Why Chemical Reactions Occur - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Why Chemical Reactions Occur
Description:
Lecture 15.1. Why Chemical Reactions Occur. ENTHALPY - ENTROPY - GIBBS FREE ENERGY ... can be added & subtracted in the same way as enthalpies (Hess' Law) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Why Chemical Reactions Occur
1
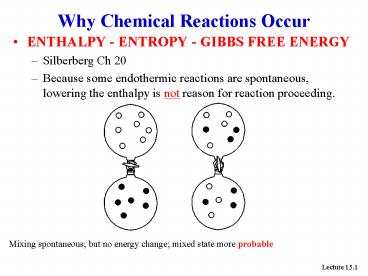
Why Chemical Reactions Occur
- ENTHALPY - ENTROPY - GIBBS FREE ENERGY
- Silberberg Ch 20
- Because some endothermic reactions are
spontaneous, lowering the enthalpy is not reason
for reaction proceeding.
Mixing spontaneous but no energy change mixed
state more probable
2
Recap
- The system - the portion of the universe being
studied (usually the chemical reaction) - The surroundings - everything that is outside the
system (usually the immediate surroundings to the
chemical reaction) - The universe - the system the surroundings
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- The energy of the universe is constant.
3
Entropy S
- Entropy is a thermodynamic quantity that
describes the number of arrangements that are
available to the system in a given state - Theoretically
- S R ln W
- W number ways molecules can be arranged in
that configuration - R gas constant
4
- The more ways a particular state can be achieved
the greater is the likelihood of finding it in
that state
- The black and white balls have more freedom if
they can move around the entire system
5
Entropy Qualitative
- More disordered higher S
- For given substance Sgas gt gt Sliquid gt
Ssolid
Fig 20.5
- Same substance higher T higher S
6
- Two similar substances more complex molecule has
higher S - eg at 298K
S / J K-1 mol-1
CH4 (g) 186
H2O (l) 70
H2O (g) 189
CH3(CH2)3CH3 (g) 388
H2S (g) 206
C(CH3)4 (g) 306
Fig 20.9
7
Summary - Entropy
- For given substance Sgas gt gt Sliquid gt
Ssolid - Same substance higher T higher S
- Two similar substances more complex molecule
has higher S - In solution more dilute higher S
- Similar compounds higher mass higher S
(eg H2S gt H2O)
8
Entropy Of Reaction
- Entropies in reactions can be added subtracted
in the same way as enthalpies (Hess Law) - Eg calculate DSrxn for urea
S 2 ? 193 214 174
70 J mol1 K1 DSrxn
SSproducts S Sreactants DSrxn (174
70) (2 ? 193 214) 356 J mol1 K1
We would expect ?So lt 0 Why?
9
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
- In a spontaneous process the entropy of the
universe must increase - DSsystem DSsurroundings gt 0
- universe becomes more disordered
10
Third Law of Thermodynamics
- At 0 K, all substances have the same entropy
- (the baseline for entropy define this as S
0)
Eg A perfect crystal has zero entropy at absolute
zero.
11
Examples Of Entropy Change
- 1. Predict sign of DSsys for following processes
- Alcohol evaporating
- Goes from liquid to gas (vapour),
- DSsys S(gas) S(liquid) gt 0
- Lake freezing in winter
- Goes from liquid to solid,DSsys S(solid)
S(liquid) lt 0 - 2. Arrange in order of decreasing standard molar
entropy, S, ClO4, ClO2, ClO3 - More complex has higher entropy, so S values go
- ClO4 gt ClO3 gt ClO2
12
Health Advice
- do the tutorial problem sheets and quizes
- past exam papers from 1st year Office(sold for
3.30 for our copying costs) - re-do ALL examples given in lectures without
help from your notes - ask a tutor or me for help
- university counselling service
- Reminder Quiz next week
- Ideal Gases - Kinetics - Equilibrium - Acids
Bases - Bring a calculator