12-15 is reabsorbed in the distal
collecting tubuli
9
Function of the Kidney Damage of the glomerulus
- 3 different kinds of damage
- Inflammation of the kidney causing damage to the
filter and a decrease of the flow through the
glomerulus - Loss of charge of the membrane resulting in a
higher permeability for proteins - Scar forming after inflammation causing loss of
functional tissue and filtering surface - and the adaptations made by the kidney
- Functional adaptation loss of nephrons results
in a rise in blood pressure - Arteriole resistance in the glomerulus decreases
- Qa increases
- Pgc (total filtration pressure) increases
- fn (filtration fraction) increases
- Structural adaptation hypertrophy of kidney
tissue resulting in an increase in filtering
surface - Kf (permeability filtration capacity) remains
the same or decreases causing kidney
insufficiency
10
Function of the Kidney Glomerulosclerosis
- Glomerulosclerosis the degeneration of
capillary walls due to e.g. diabetes or subtotal
nephrectomy ( clinically removal of part of the
kidney) - A sign of glomerulosclerosis is proteinuria
(urine contains large amount of proteins) - Glomerulosclerosis is caused by hyper filtration
due to high blood pressure in the capillaries
11
Function of the Kidney Kidney insufficiency
- Kidney insufficiency may be caused by
- Nefritis (inflammation of the kidney)
- Nefricalcinosis (kidney stones in tubuli)
- Nefrocirrhosis (shrinking of the kidney)
- Solutions are
- Hemo dialysis outside of the body the blood is
made to flow past a membrane. Differences in
concentration and pressure make the waste pass
through the membrane into the dialysis solution
- Perioneal dialysis the abdomen is filled with
dialysis solution. Waste passes through the
abdominal membrane (peritoneum) into the fluid - Kidney transplantation
12
Function of the Kidney Hemo dialysis machines
- Hemo dialysis machines contain a semi permeable
membrane - The membrane is non permeable for proteins and
blood cells - Transport of wastes takes place by osmotic and
pressure difference - A dialysis machine should have the following
qualities - Efficient removal of metabolic wastes
- Removal of excess water
- No damage to the blood
- No blood clotting inside machine
- Sterile
- Disposable
Dialysis solution is non-sterile. Therefore blood
pressure should be higher than dialysate pressure
13
Function of the Kidney Hemo dialysis machines
- Types of hemo dialysis machines
- (Twin) coil type (1956) blood flows through
celluloid tubes - Dialysate flows in perpendicular direction
- Membrane surface 1,0 -1,5 m2
- Priming volume 120 -240 ml
- Dialysate is recycled
- Needs pump
- Plate type (1948) blood flows between two
membranes Dialysate flows in opposite direction - Membrane surface 1,0 -1,6 m2
- Priming volume 140 -300 ml
- Needs 300 l dialysate per dialysis
- Does not need pump
- Capillary type blood flows through hollow,
celluloid fibres (13.500) inside a plastic tube - Dialysate flows in the tube,outside the fibres
- Membrane surface 1,3 -2,5 m2
- Priming volume 100 -180 ml
- Needs pump